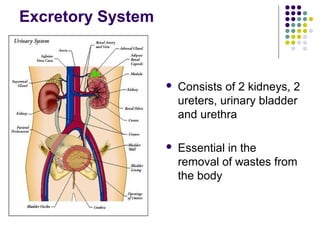
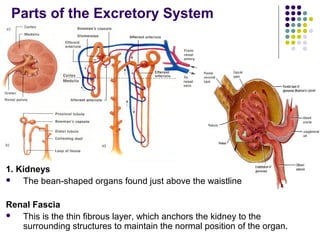
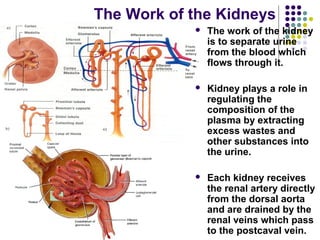
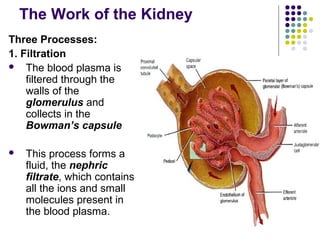
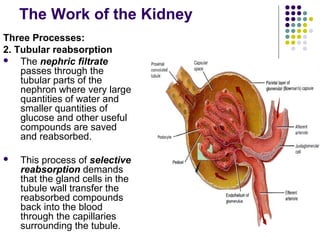
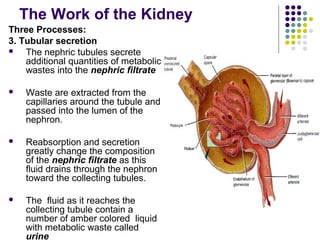
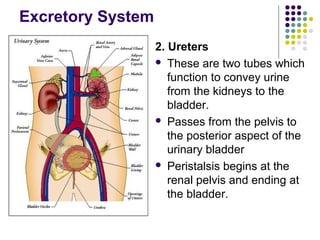
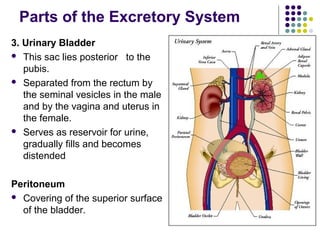
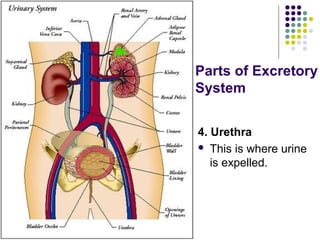
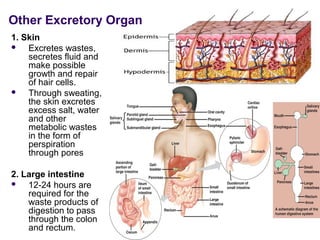
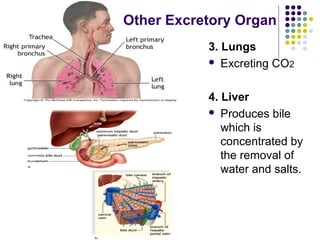
The excretory system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra which work together to remove waste from the body. The kidneys filter blood and regulate waste removal by selectively reabsorbing useful compounds while secreting metabolic wastes into urine. This urine is then transported through the ureters to the bladder and finally expelled from the body through the urethra, aided by other excretory organs like the skin, lungs, large intestine and liver.