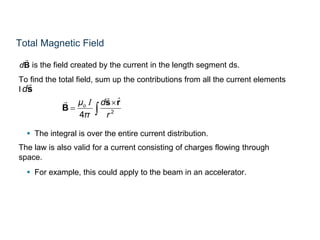
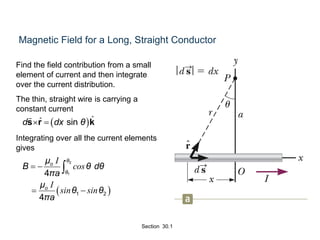
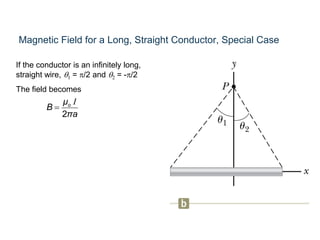
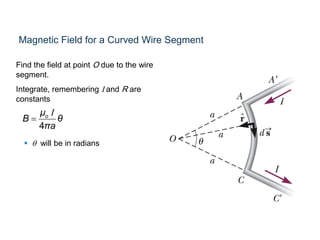
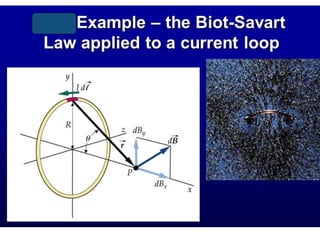
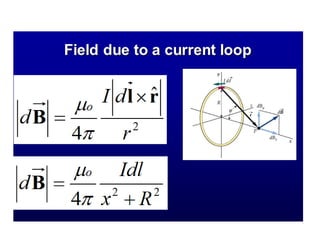
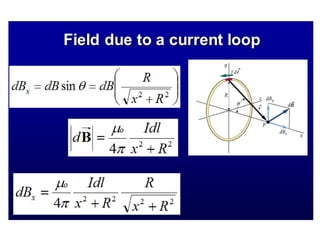
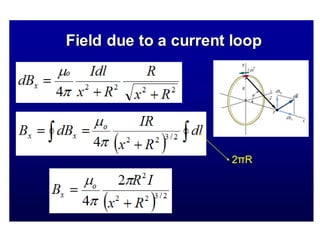
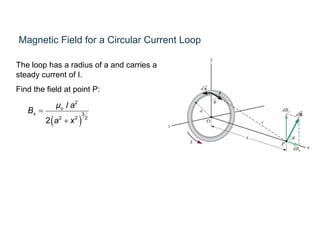
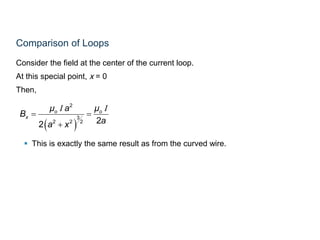
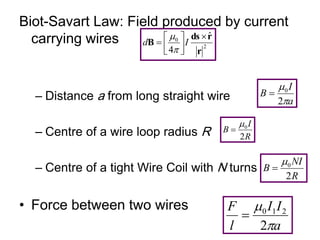
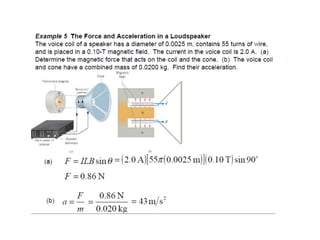
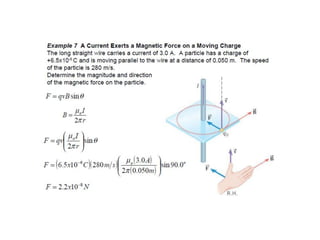
The Biot-Savart law describes the magnetic field generated by electric currents. It states that the magnetic field at a point P due to a current element I ds is proportional to the current I and inversely proportional to the distance r from the current element to the point P. The field is also proportional to the length of the current element ds and perpendicular to both r and ds. Integrating this contribution from all current elements gives the total magnetic field generated by the current distribution. Specific applications include calculating the field from a long straight wire, circular loop, and tightly wound coil.