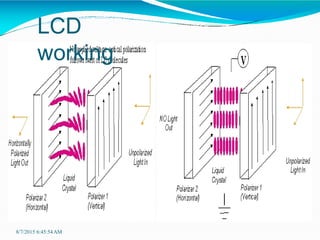
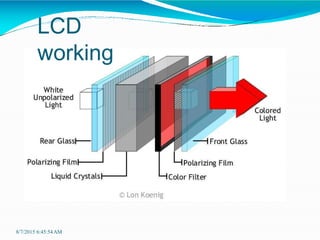
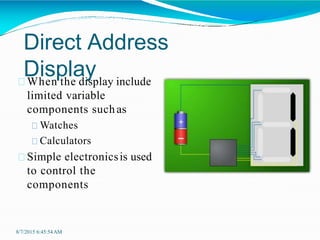
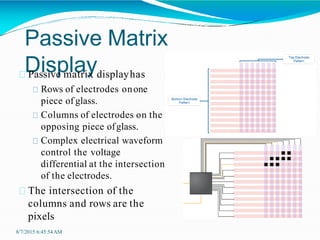
Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) are thin, flat panel displays that use liquid crystals and polarization of light to electronically display text, images, and video. LCDs have advantages over older cathode ray tube (CRT) displays such as smaller size, lower power consumption, lighter weight, and no electromagnetic field emissions. LCDs work by using liquid crystals that can be precisely aligned with electric fields between two polarized filters - when electricity is applied, the crystals straighten out and light cannot pass through, making pixels appear dark. There are different types of LCDs including direct address, passive matrix, and active matrix displays, with active matrix allowing for higher resolutions and better image quality.