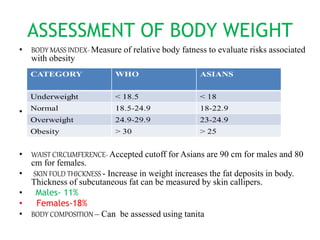
Obesity is defined as excess body weight, with types including android and gynecoid obesity, and is assessed through methods like BMI and waist circumference. The condition can lead to various health issues including psychological problems, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders, and is influenced by genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors. Dietary management and regular exercise are critical for weight reduction, with specific recommendations for macronutrient distribution and lifestyle modifications.