The document provides an overview of key concepts related to balance sheets:
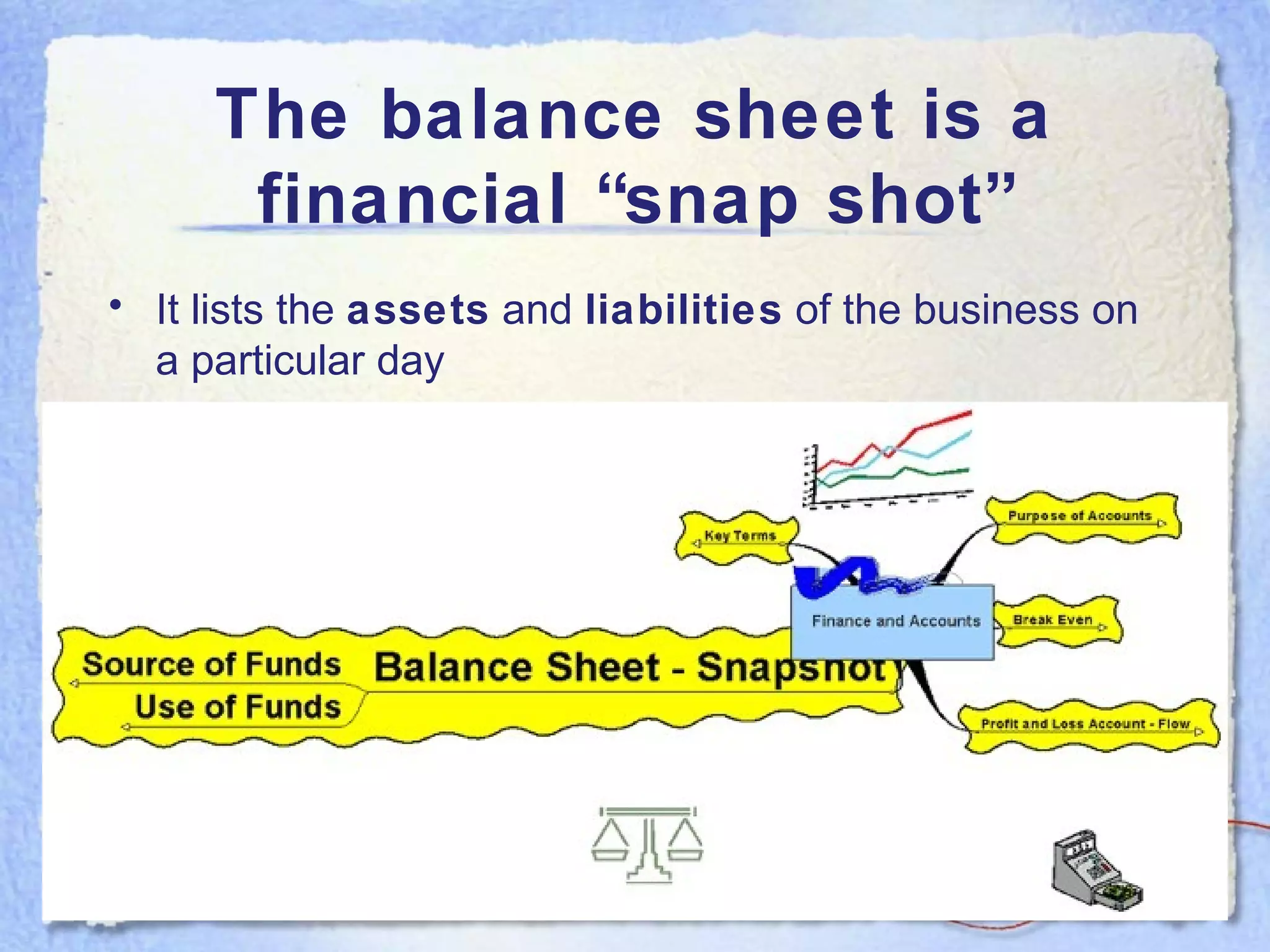
