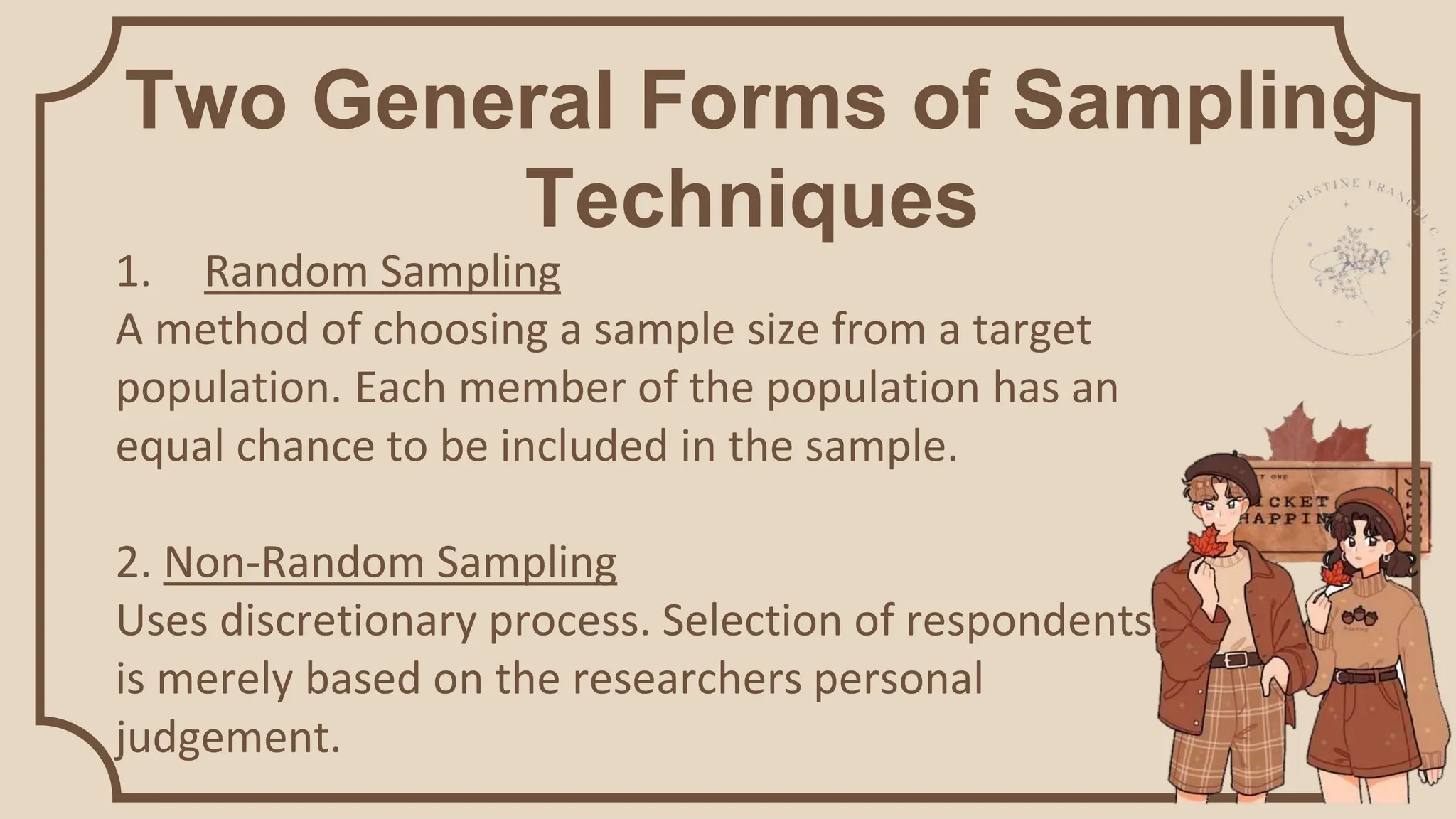
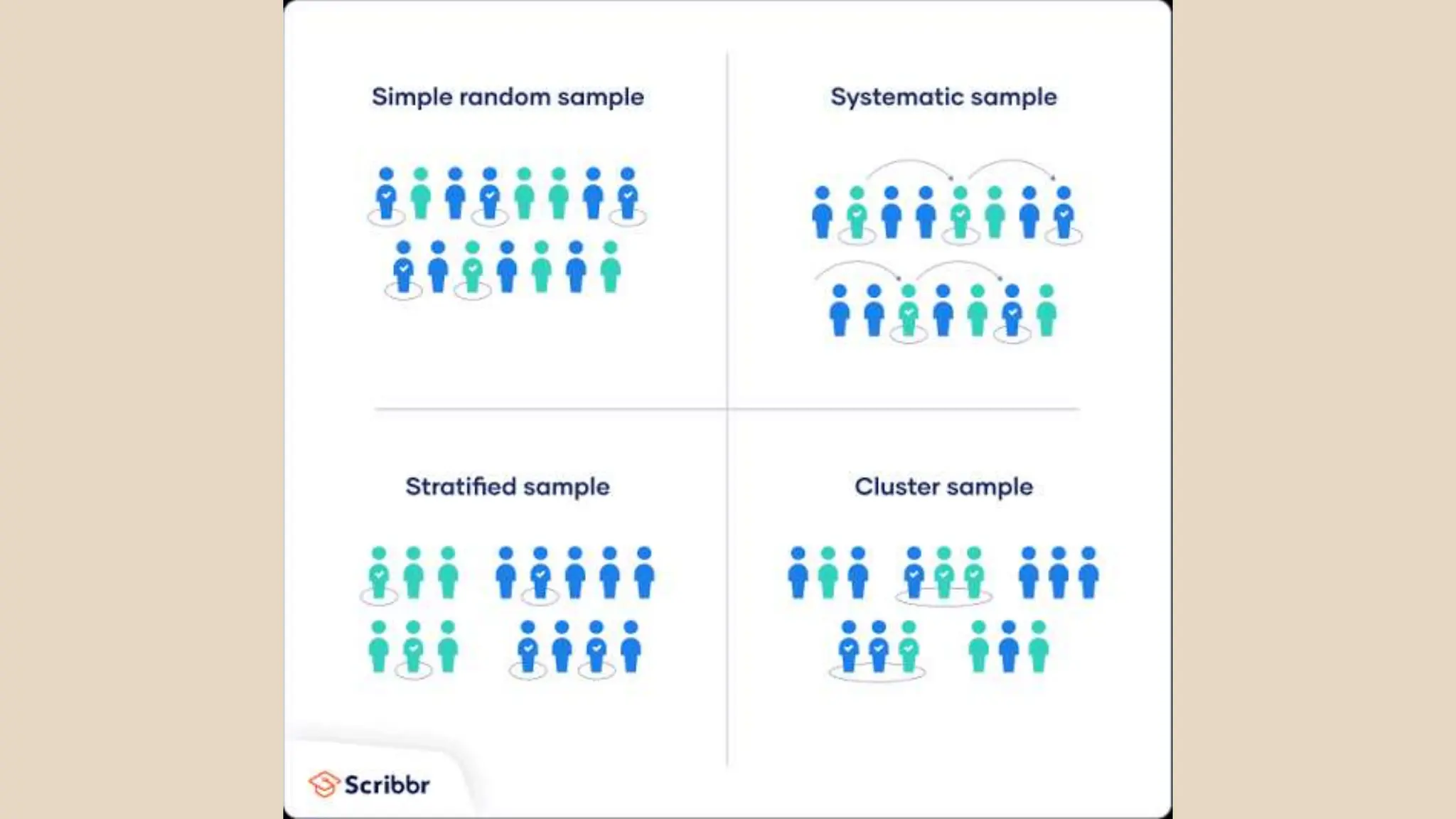
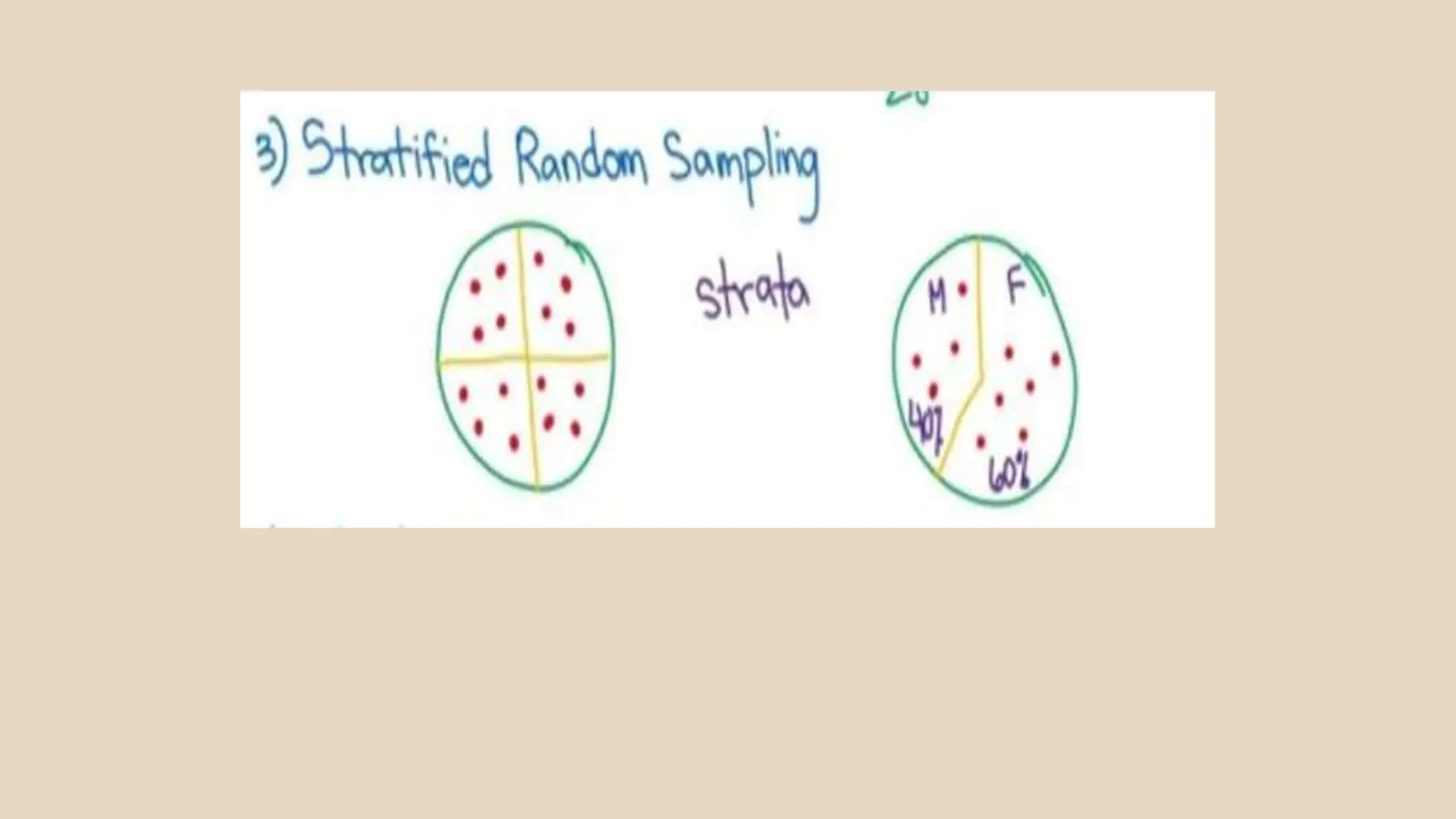
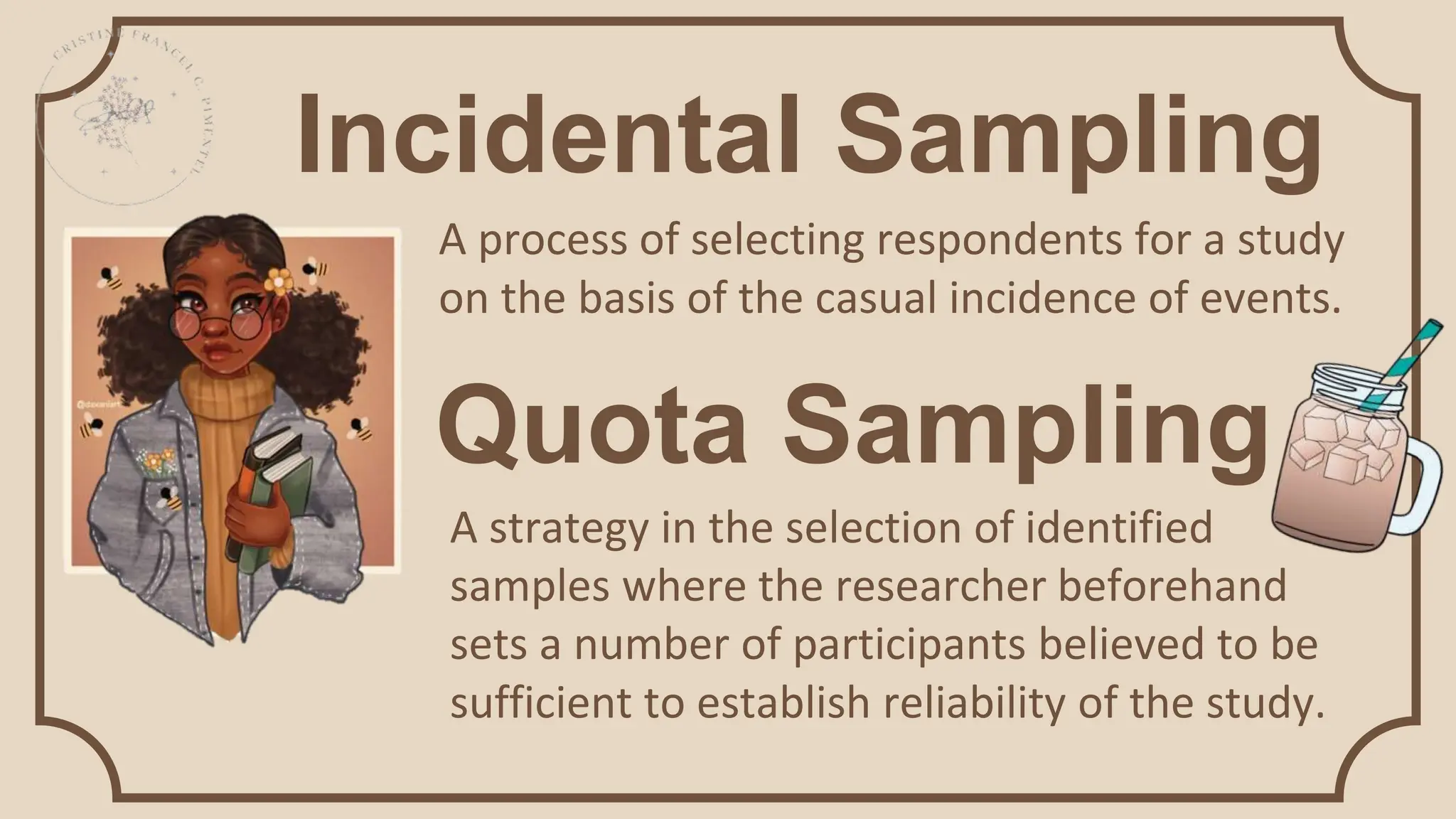
Sampling techniques are tools used to select respondents for research in a way that establishes reliable and valid findings. There are two main types of sampling: random and non-random. Random sampling gives each member of the population an equal chance of being selected, while non-random sampling uses the researcher's judgment. Some specific sampling techniques are fishbowl or lottery sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, purposive sampling, convenience sampling, incidental sampling, quota sampling, total sampling, and snowball sampling.