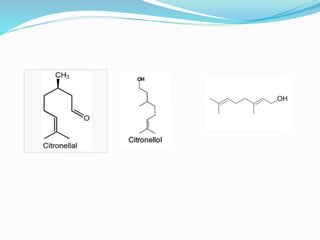
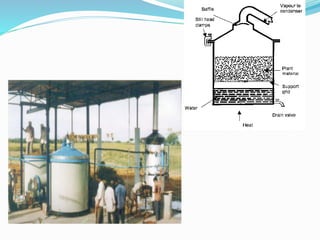
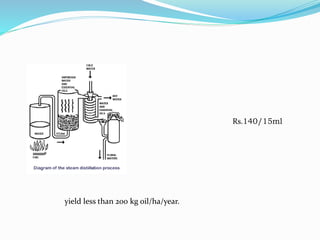
This document summarizes information about lemongrass oil, including its botanical name, production, cultivation parameters, uses, and trade. Lemongrass oil is extracted from Cymbopogon citratus grass through steam distillation. It grows in tropical climates with high sunlight and humidity. Common uses of lemongrass oil include use in insect repellents and as a preservative, pesticide, and culinary herb. Global production is around 1300 tonnes annually, with major producers including China, Indonesia, and India.