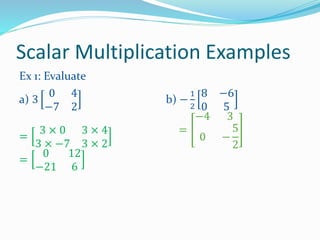
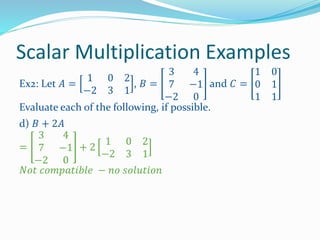
Students will learn that a scalar is a single number that can scale each value in a matrix. They will practice multiplying matrices by scalars and performing scalar addition and subtraction of matrices. For a matrix A and scalar c, the scalar product cA means multiplying each element of A by c. Examples show multiplying matrices by scalars like 2A and -1/2A, and adding or subtracting matrices with scalar coefficients like 5C - B.