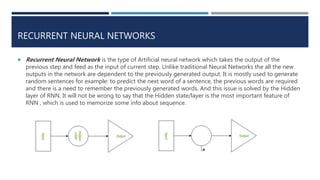
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are a type of artificial neural network that can process sequential data of varying lengths. Unlike traditional neural networks, RNNs maintain an internal state that allows them to exhibit dynamic temporal behavior. RNNs take the output from the previous step and feed it as input to the current step, making the network dependent on information from earlier steps. This makes RNNs well-suited for applications like text generation, machine translation, image captioning, and more. RNNs can remember information for long periods of time but are difficult to train due to issues like vanishing gradients.