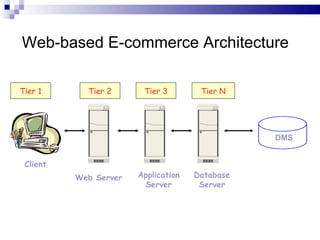
The document discusses electronic commerce (e-commerce), providing a brief history from the 1970s to the 1990s. It outlines the main elements of e-commerce including business-to-consumer and business-to-business transactions. The advantages and disadvantages of e-commerce are presented. Key components of e-commerce infrastructure and technologies are also described.