This document provides an overview of linear programming, including its history, key components, assumptions, and applications. Linear programming involves maximizing or minimizing a linear objective function subject to linear constraints. It was developed in 1947 and can be used to optimize problems involving allocation of limited resources. The key components of a linear programming problem are the objective function, decision variables, constraints, and parameters. It makes assumptions of proportionality, additivity, continuity, determinism, and finite choices. Common applications of linear programming include production planning, facility location, and transportation problems.







![Compiled by Tsegay Berhe MSc in Production Engineering and Management 8
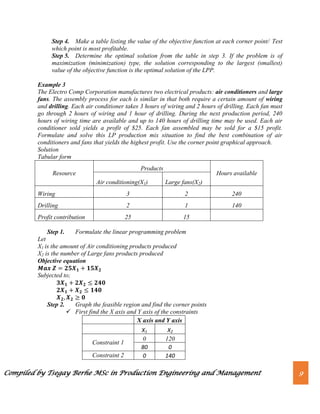
M3 1 1 15
Profit contribution 5 4
Decision variables
Let
X1 is the amount of X products produced
X2 is the amount of Y products produced
Objective equation
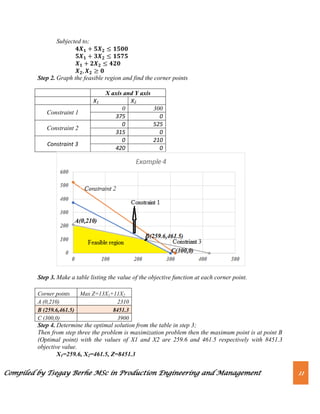
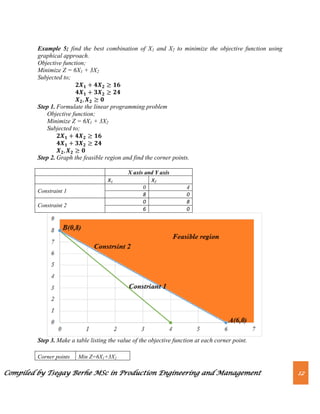
Subjected to;
Graphical Solution to A Linear Programming Problem
The graphical method of solving a linear programming problem is used when there are only two
decision variables. If the problem has three or more variables, the graphical method is not
suitable. In that case we use the simplex method which is discussed in the next section.
We begin by giving some important definitions and concepts that are used in the methods of
solving linear programming problems.
Solution; A set of values of decision variables satisfying all the constraints of a linear
programming problem is called a solution to that problem.
Feasible solution; Any solution which also satisfies the non-negativity restrictions of the
problem is called a feasible solution.
Optimal feasible solution; Any feasible solution which maximizes or minimizes the
objective function is called an optimal feasible solution.
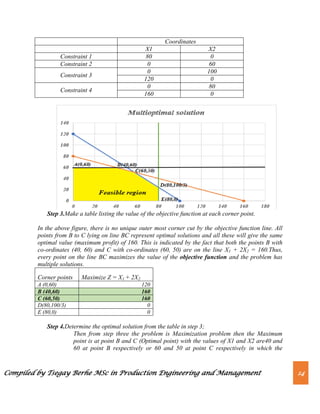
Feasible region; The common region determined by all the constraints and non-
negativity restriction of a LPP is called a feasible region.
Corner point; A corner point of a feasible region is a point in the feasible region that is
the intersection of two boundary lines.
If the optimal value of the objective function in a linear programming problem exists, then that
value must occur at one (or more) of the corner points of the feasible region.
To solve a linear programming problem with two decision variables using the graphical method
we use the procedure outlined below;
Graphical method [corner point /extreme approach] of solving a LPP
Step 1. Formulate the linear programming problem by writing the objective function
(generally maximize profit or Minimize cost) and the constraints.
Step 2. Plot the constraints on the graph and graph the feasible region and find the
corner points by changing the constraints into equalities.
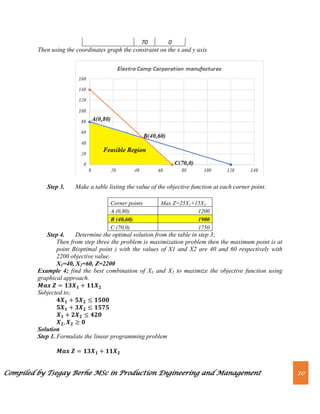
Step 3. The coordinates of the corner points can be obtained by either inspection or by
solving the two equations of the lines intersecting at that point.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-230820064634-ab623cf6/85/Chapter-2-Linear-Programming-pdf-8-320.jpg)



![Compiled by Tsegay Berhe MSc in Production Engineering and Management 20
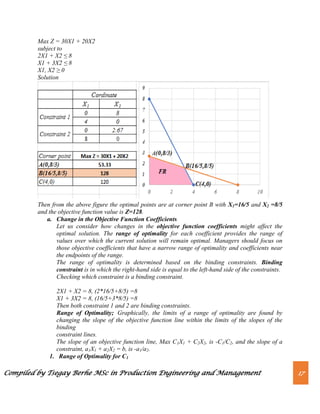
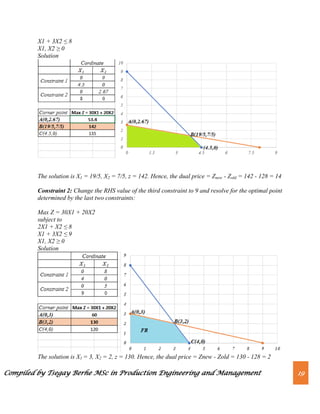
The dual price is also equal to the shadow price.
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
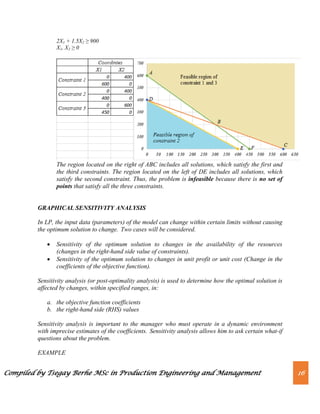
Range of Feasibility; The range of feasibility for a change in the right-hand side value is the
range of values for this coefficient in which the original dual price remains constant.
Graphically, the range of feasibility is determined by finding the values of a right-hand side
coefficient such that the same two lines that determined the original optimal solution continue to
determine the optimal solution for the problem.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-230820064634-ab623cf6/85/Chapter-2-Linear-Programming-pdf-20-320.jpg)