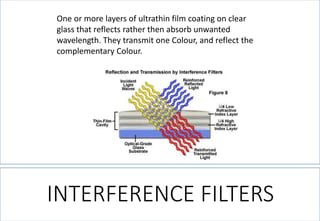
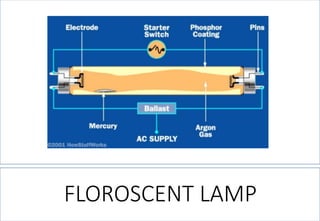
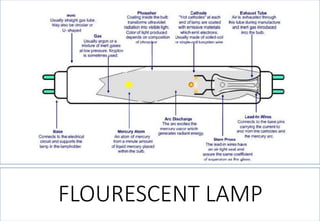
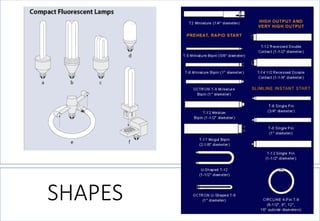
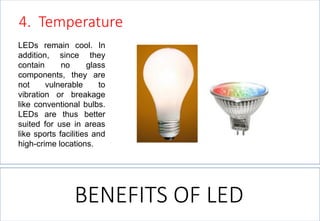
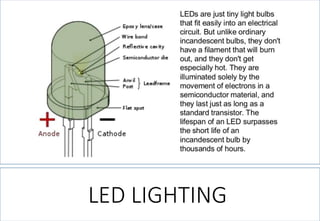
This document discusses lighting design for commercial and residential spaces. It covers various topics such as:
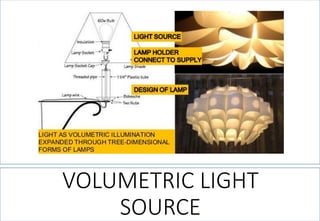
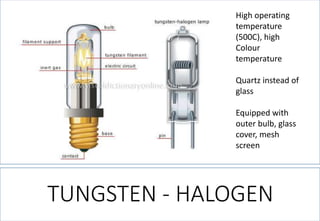
1. The different types of light sources including incandescent, fluorescent, halogen, and LED lamps.
2. Factors that influence light quality like color temperature, color rendering index, and lighting fixtures.
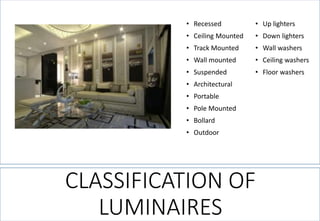
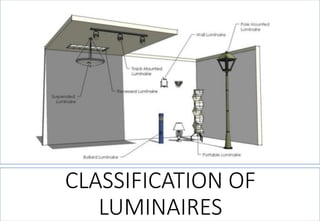
3. Classifications of lighting fixtures and the different types of lighting like general, accent, task, and decorative lighting.
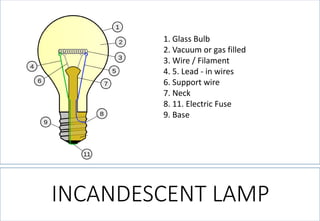
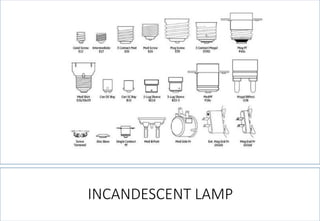
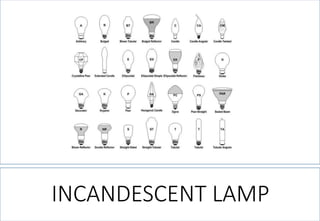
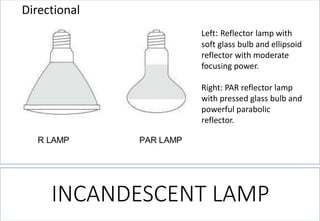
4. Detailed information about incandescent lamps, their construction, advantages, disadvantages and types.