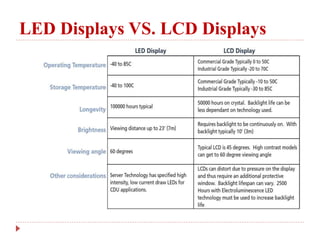
This document discusses pixels, LCD displays, LED displays, and compares LED and LCD displays. It provides information on:
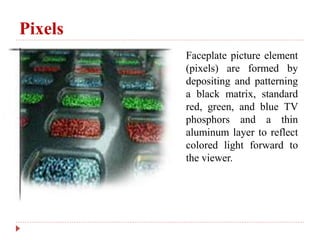
1. How pixels are formed using a black matrix, red, green, and blue phosphors and aluminum layer.
2. LCD displays being the most mature flat panel technology but having poor viewing angles, requiring backlighting, and being inefficient.
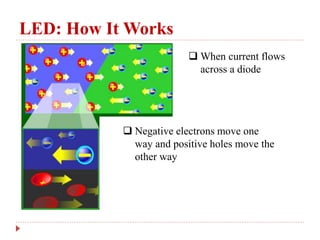
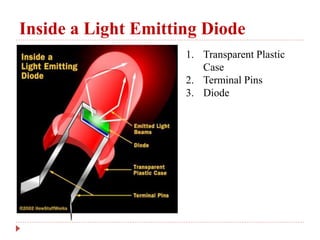
3. How LEDs work by emitting photons when electrons fall to a lower energy level and the color is determined by the electron energy level.