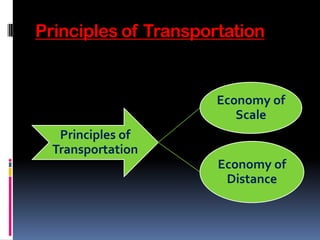
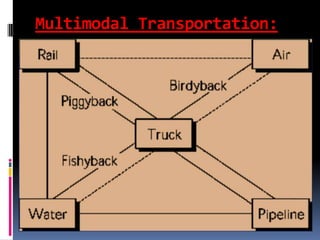
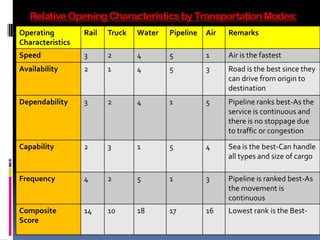
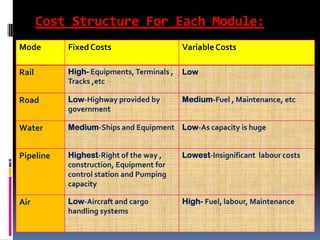
Group 1 members are Akshay Samant (Roll No. 04) and Harshita Deotare (Roll No. 19). Transportation is the movement of items from one place to another and is crucial for logistics. It allows for the efficient movement of goods and impacts areas through its speed, costs, and capabilities. Different modes of transportation like rail, road, water, and air each have their own advantages and disadvantages.




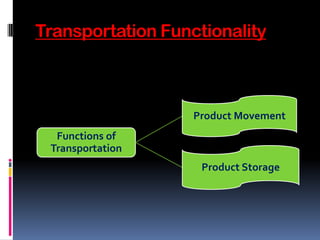
![Product Movement
Temporal:
-Product is locked up during transit, hence inaccessible
-Positive amount of time is spent in transporting material
-Time is a resource[Temporal Resource] expended in
Transportation
-During the time product is locked up costs are incurred
in proportion of time
Financial:
-Administration costs, Salaries, Maintenance costs are
expended
Environmental:
Fuel costs are high[Creates air
pollution, congestion, Noise pollution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transportationppt-111106140555-phpapp02/85/Transportation-ppt-7-320.jpg)
![Product Storage
When unloading and loading is more
expensive then storage
When storage space is limited[situation
when inventory levels are high]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transportationppt-111106140555-phpapp02/85/Transportation-ppt-8-320.jpg)