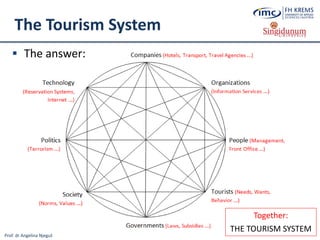
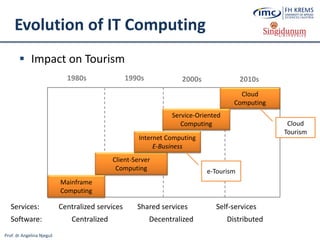
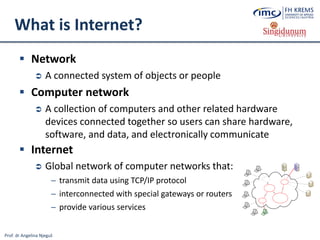
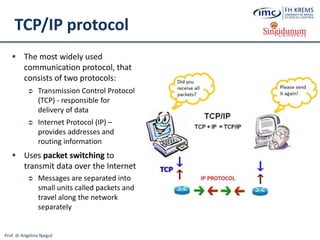
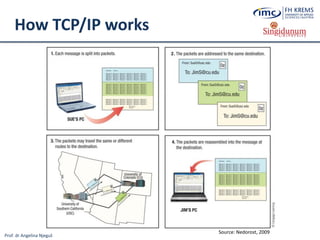
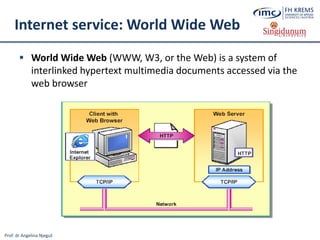
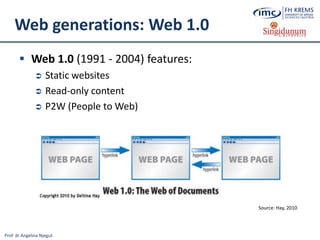
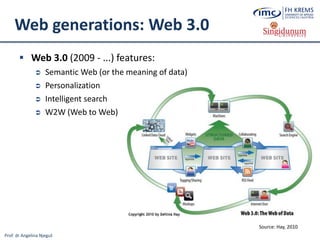
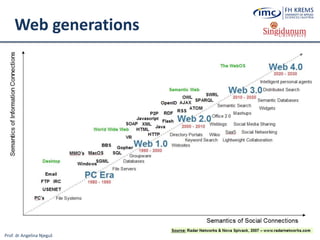
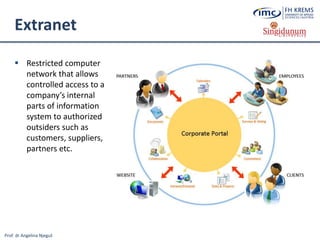
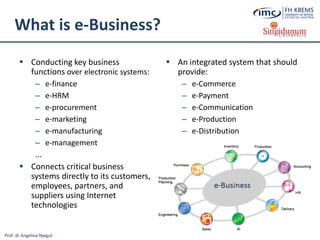
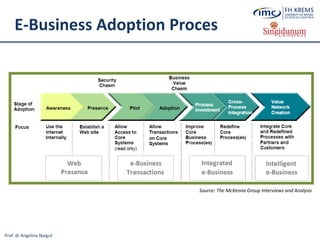
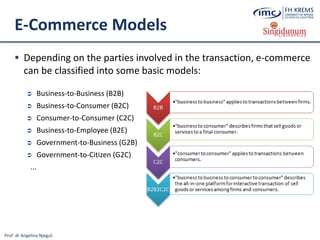
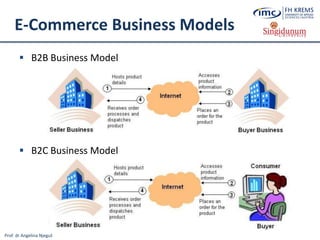
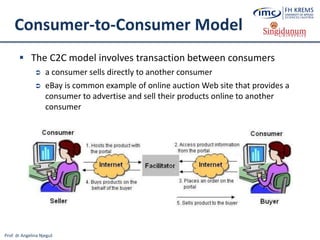
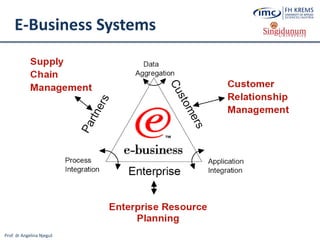
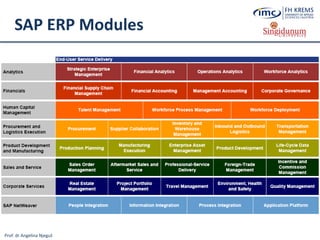
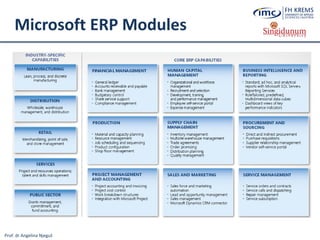
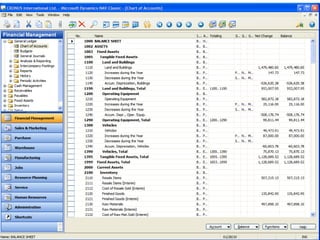
The document discusses the integration of e-business systems within the tourism industry, covering concepts such as the tourism system, e-tourism, and cloud computing. It explains the evolution of tourism driven by technology, detailing various e-commerce models and the roles of CRM and ERP systems. Additionally, it describes the benefits of cloud computing for small and large organizations in the tourism sector.









