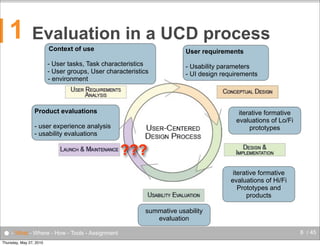
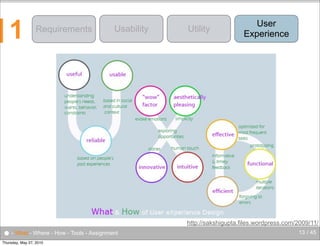
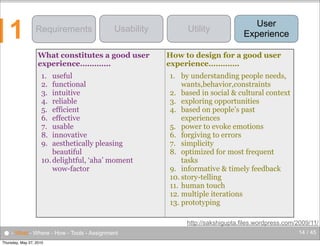
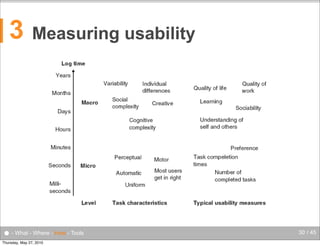
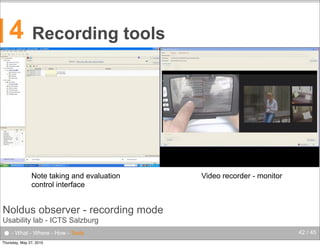
The document discusses the complexities of evaluating human-computer interaction (HCI) and usability, particularly in the context of unconventional interfaces beyond traditional desktop applications, like tangible user interfaces and augmented reality. It highlights the challenges of usability assessments in mobile and ubiquitous computing environments, emphasizing the need for tailored evaluation methods and tools suited to various contexts. Additionally, it outlines best practices for user experience analysis, including iterative testing, understanding user needs, and utilizing appropriate evaluation environments.