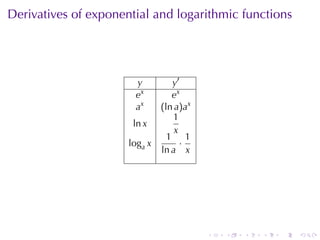
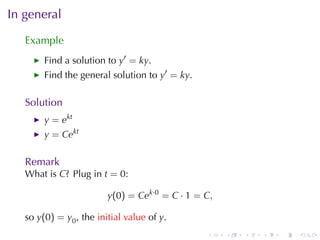
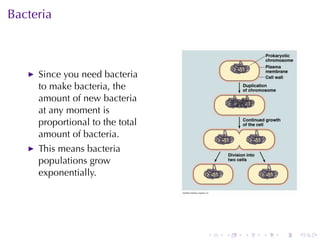
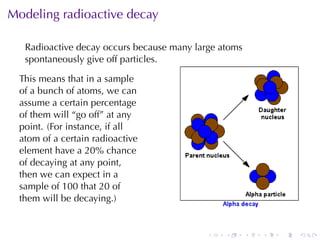
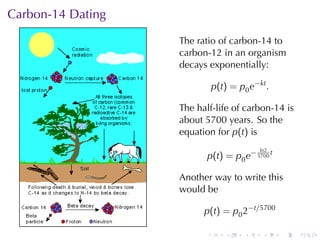
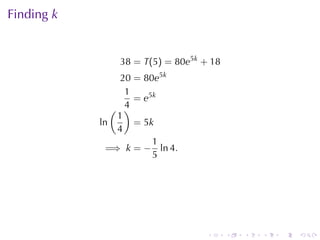
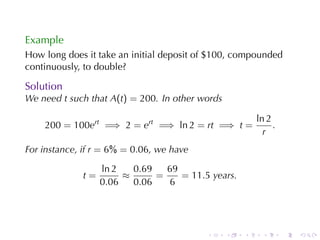
This document discusses exponential growth and decay within the context of calculus, detailing differential equations and their applications in models such as population growth, radioactive decay, and Newton's law of cooling. It covers specific examples and solutions, including bacterial growth and carbon-14 dating, while also explaining concepts such as half-life and continuously compounded interest. Overall, it illustrates how mathematical principles are used to model natural phenomena and solve real-world problems.