![Prof. dr Angelina Njeguš
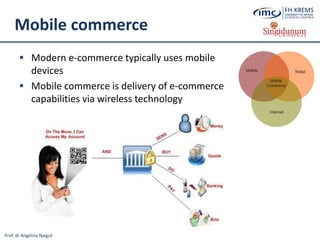
e-Commerce
e-Commerce is a subset of an overall e-business strategy
the sales aspect of e-business
e-Commerce involves conducting business transactions over
electronic systems
It is usually associated with buying and selling over the Internet, or
conducting any business transaction involving the transfer of
ownership or rights to use goods or services [6]
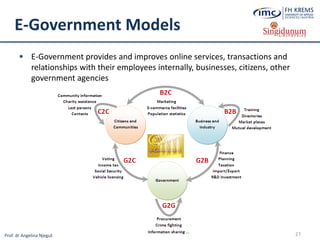
The main e-commerce actors are represented as:
B – Business
C – Customer/Consumer/Citizen
G – Government
E – Employee](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson2-ebusinessintourism-130719073355-phpapp02/85/Lesson-2-e-Business-Systems-in-Tourism-23-320.jpg)





![Prof. dr Angelina Njeguš
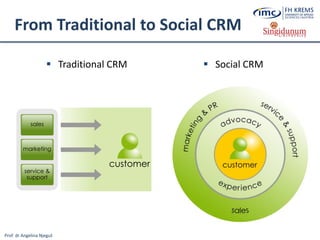
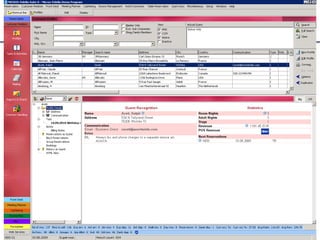
CRM software
CRM software provides sales,
marketing, and support teams
with powerful tools to efficiently
and effectively manage
customer relationships [7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson2-ebusinessintourism-130719073355-phpapp02/85/Lesson-2-e-Business-Systems-in-Tourism-36-320.jpg)

