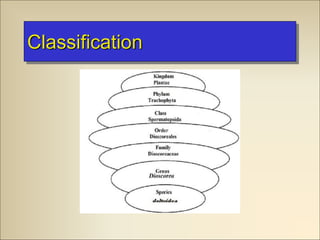
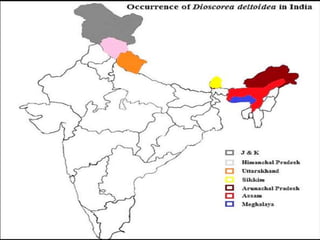
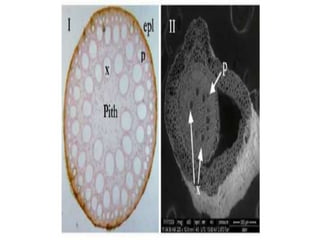
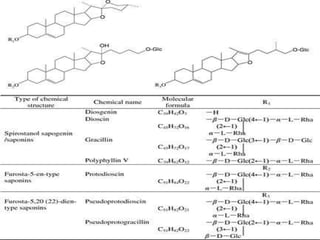
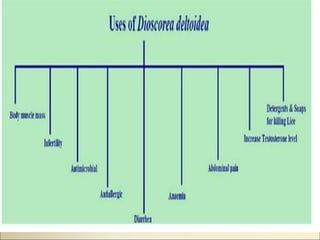
This document provides information on the plant Dioscorea deltoidea. It discusses the plant's classification (genus Dioscorea, family Dioscoreaceae), synonyms, geographical distribution in Nepal and northwest Himalayas, morphology and microscopic characteristics of its tubers/rhizomes. It also covers the plant's cultivation, chemical constituents including diosgenin, traditional medicinal uses to treat gastric issues, dysentery and as a source of steroidal drugs, and formulations/dosage. Safety of D. deltoidea is considered relatively low risk.