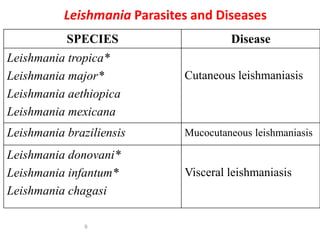
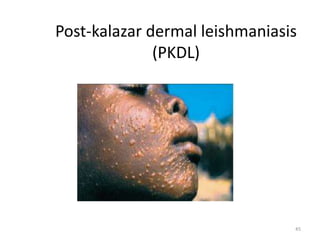
Leishmaniasis is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Leishmania and is transmitted by sand flies. Kala-azar, also known as visceral leishmaniasis, is caused by L. donovani and presents with fever, weight loss, enlarged liver and spleen. It is diagnosed by identifying the parasites in bone marrow or spleen aspirates under microscopy. Treatment involves pentavalent antimony compounds. Control relies on vector control measures and treating infected individuals to reduce the reservoir and prevent epidemics. Some patients may later develop a skin condition called post-kala azar dermal leishmaniasis.