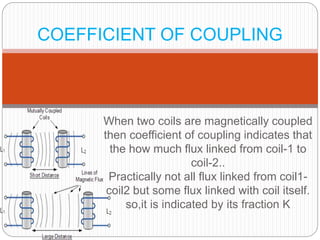
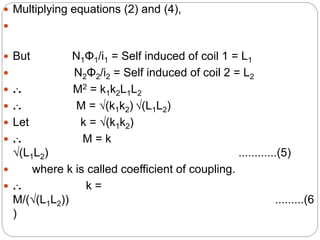
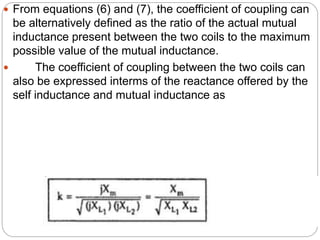
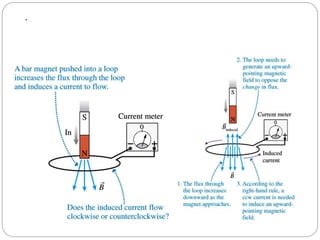
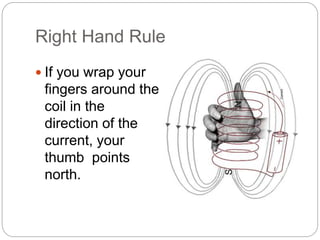
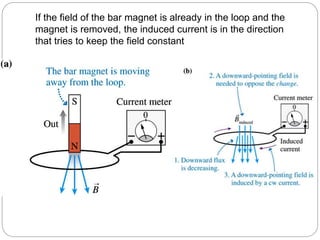
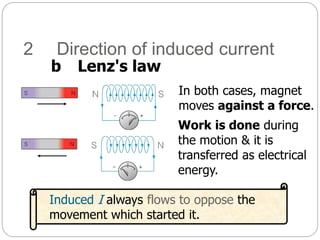
Lenz's law describes the direction of induced current in a coil due to a changing magnetic flux. The coefficient of coupling (k) indicates the amount of flux from one coil that is linked to another coupled coil. k is defined as the ratio of the actual mutual inductance between the coils to the maximum possible mutual inductance. When k=1, the coils are perfectly coupled and the mutual inductance is at its maximum value. When coils are loosely coupled, k is very small and only a small fraction of flux links between the coils. Lenz's law states that any change in magnetic flux through a coil will induce a current whose direction opposes the change in flux.