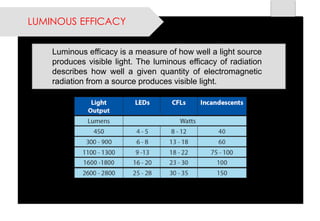
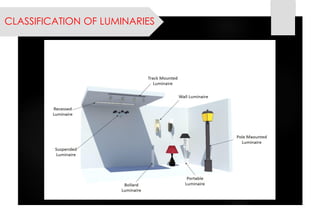
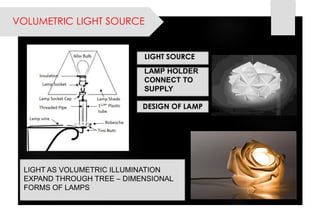
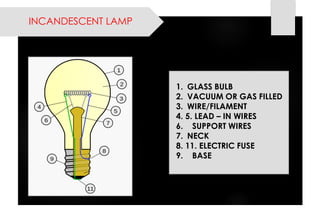
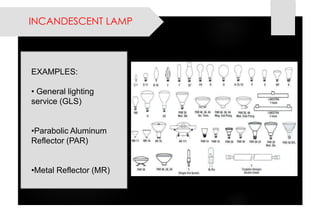
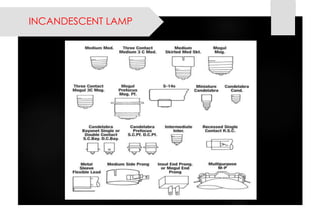
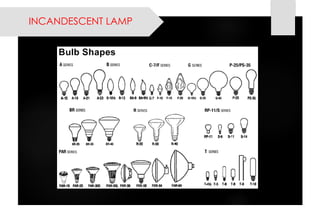
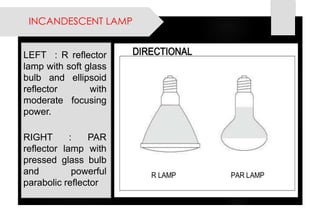
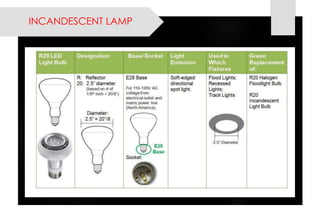
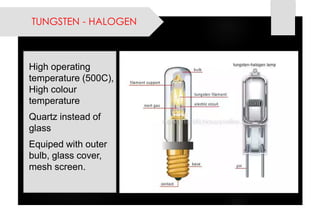
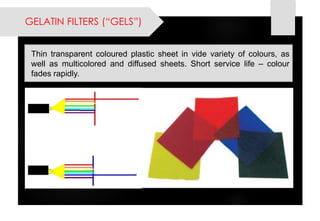
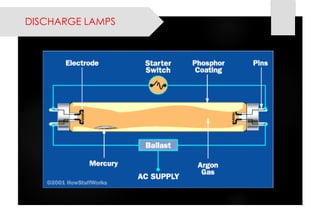
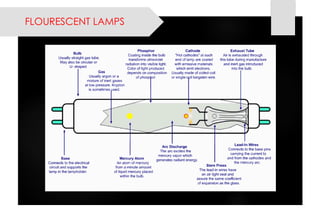
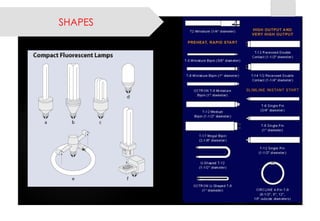
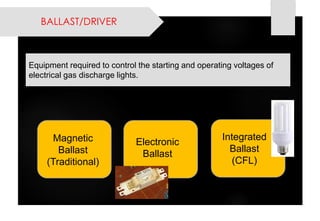
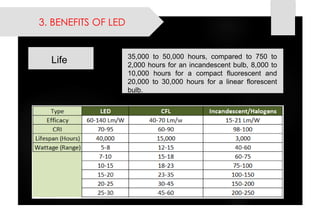
This document provides information on lighting design and different types of light sources. It discusses key lighting concepts like color temperature, lumens, footcandles and lux. It describes different types of lighting fixtures and luminaires. Common artificial light sources are covered, including incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps, high intensity discharge lamps, and LEDs. Details are given on incandescent lamp construction and types, as well as tungsten-halogen and low-voltage lamps.