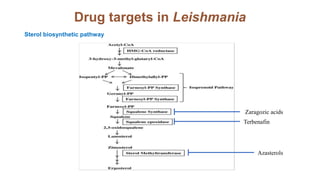
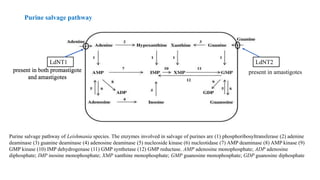
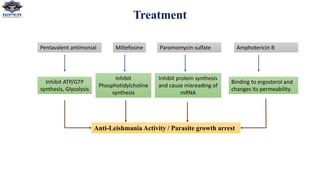
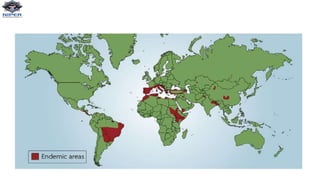
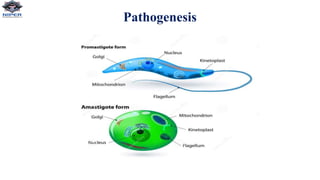
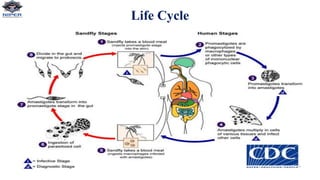
Leishmania donovani is the causative agent of visceral leishmaniasis (VL), a neglected tropical disease predominantly affecting impoverished populations in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. VL presents with symptoms like fever, weight loss, and splenomegaly, and can be fatal if untreated; the disease is transmitted through bites from infected female sandflies. Diagnosis relies on various methods including parasitological examination and serological tests, while treatment options include medications like pentavalent antimonial and miltefosine, with no available vaccine for prevention.






![Diagnosis
1. Parasitology Diagnosis
• Current gold standard for diagnosis relies on visualization of amastigote form of parasite within macrophages by
microscopic examination of tissue aspirates (spleen, Bone marrow or lymph nodes) after Giemsa staining
• In-vitro culture- require special media (Novy-MacNeal-Nicolle[NNN] media) and is not widely available in most endemic
regions
2. Serologic Diagnosis
• Direct agglutination test (sensitivity 95%, specificity 86%)
• rK39- based immunochromatographic strip test (sensitivity 94%, specificity 95%)
• IFA(Immunofluorescent assay), ELISA, Immunoblotting
3. Antigen Detection Test
• Kala-azar latex agglutination test (KAtex), detecting a heat-stable leishmania antigen in the urine of VL patient.
4. Molecular Diagnosis
• PCR-based assay to detect parasite DNA
• PCR on peripheral blood has been recommended as non-invasive first line screening test for both immunocompetent and
immunocompromised patients
NOTE: Diagnosis of PKDL relies on microscopic demonstration of parasites in skin specimens](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leshmania-220331091149/85/Leshmania-pptx-12-320.jpg)