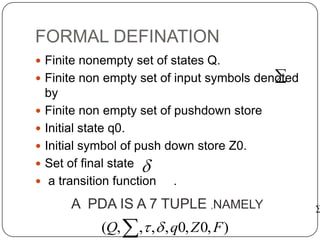
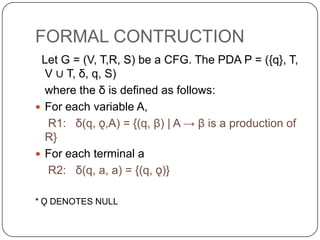
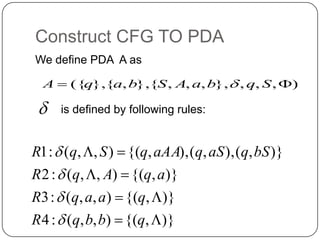
This document discusses pushdown automata (PDA) and how they can be used to accept context-free languages. It defines a PDA as a 7-tuple that includes a finite set of states, input symbols, stack symbols, initial state, initial stack symbol, set of final states, and a transition function. A context-free grammar is also defined as a 4-tuple that includes variables, terminals, production rules, and a start symbol. The document then shows how to construct a PDA that is equivalent to a given context-free grammar by defining transition rules based on the grammar productions. An example of converting a grammar to a PDA using this construction method is also provided.