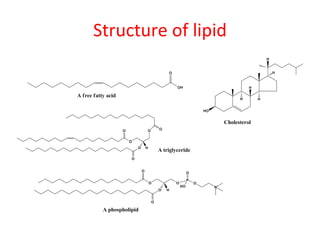
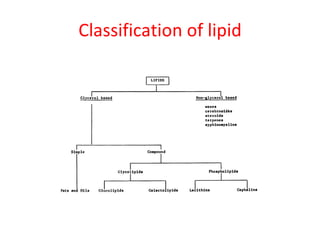
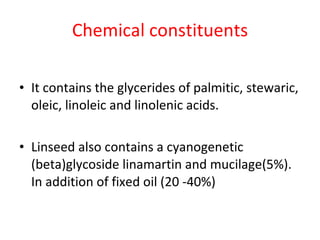
The document discusses several plant-derived fixed oils, including their biological sources, methods of preparation, descriptions, chemical constituents, and uses. Arachis (peanut), castor, olive, linseed, sesame, safflower and neem oils are summarized. Arachis oil is expressed from peanut kernels and used as an edible oil, lubricant and in cosmetics and injections. Castor oil from castor seeds is used orally and in soaps, hair oils and lubricants. Olive oil from olive fruits is used topically as an emollient and in ear wax. Linseed oil from flax seeds is used in paints, varnishes and skin treatments. Sesame oil from