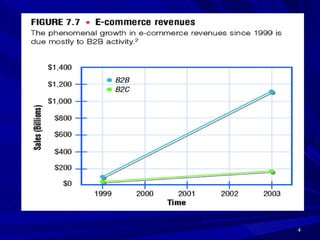
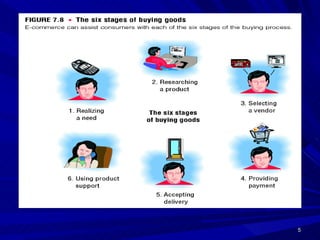
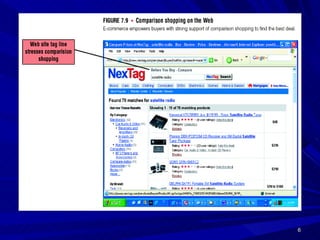
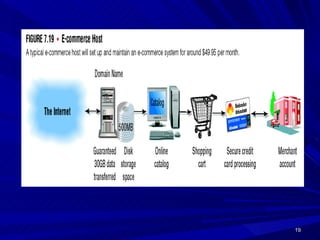
This document defines e-commerce and discusses its various types and applications. It outlines the key components of an e-commerce system, including the three main types (B2C, B2B, C2C), benefits and challenges, and how mobile commerce is impacting the industry. The implementation of an e-commerce system requires investment in infrastructure, hardware, networking, and security to support online transactions and build customer trust.