This document discusses the lecture method of teaching, which is a teacher-centered approach where the teacher orally delivers content to passive students. Key points include:
- The lecture method is the most commonly used method for teaching science and involves the teacher carefully planning and presenting expository content to students.
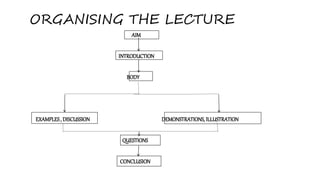
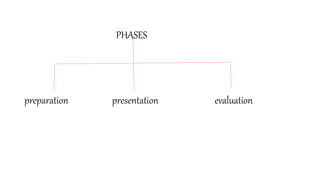
- Effective lectures have clear objectives, introduction, body, examples/illustrations, questions, and conclusion. Preparation, presentation, and evaluation are important phases.
- Lectures are best for introducing new topics, reviewing material, and efficiently covering content, but do not promote student participation or skills development.
- Advantages are that it is economical, imparts knowledge quickly, and allows the