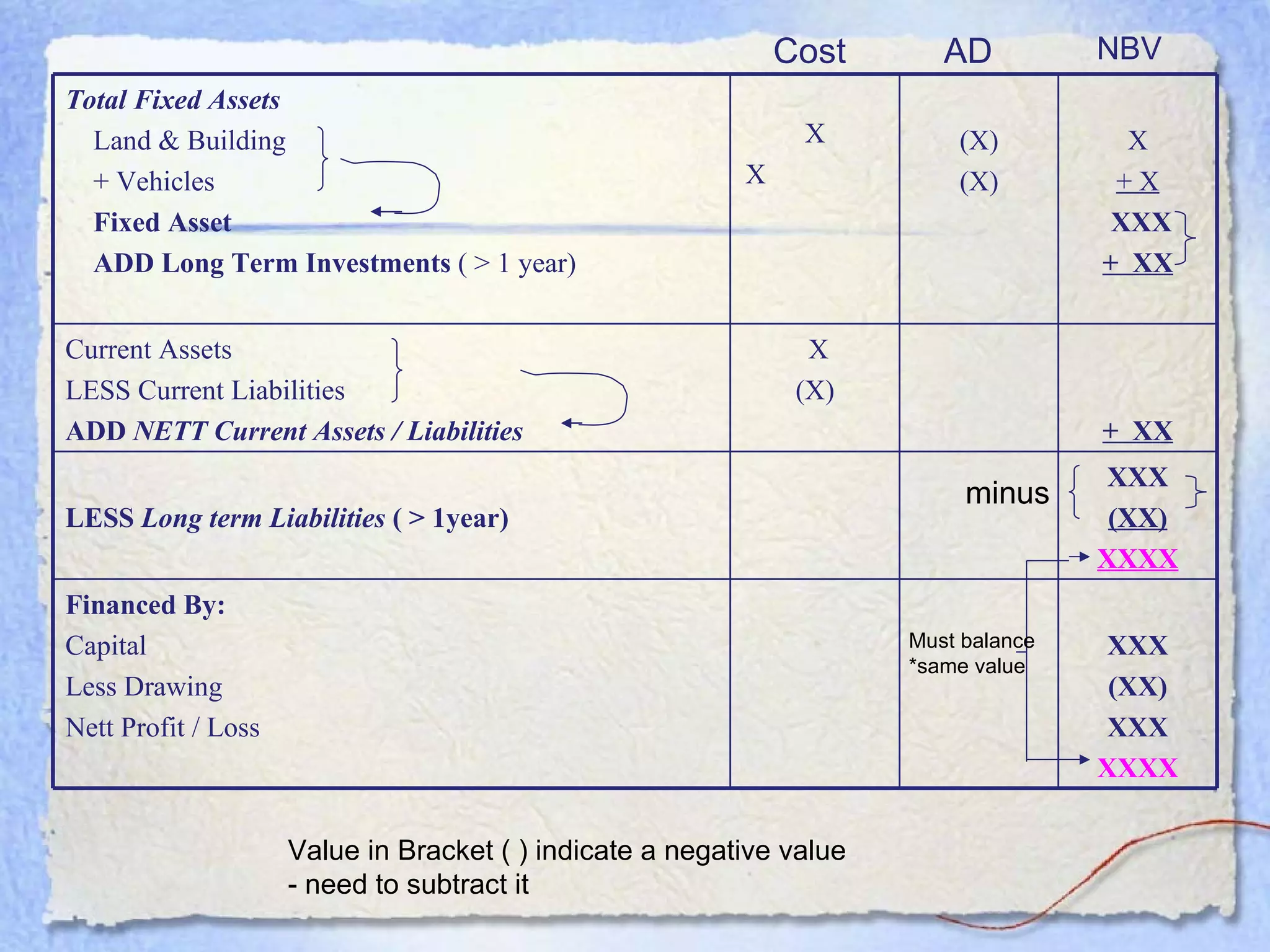
