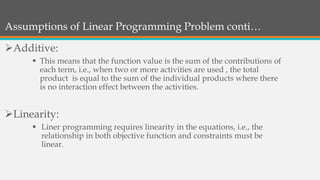
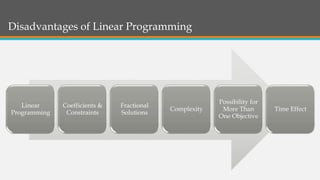
Linear programming is a mathematical optimization technique used to maximize or minimize an objective function subject to constraints. It involves decision variables, an objective function that is a linear combination of the variables, and linear constraints. The key assumptions of linear programming are certainty, divisibility, additivity, and linearity. It allows improving decision quality through cost-benefit analysis and considers multiple possible solutions. However, it has disadvantages like fractional solutions, complex modeling, and inability to directly address time effects.