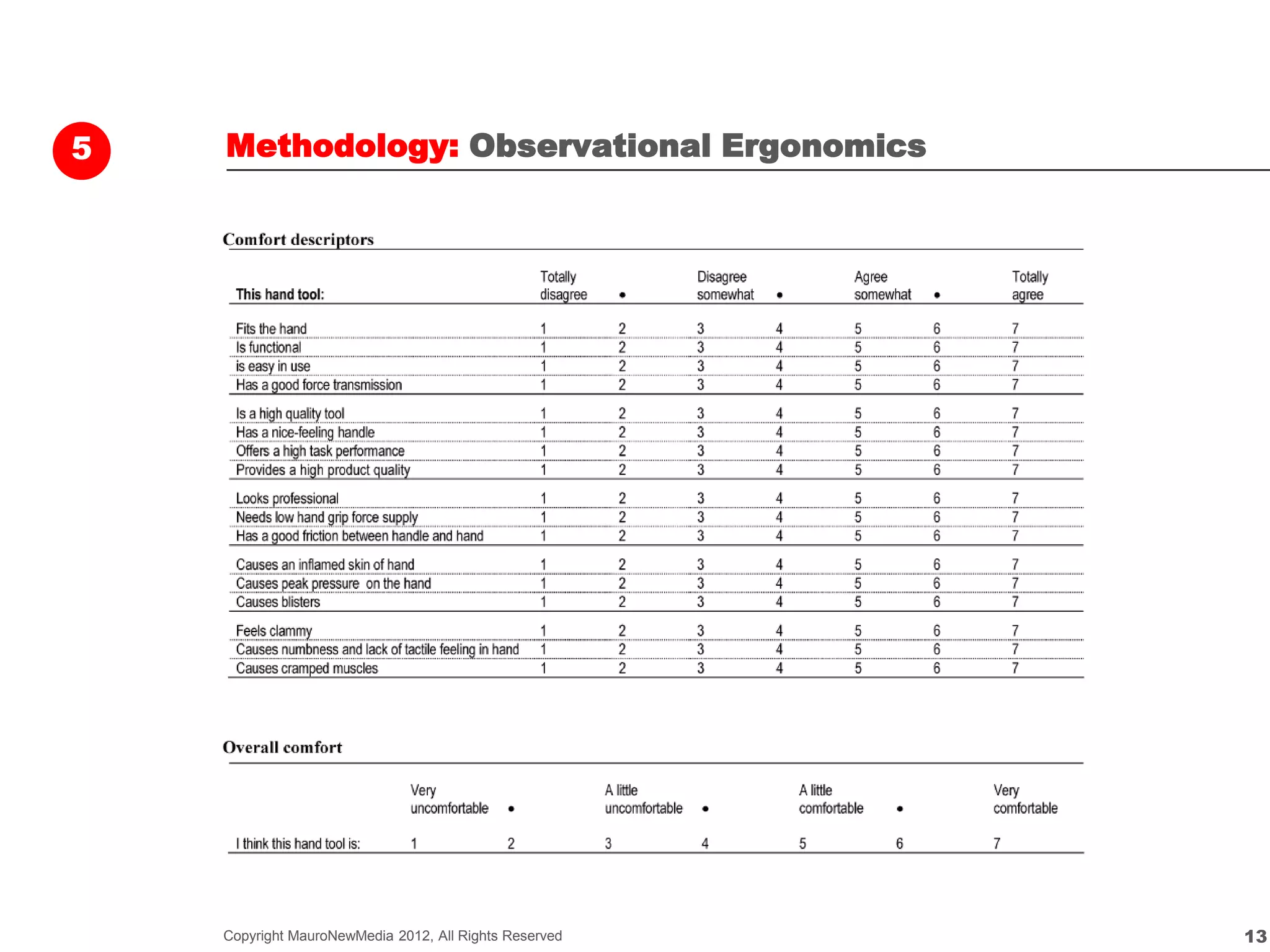
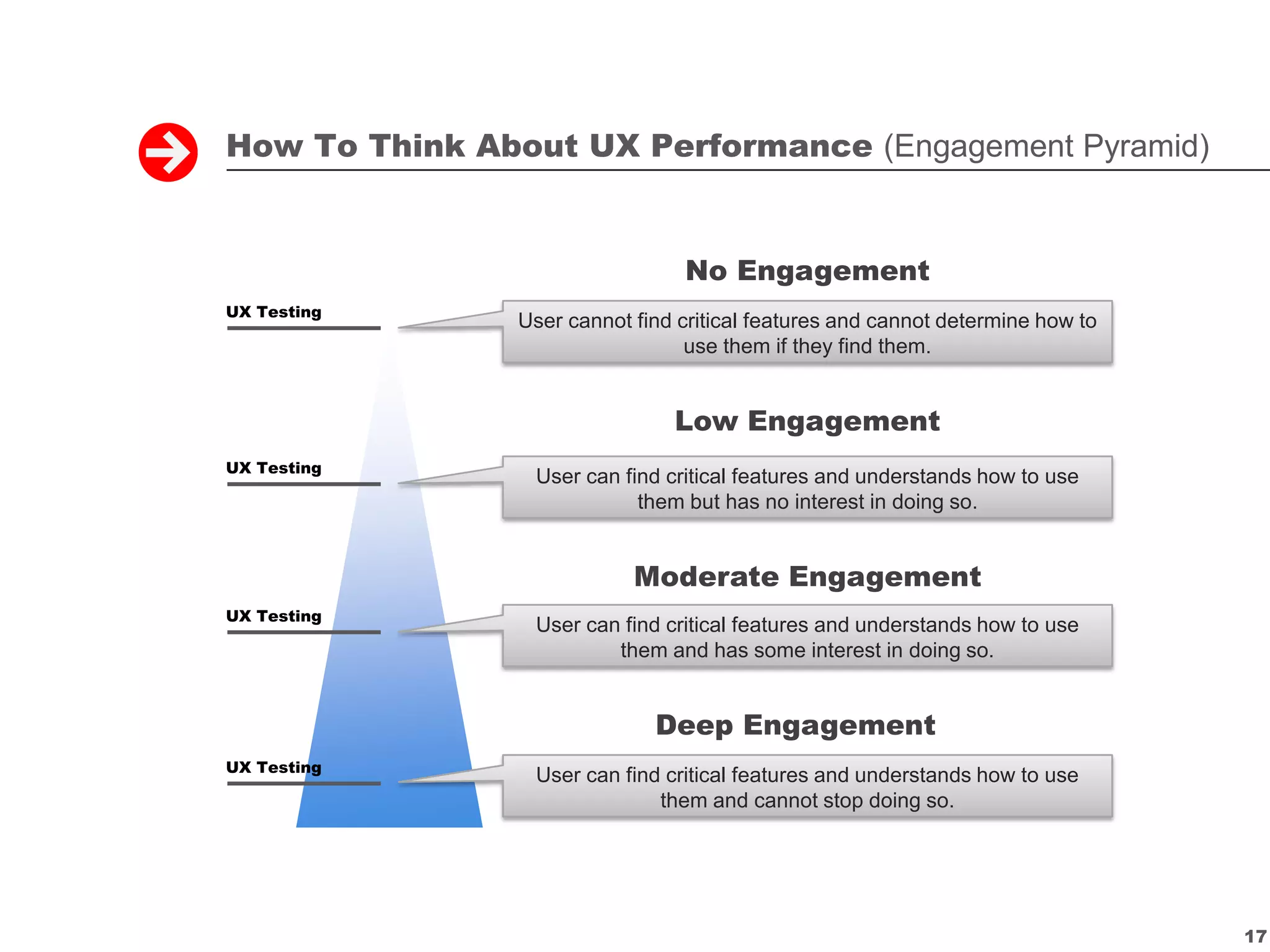
The document outlines various methodologies for measuring user experience (UX) design to ensure user acceptance and business success. It emphasizes the importance of identifying critical problems and opportunities through diverse research methods, including contextual observation, remote ethnography, qualitative data analysis, focus groups, and quantitative techniques. Organized by Charles L. Mauro, the content serves as a guide for UX professionals to understand and apply effective research methods in their projects.