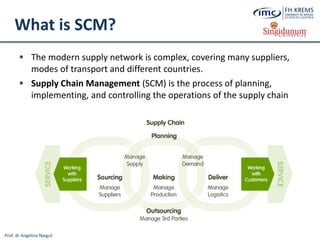

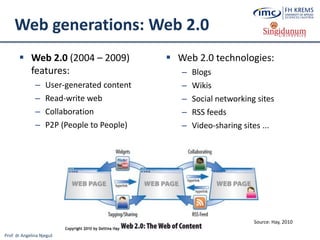
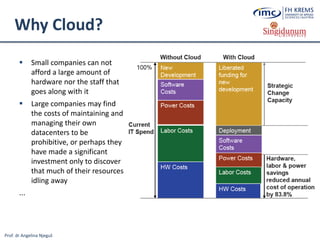
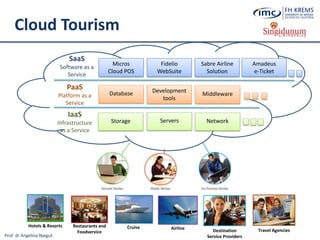
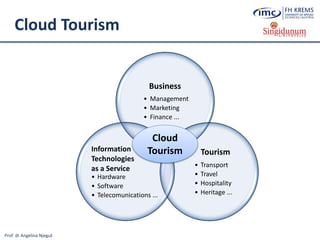
![Prof. dr Angelina Njeguš
Cloud Tourism
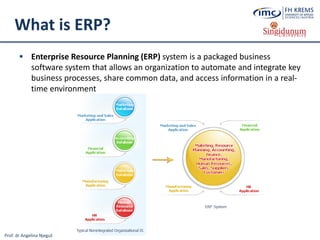
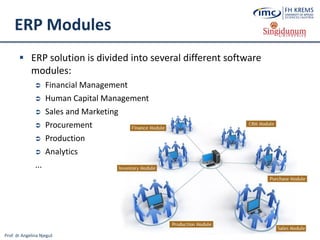
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing (often referred to as simply „the cloud“) is the delivery of
on-demand computing resources (software, infrastructure, platforms and
information) over the Internet and on a pay-for-use basis [8] without the
need to install, store, purchase and maintain them locally on client computers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson2-ebusinessintourism-130719073355-phpapp02/85/Lesson-2-e-Business-Systems-in-Tourism-51-320.jpg)

![Prof. dr Angelina Njeguš
References
1. Swindoll, C. (2011) „Redefining Fundraising – Data“, Pursuant [Online]. Available at: http://www.pursuant.com/blog/tag/dikw-model/
(accessed: 1.11.2012)
2. Nedorost, T. (2009) „CGS1060 Introduction to Computer Science“, PowerPoint presentation [online]
3. Hay, D. (2010) „Web 3.0 demystified: An explanation in pictures“, Social Media. Available at: http://socialmedia.biz/2010/10/21/web-3-0-
demystified-an-explanation-in-pictures/ (accessed: 30.11.2012)
4. Venema, M. (2011) „An Introduction to the Tourism System“, Education for Tourism, Edutour BV.
5. Njeguš, A. (2012) Information Systems in Tourism Industry, Singidunum University, Belgrade.
6. WikiBooks, „E-Commerce and e-Buisness – Concepts and Definitions“. Available at: http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/E-Commerce_and_E-
Business/Concepts_and_Definitions (accessed: 16.01.2013)
7. Sage CRM (2010) „Creating a customer focused business with CRM“. Available at: http://www.sagecrm.com/northamerica/what-is-crm/
(accessed: 17.01.2013)
8. IBM Smart Cloud, „Computing as a service over the Internet“, IBM. Available at: http://www.ibm.com/cloud-computing/us/en/what-is-cloud-
computing.html (accessed: 18.01.2013)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson2-ebusinessintourism-130719073355-phpapp02/85/Lesson-2-e-Business-Systems-in-Tourism-56-320.jpg)