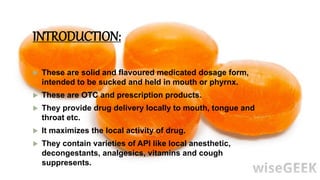
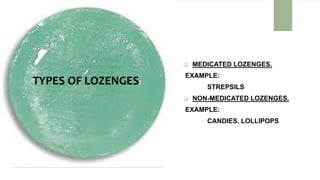
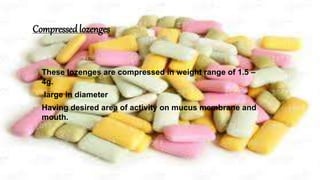
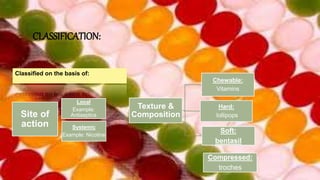
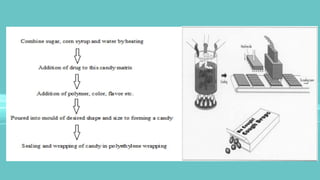
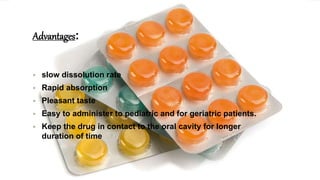
This document provides information about lozenges, including their definition, introduction, shapes, types, classification, raw materials, manufacturing, advantages, disadvantages, uses, examples, storage and packaging. It defines lozenges as solid dosage forms containing drugs and flavoring intended to dissolve slowly in the mouth. Lozenges are used for local effects in the oral cavity and sometimes systemically. They are available in various shapes and types, including medicated and non-medicated, and are classified based on site of action, texture and composition.