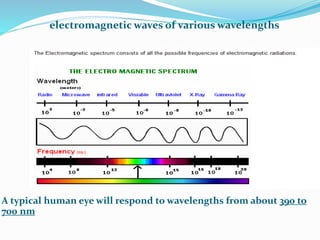
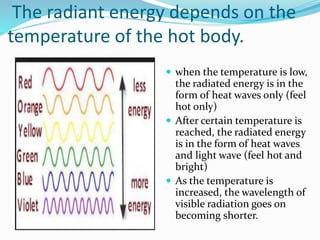
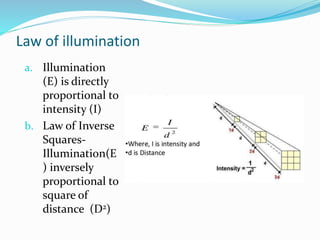
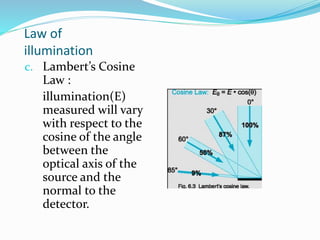
This document presents information about illumination and artificial lighting. It explains that illumination occurs when a material is heated above a certain temperature and begins radiating energy in the form of light. Various types of artificial lights are discussed, including incandescent, fluorescent, sodium vapor, and mercury vapor lamps. Their working principles, startup times, light colors, costs, and common applications are compared. Lighting schemes like direct, indirect, semi-direct, and general diffusing are also explained. The document also covers the laws of illumination, what floodlighting is, and provides references used.


















![References:
1. Laws Of Illumination Help for Electrical Energy – Trans tutors . 2015. Laws
Of Illumination Help for Electrical Energy – Trans tutors . [ONLINE]
Available at: http://www.transtutors.com/homework-help/electrical-
engineering/electrical-energy-utilization/laws-of-illumination.aspx.
[Accessed 26 October 2015].
2. Types Of Lighting Schemes Help for Electrical Energy - Transtutors . 2015.
Types Of Lighting Schemes Help for Electrical Energy - Transtutors .
[ONLINE] Available at: http://www.transtutors.com/homework-
help/electrical-engineering/electrical-energy-utilization/types-of-
lighting-schemes.aspx. [Accessed 26 October 2015].
3. Floodlights | Lighting | Screwfix.com. 2015. Floodlights | Lighting |
Screwfix.com. [ONLINE] Available at:
http://www.screwfix.com/c/electrical-
lighting/floodlights/cat840908. [Accessed 26 October 2015].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/illuminationproject-160205070226/85/Illumination-project-23-320.jpg)
![4. Incandescent Lamps . 2015. Incandescent Lamps . [ONLINE] Available
at:
http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CVonline/LOCAL_COPIES/RUSK/I
ncLamps.html. [Accessed 26 October 2015].
5. How Fluorescent Lamps Work - HowStuffWorks. 2015. How
Fluorescent Lamps Work - HowStuffWorks. [ONLINE] Available at:
http://home.howstuffworks.com/fluorescent-lamp.htm. [Accessed 26
October 2015].
6. High-pressure sodium vapor lamps for open and enclosed luminaires |
OSRAM. 2015. High-pressure sodium vapor lamps for open and
enclosed luminaires | OSRAM. [ONLINE] Available at:
http://www.osram.com/osram_com/products/lamps/high-intensity-
discharge-lamps/high-pressure-sodium-vapor-lamps-for-open-and-
enclosed-luminaires/index.jsp. [Accessed 26 October 2015].
7. The Mercury Vapor Lamp - How it works & history. 2015. The Mercury
Vapor Lamp - How it works & history. [ONLINE] Available at:
http://www.edisontechcenter.org/MercuryVaporLamps.html.
[Accessed 26 October 2015].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/illuminationproject-160205070226/85/Illumination-project-24-320.jpg)
