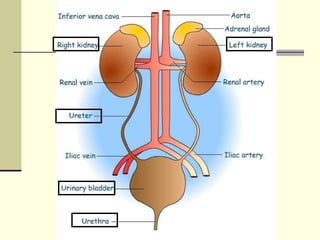
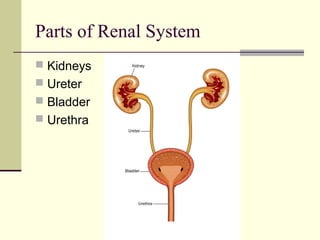
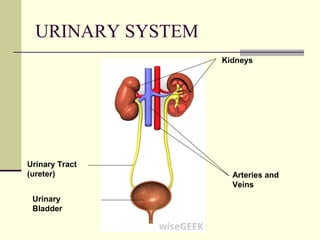
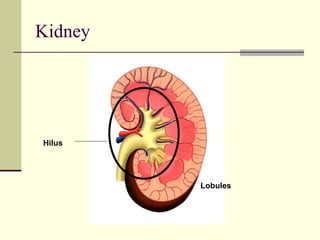
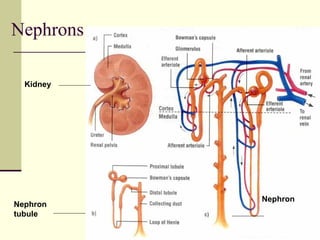
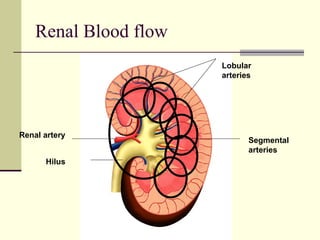
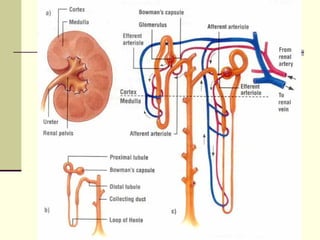
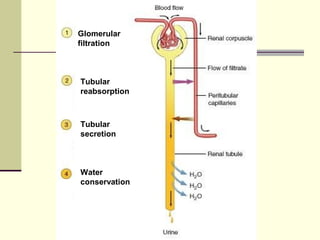
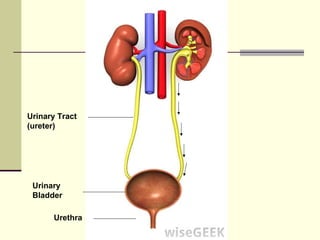
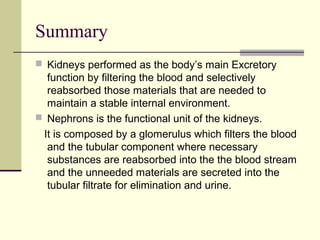
The urinary system, also known as the renal system, is responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine, which travels through the ureters to the bladder for storage and then exits through the urethra. The functional unit of the kidneys is the nephron, which filters blood in the glomerulus and reabsorbs necessary substances or secretes waste in the tubular component to regulate water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance.