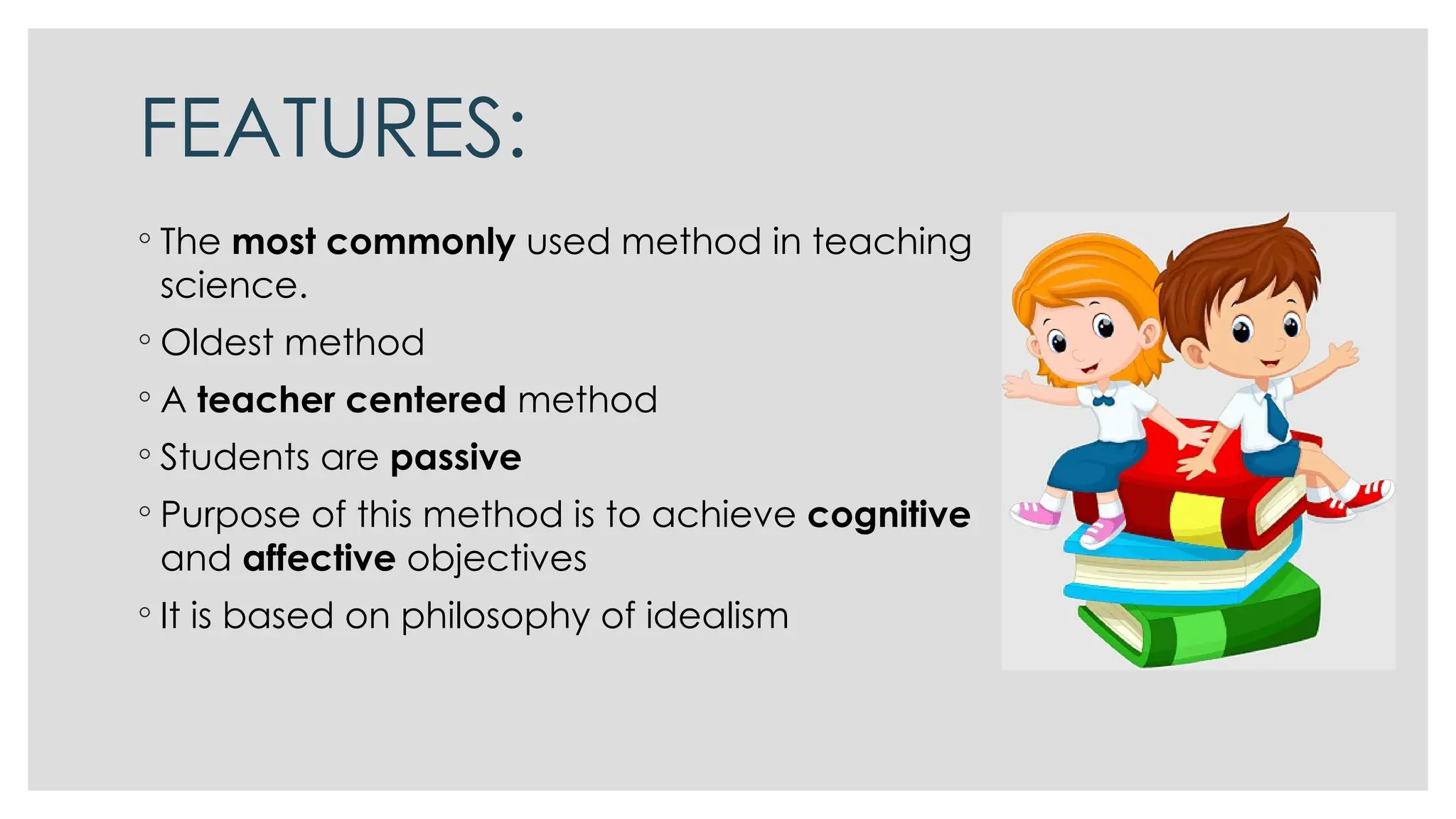
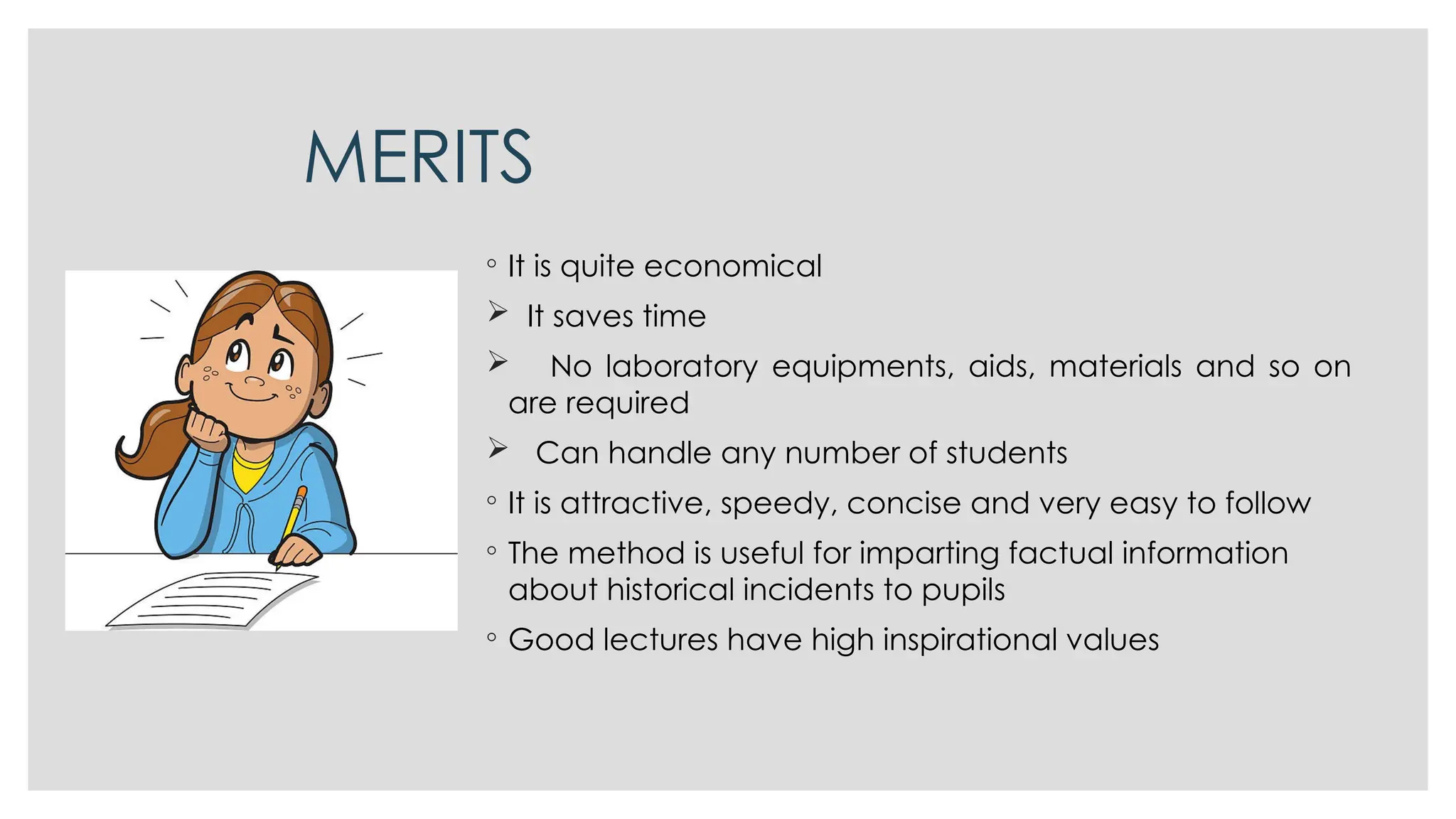
The lecture method is a traditional, teacher-centered approach for presenting information and teaching concepts, primarily in science education. It has distinct phases of preparation, development, and consolidation, aiming to impart knowledge efficiently but often resulting in passive learning without fostering independent thinking or scientific inquiry. While it can be economical and inspirational, it has notable drawbacks such as not accommodating individual needs and over-relying on memory.