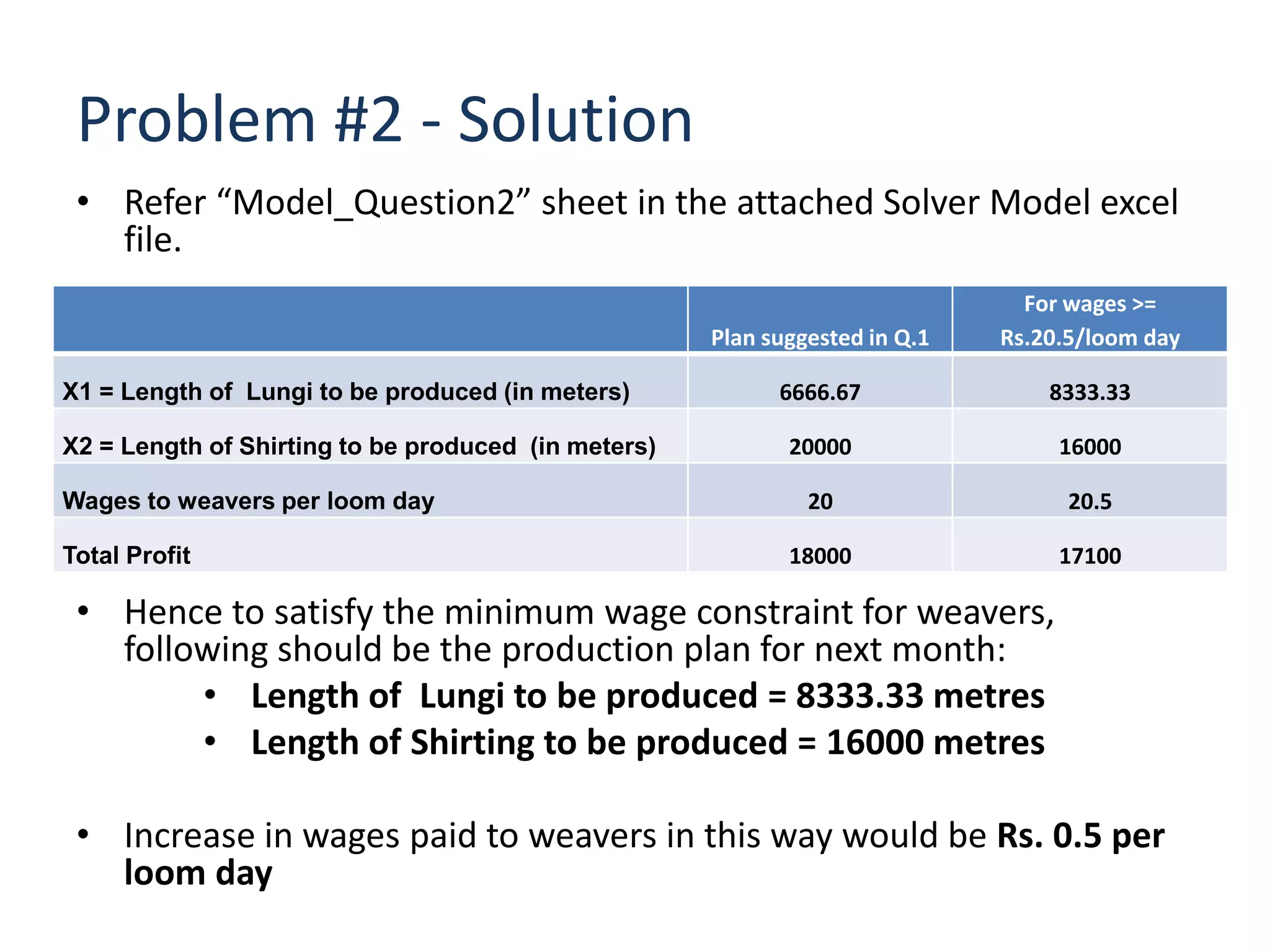
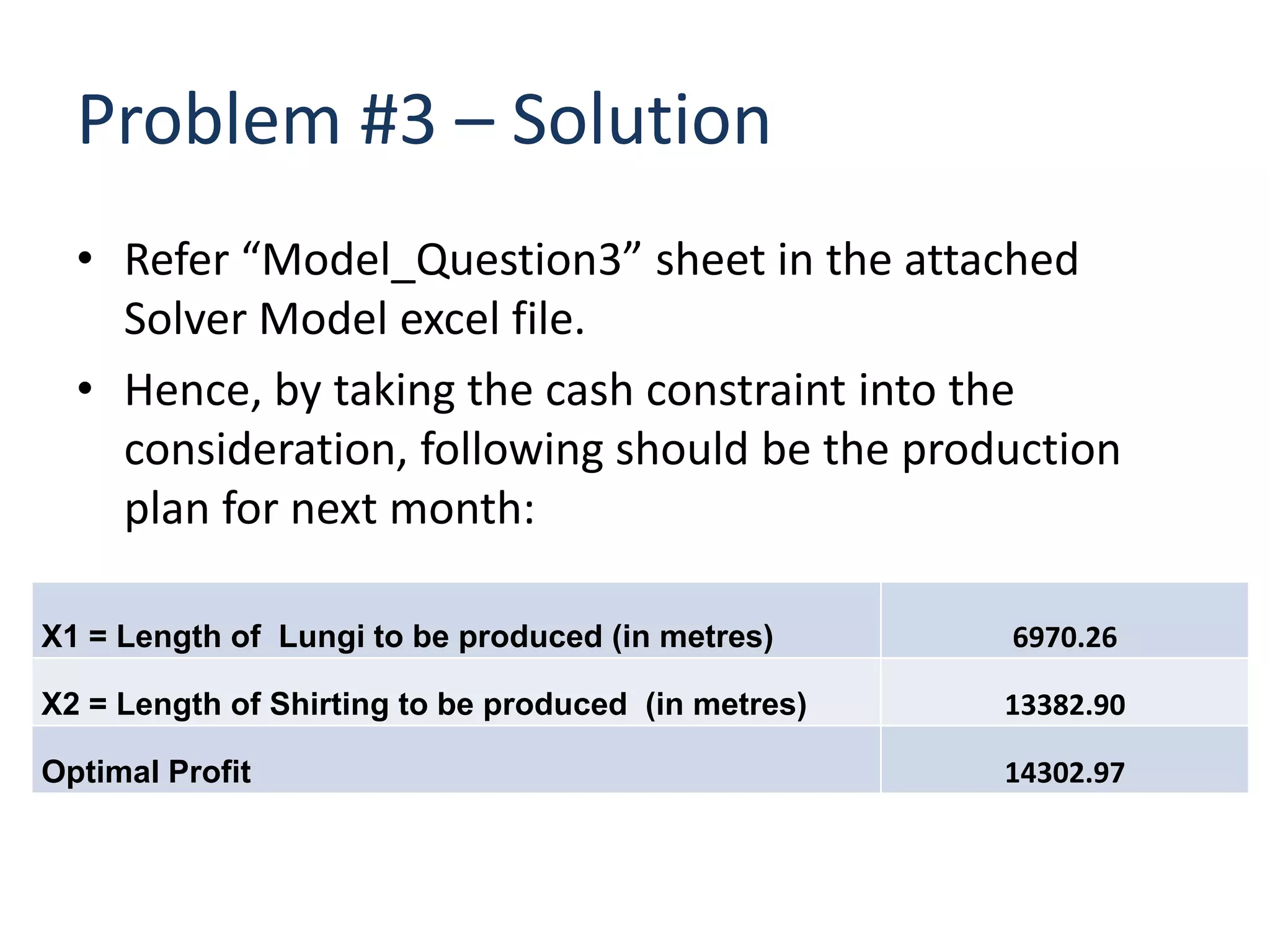
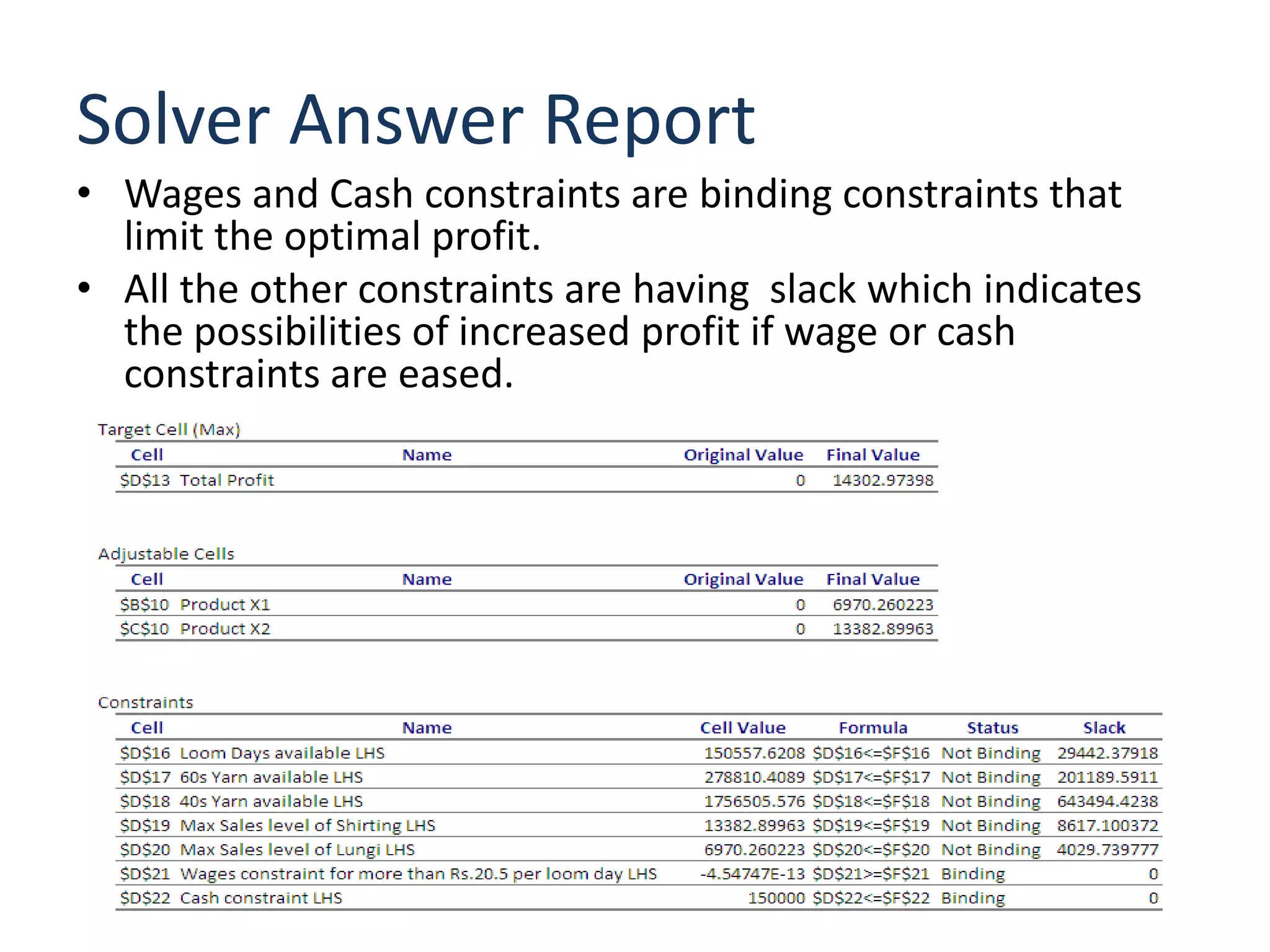
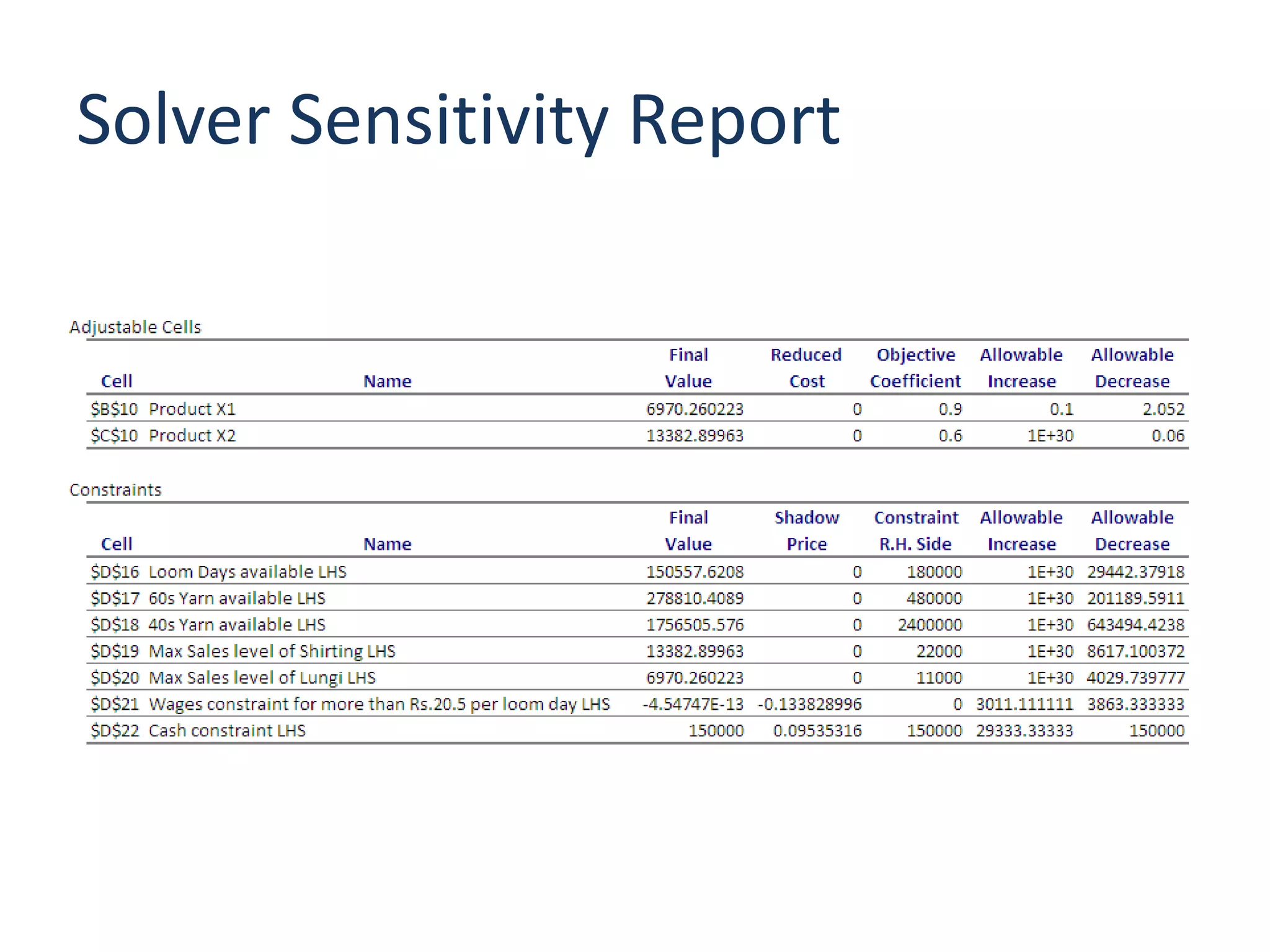
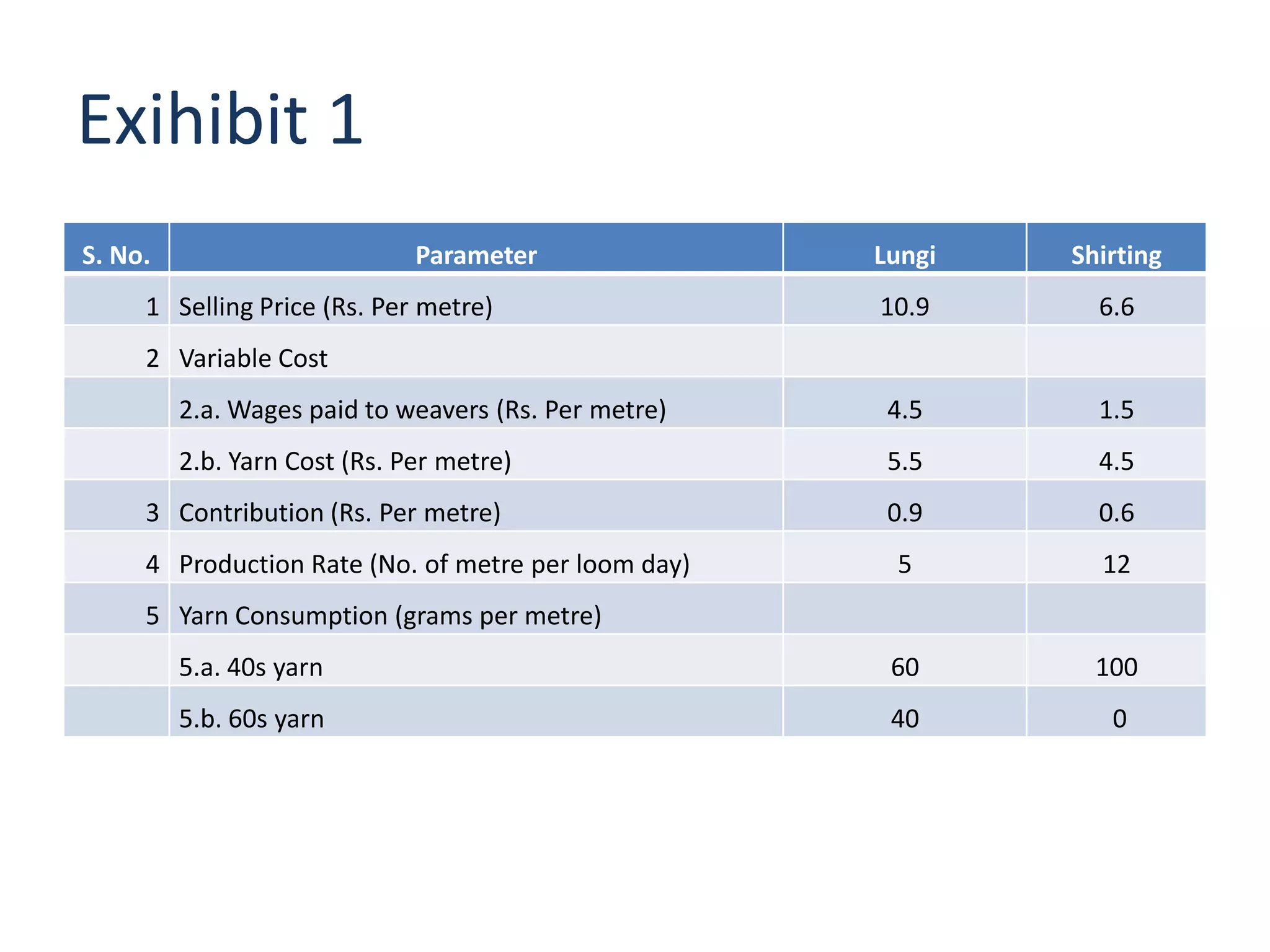