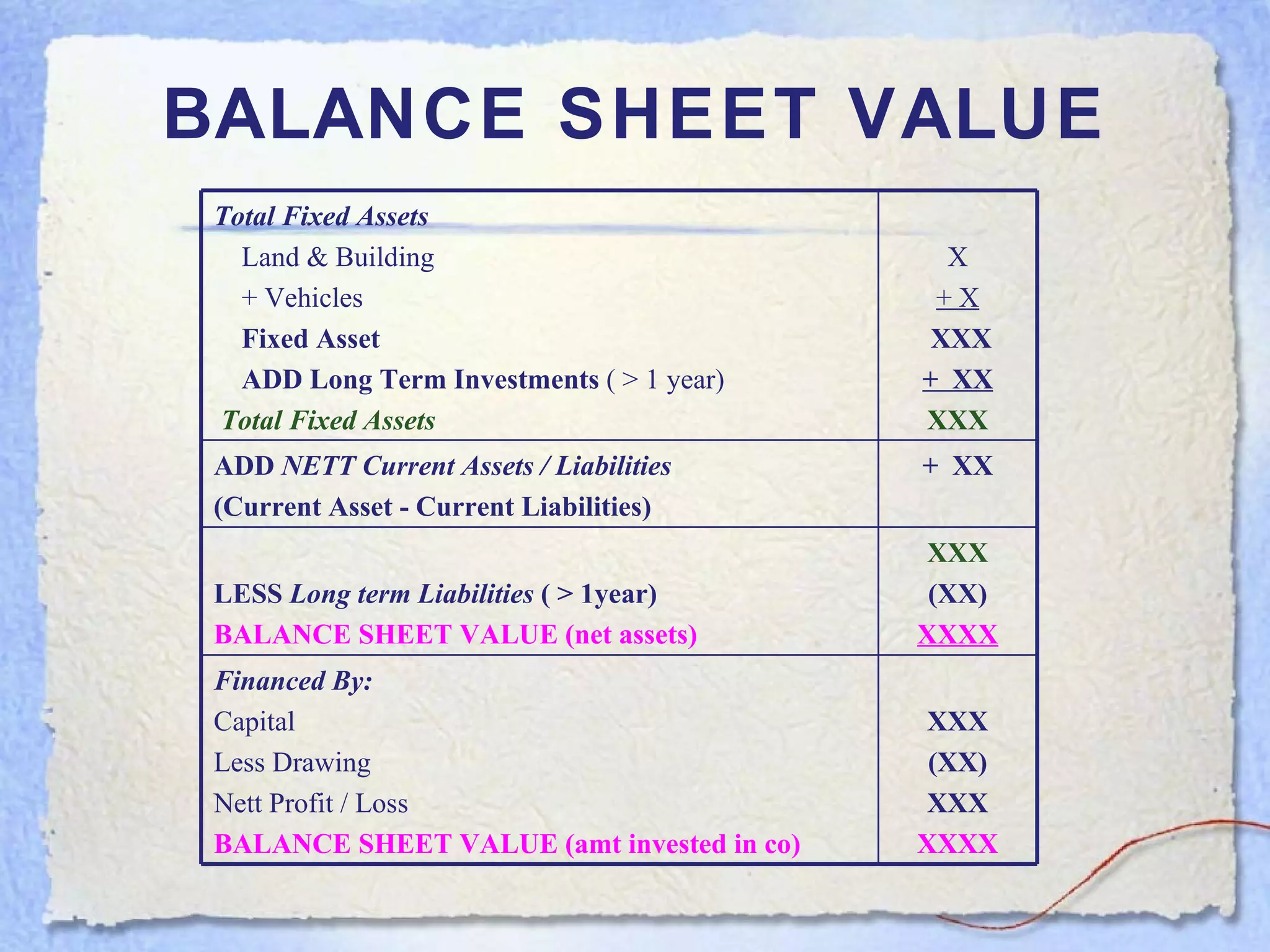
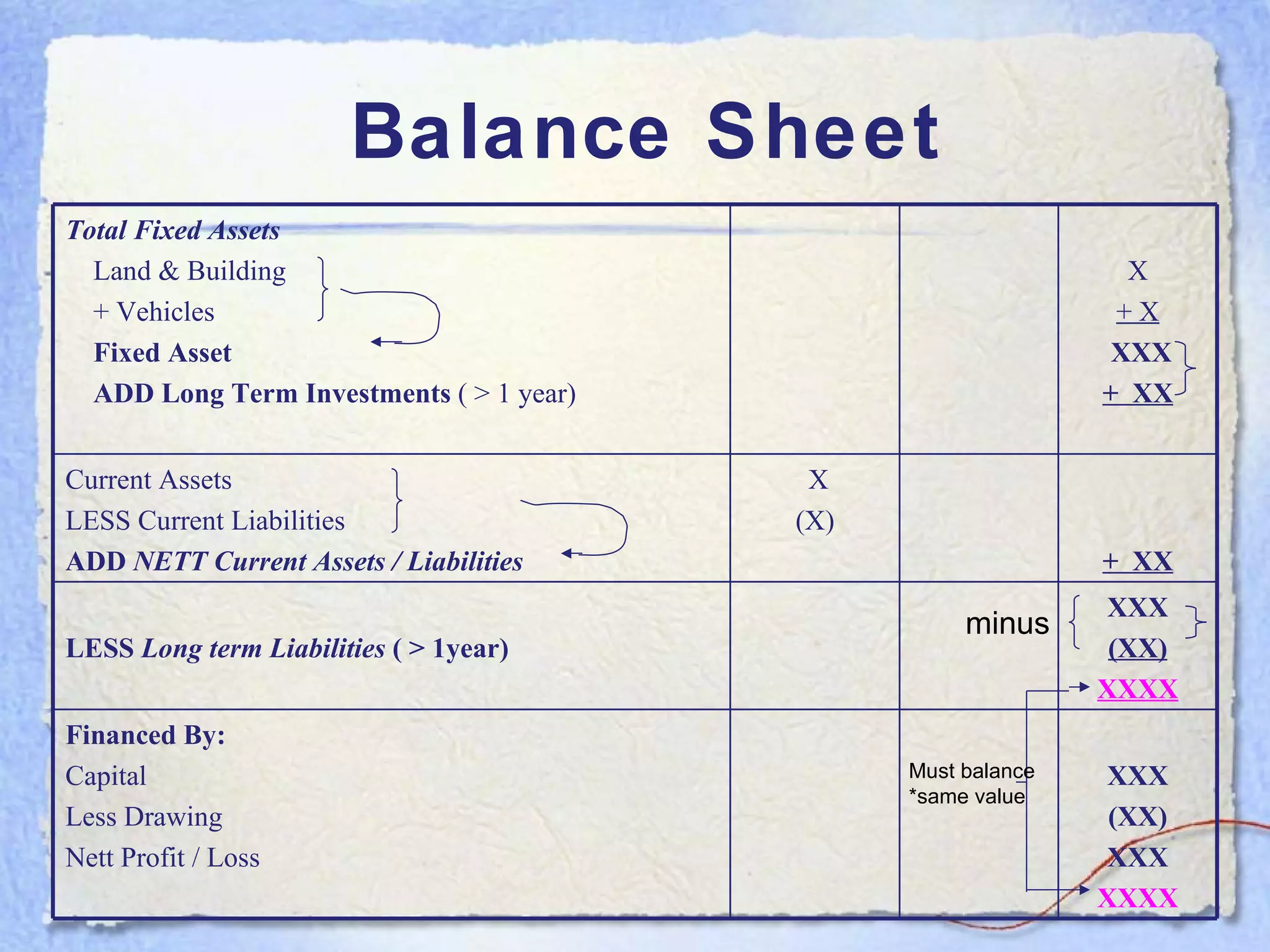
