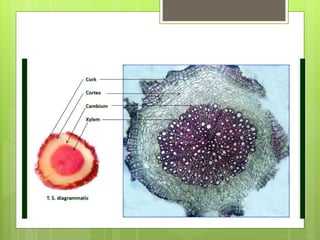
Rauwolfia serpentina, commonly known as Indian snakeroot or serpent wood, is a plant native to the Himalayan region. It contains several important alkaloids such as reserpine, ajmaline, and serpentine that have pharmacological effects including lowering blood pressure and acting as a sedative. The dried roots are used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat hypertension, anxiety, and intestinal disorders. The plant is cultivated for its medicinal properties, and its dried roots are an important crude drug that is exported internationally.