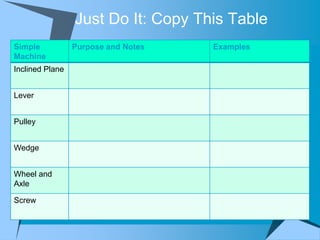
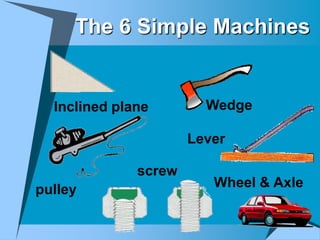
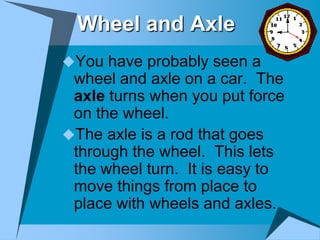
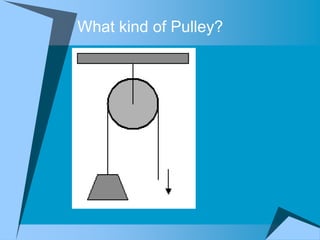
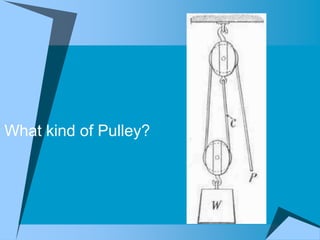
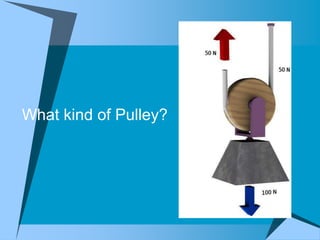
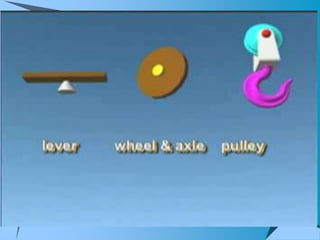
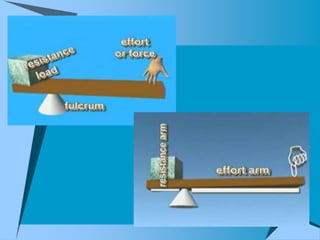
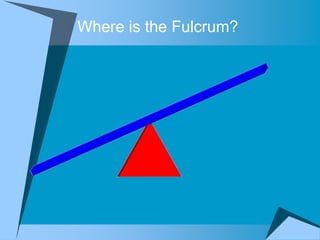
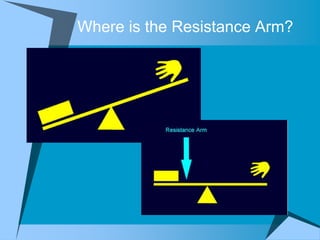
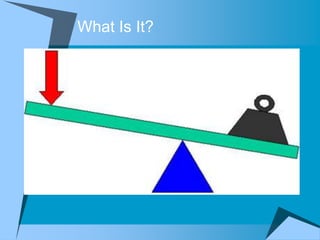
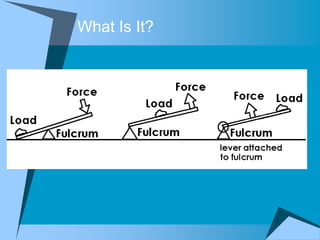
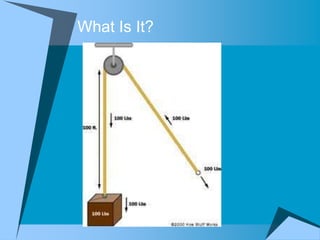
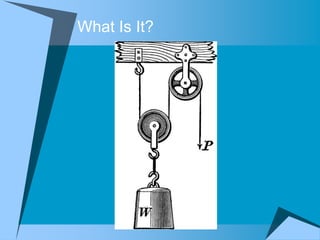
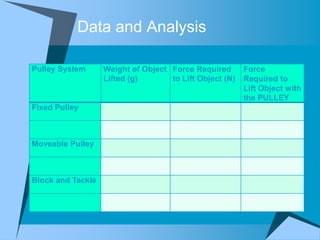
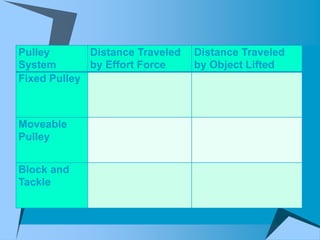
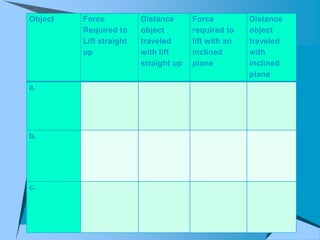
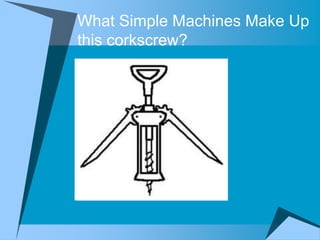
This document provides an overview of simple machines, including inclined planes, screws, levers, pulleys, wedges, and wheel and axle systems, explaining their functions and how they reduce the force needed to perform work. It includes definitions, examples, and activities related to each type of machine, along with illustrations and questions for comprehension. The document serves as a guide for learning about these machines and applying the concepts in practical scenarios.