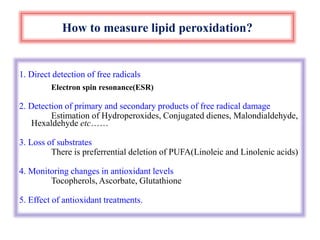
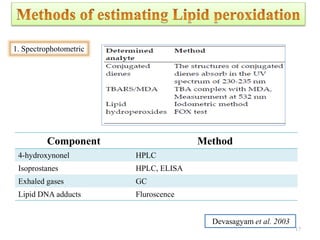
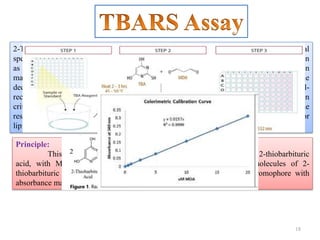
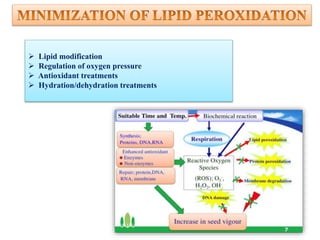
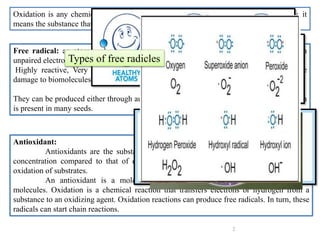
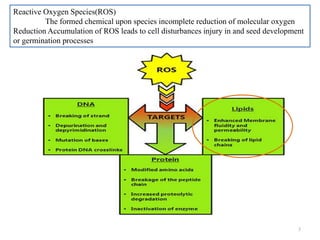
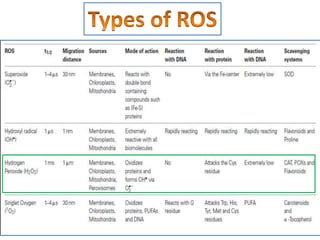
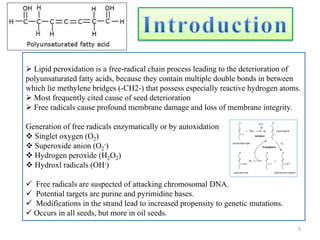
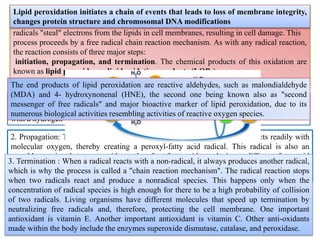
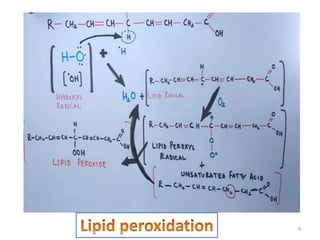
The document discusses lipid peroxidation in seeds and its effects. It defines lipid peroxidation as the oxidative degradation of lipids caused by reactive oxygen species that damage cell membranes. Lipid peroxidation occurs through initiation, propagation, and termination steps and produces reactive aldehydes. It is a major cause of seed deterioration that damages membranes and DNA. Levels of lipid peroxidation enzymes like lipoxygenases correlate with seed storability, with "good storers" having lower lipoxygenase activity. The document also describes methods to measure lipid peroxidation products.



![11
LOX activity in membranes can be reduced by
Reducing the quantity of polyunsaturated fatty acids in seeds through breeding
Short time heat treatments (Peanut- 79 0C/ 90s; 60 0C/ 10min)
Inhibitors of LOX [U28938 (300μg/mg protein), Nordihydroguaiaretic acid (500 μM),
4-Nitrocatechol (600 μM) and Eicosa-5,8,11,14-tetraynoic acid (200 μM)]
Temperature of storage
Substrate concentration and pH.
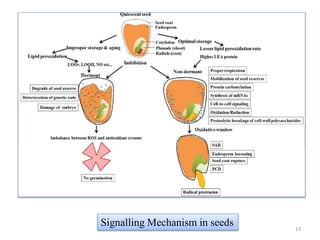
Damage of mitochondrial membrane due to lipid peroxidation leads
To reduces respiration capacity.
Reduced ATP production leading to reduced energy availability for the breakdown of
food reserves.
Reduce the supply of ATP to the growing points during germination.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipidperoxidation-200922124146/85/Lipid-peroxidation-11-320.jpg)
![14
Effect of lipid peroxidation and related parameters on the storability of soybean
(Glycine max) seeds
Vaibhav Kumar et al., 2015
Thirteen soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merill] genotypes (grouped as six “good
storers” and seven “poor storers”) were selected .
To understand the relationship between lipid peroxidation, antioxidant activity and
seed storability.
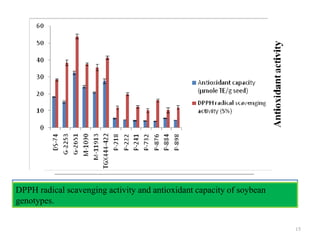
Good storers possessed significantly high activity (p<0.05) of LOX-1 and lower
activity of LOX-2 as compared to poor storers.
Significant increase (p<0.05) in HPL activity was observed in all poor storer
genotypes and correlated with higher accumulation of lipid peroxides, total MDA and
carbonyl content.
LOX-1, LOX-2 and HPL enzymes as potential indicators to determine the
storability of soybean seeds and also can be used as the parameters.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipidperoxidation-200922124146/85/Lipid-peroxidation-14-320.jpg)