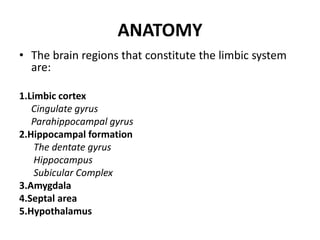
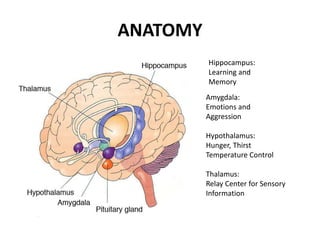
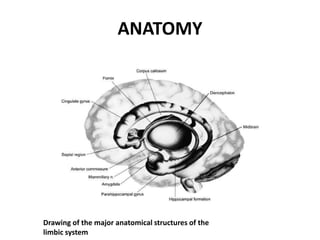
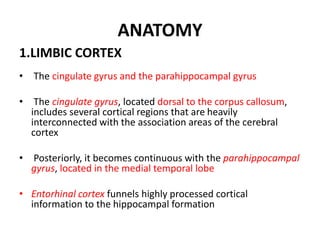
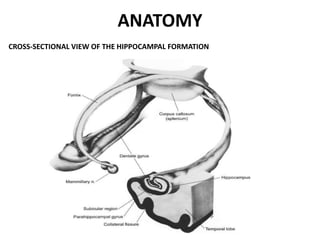
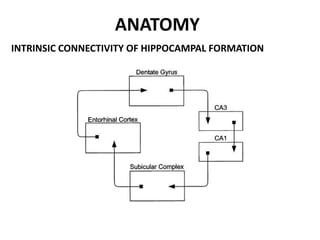
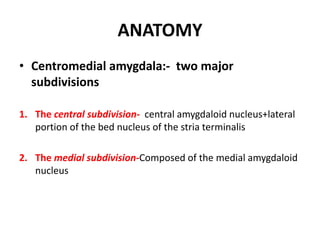
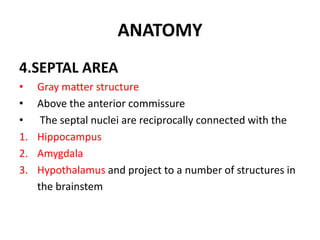
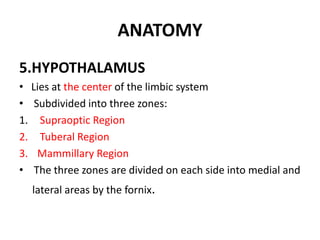
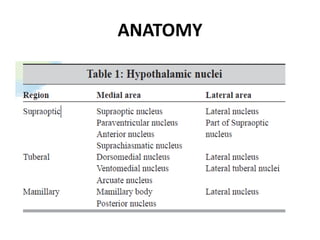
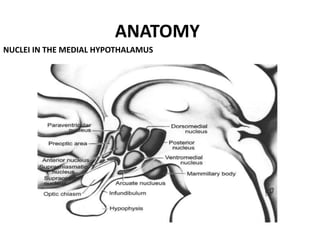
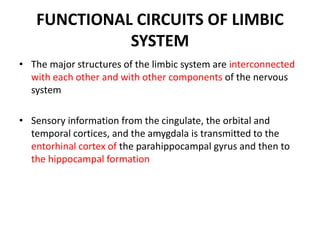
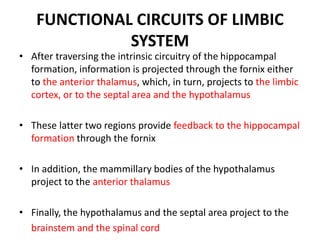
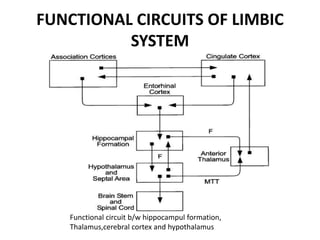
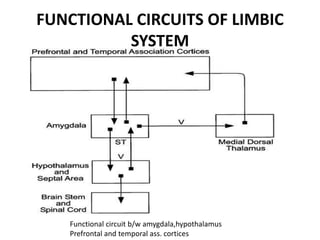
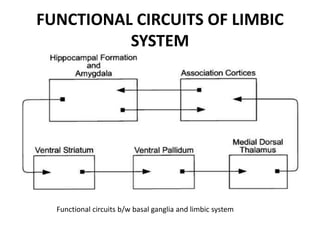
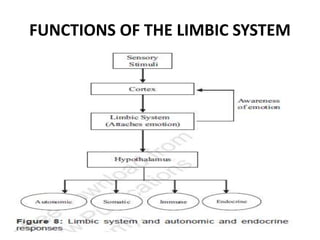
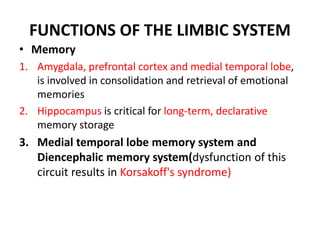
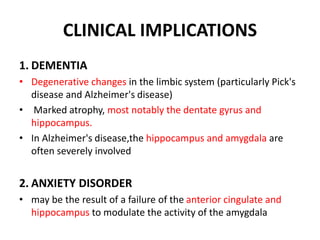
The limbic system plays an important role in emotion, motivation, learning, and memory. It consists of brain structures located deep within the cerebral hemispheres and under the cortex. These structures include the hippocampus, amygdala, septum, cingulate gyrus, hypothalamus, and others. The limbic system is involved in many psychiatric conditions due to its role in emotion regulation, memory formation, and the stress response. Dysfunction of limbic structures and circuits can lead to disorders like anxiety, depression, schizophrenia, and epilepsy. The limbic system also mediates functions like olfaction, appetite, sleep, sexual behavior, and addiction.