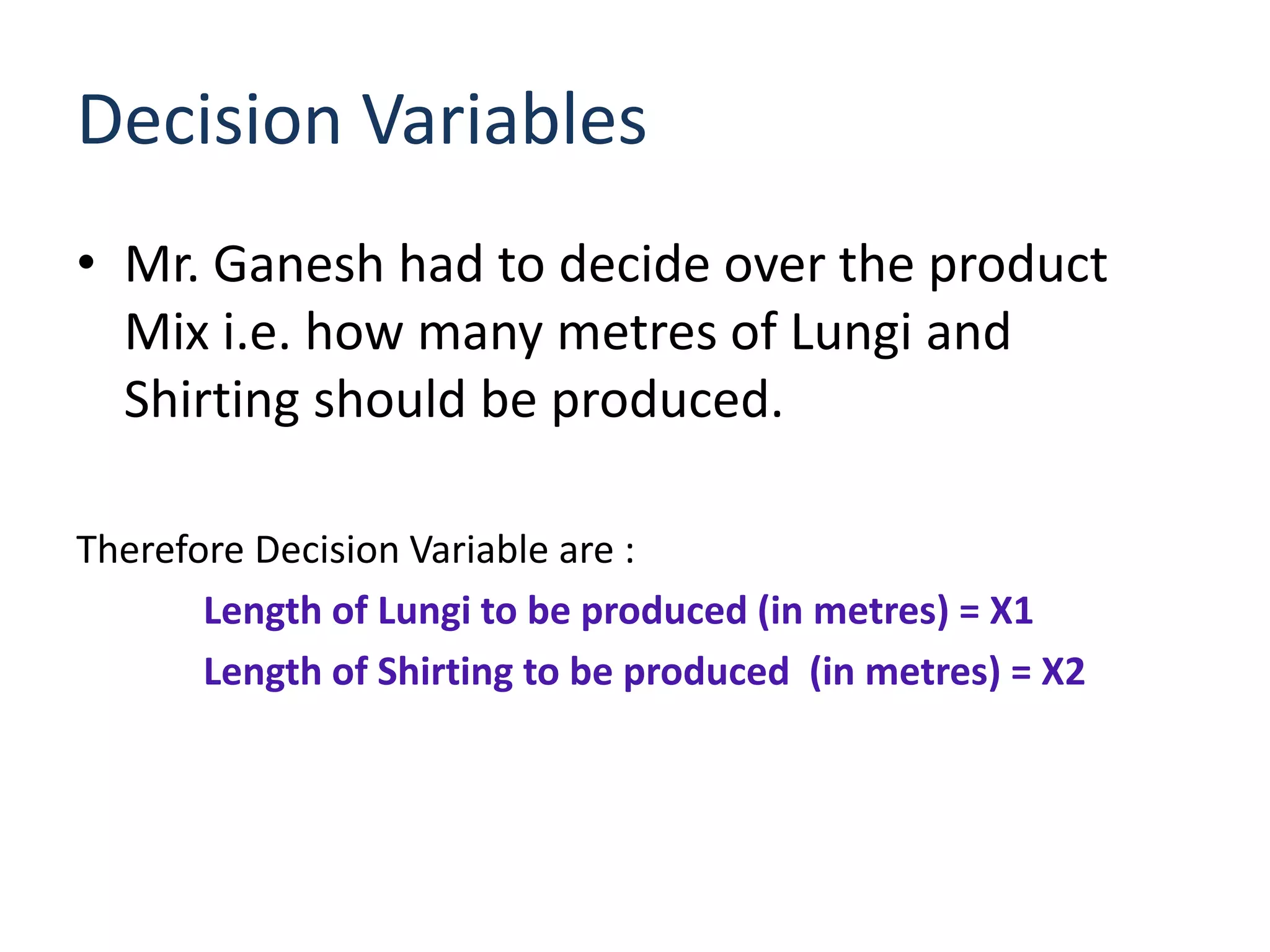
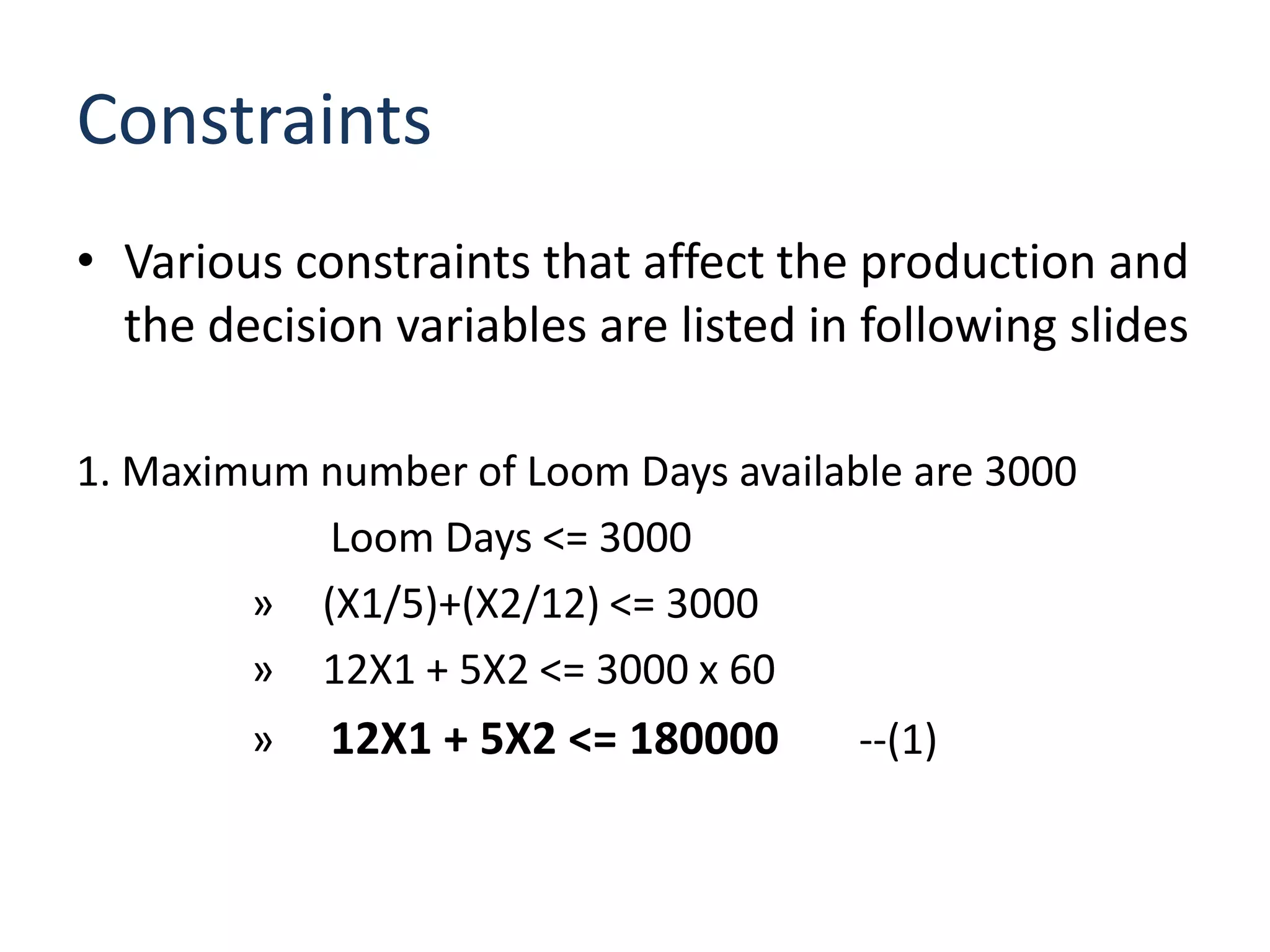
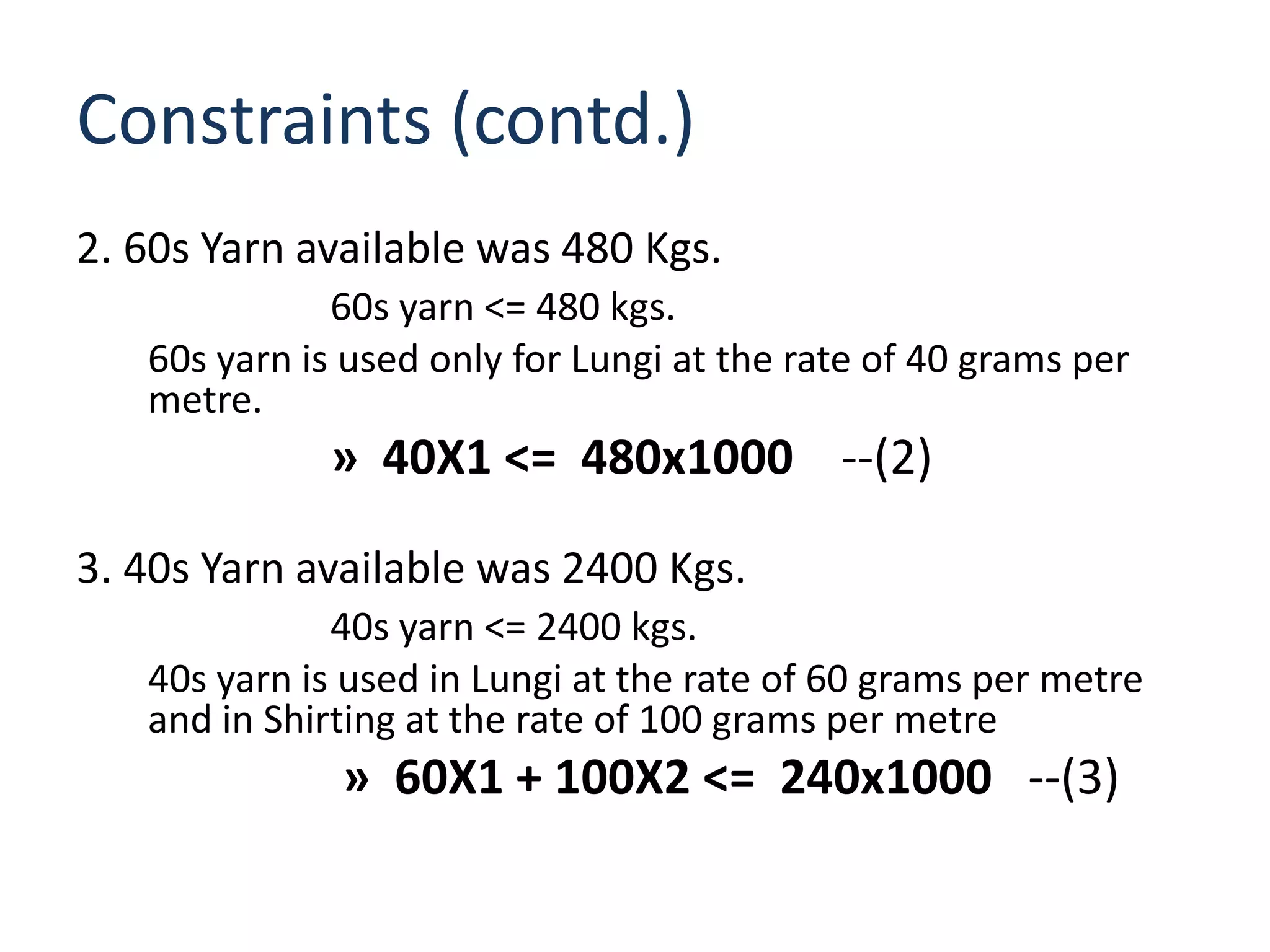
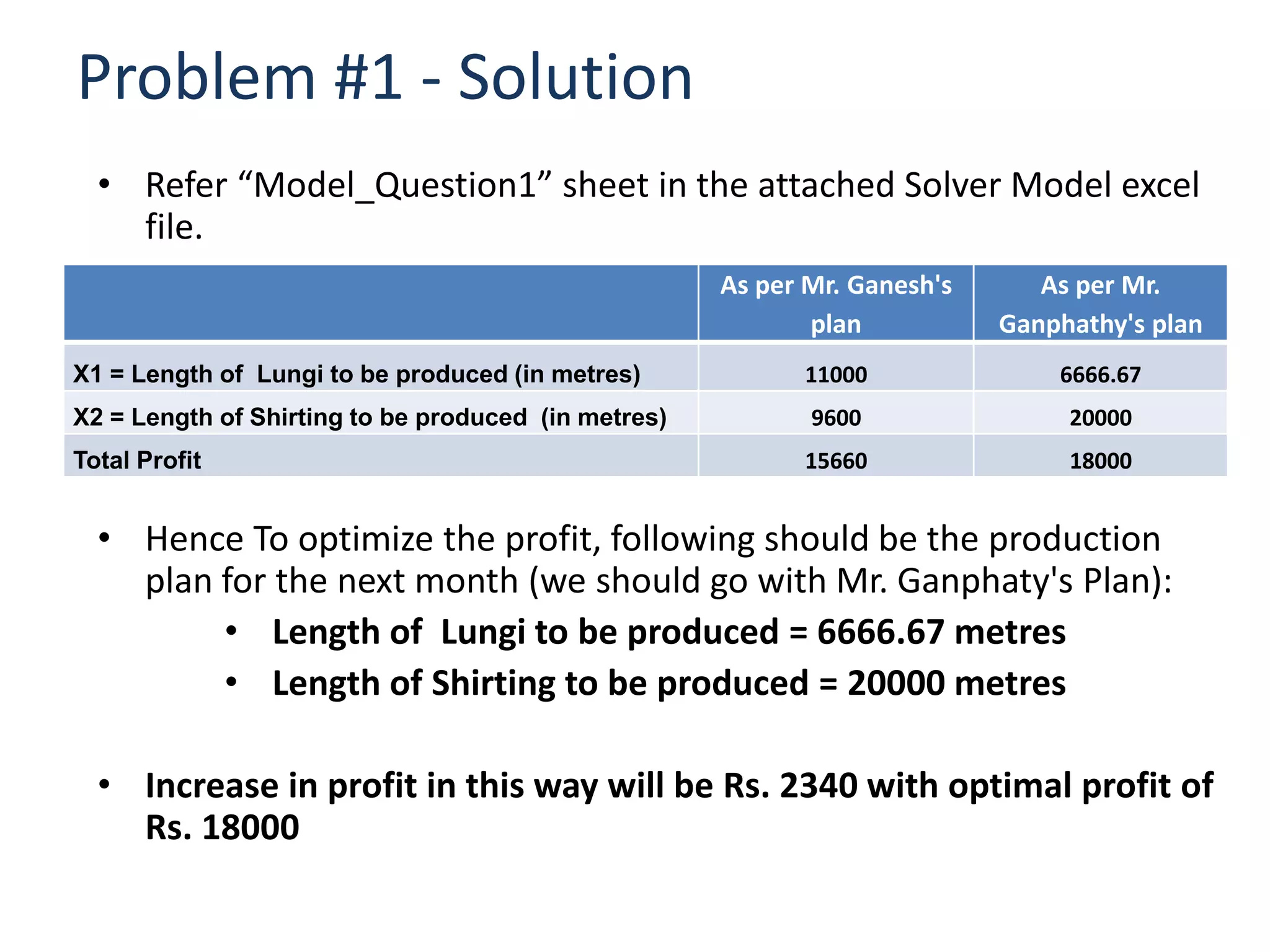
The document discusses optimizing the product mix at Panchtantra Corporation to maximize profit under various constraints. Mr. Ganesh must determine how many meters of Lungi and Shirting to produce. The objective is to maximize total sales profit. Constraints include loom days, yarn availability, sales limits, wages paid to weavers, and cash available. The optimal solution is found to be 6,970 meters of Lungi and 13,383 meters of Shirting given the cash constraint of Rs. 150,000. Wages and cash constraints limit the optimal profit while other constraints have slack.



![Problem #2 – Additional Constraint
• Additional constraint added to ensure that on an
average, the production paid as wages to the weavers at
least Rs. 20.5 per loom day.
• Total wages for the production could be given by
4.5X1 + 1.5X2
• Total number of loom days used could be given by
(X1/5) + (X2/12)
• Therefore
4.5X1 + 1.5X2 >= 20.5 x [(X1/5) + (X2/12)]
» (4.5-20.5/5)X1 + (1.5 - 20.5/12)X2 >= 0
» 0.4X1 – 0.2083X2 >= 0 -- (6)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operationresearchprojectwork-120521072424-phpapp01/75/Operation-research-project-work-11-2048.jpg)