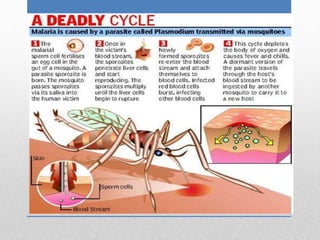
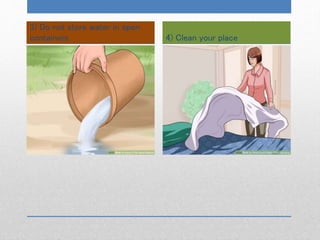
Malaria is an infectious disease caused by parasites that are transmitted through the bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. The parasites (called Plasmodium) infect red blood cells and cause symptoms that include fever, chills, and flu-like illness. Malaria was first recognized by ancient Greeks and Romans. In 1898, Ronald Ross discovered that malaria is transmitted by mosquitoes and received the Nobel Prize for this work in 1902. Malaria is treated with oral or intravenous antimalarial drugs depending on the severity of infection. Prevention involves mosquito repellent, closing doors and windows, and eliminating standing water.