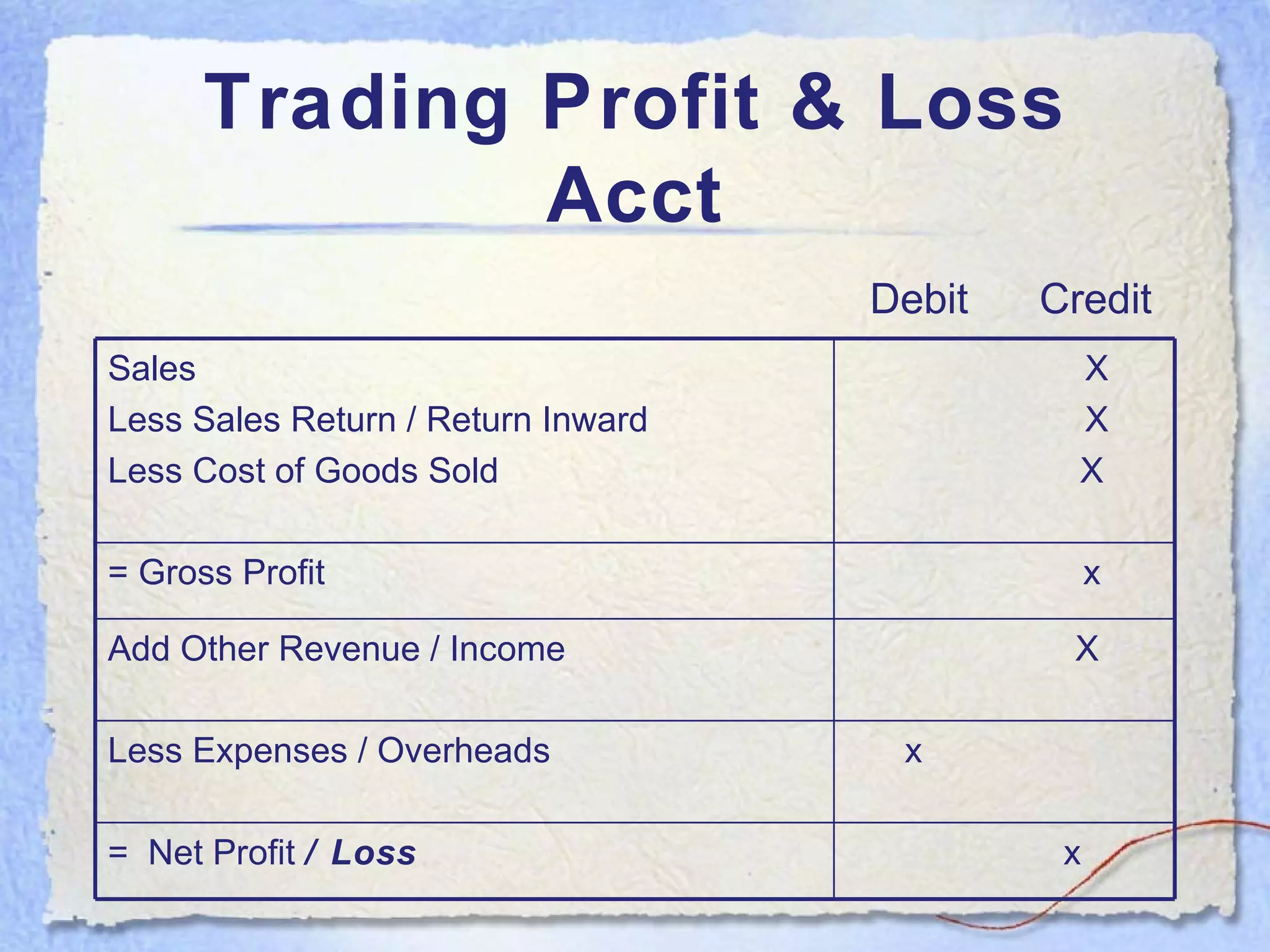
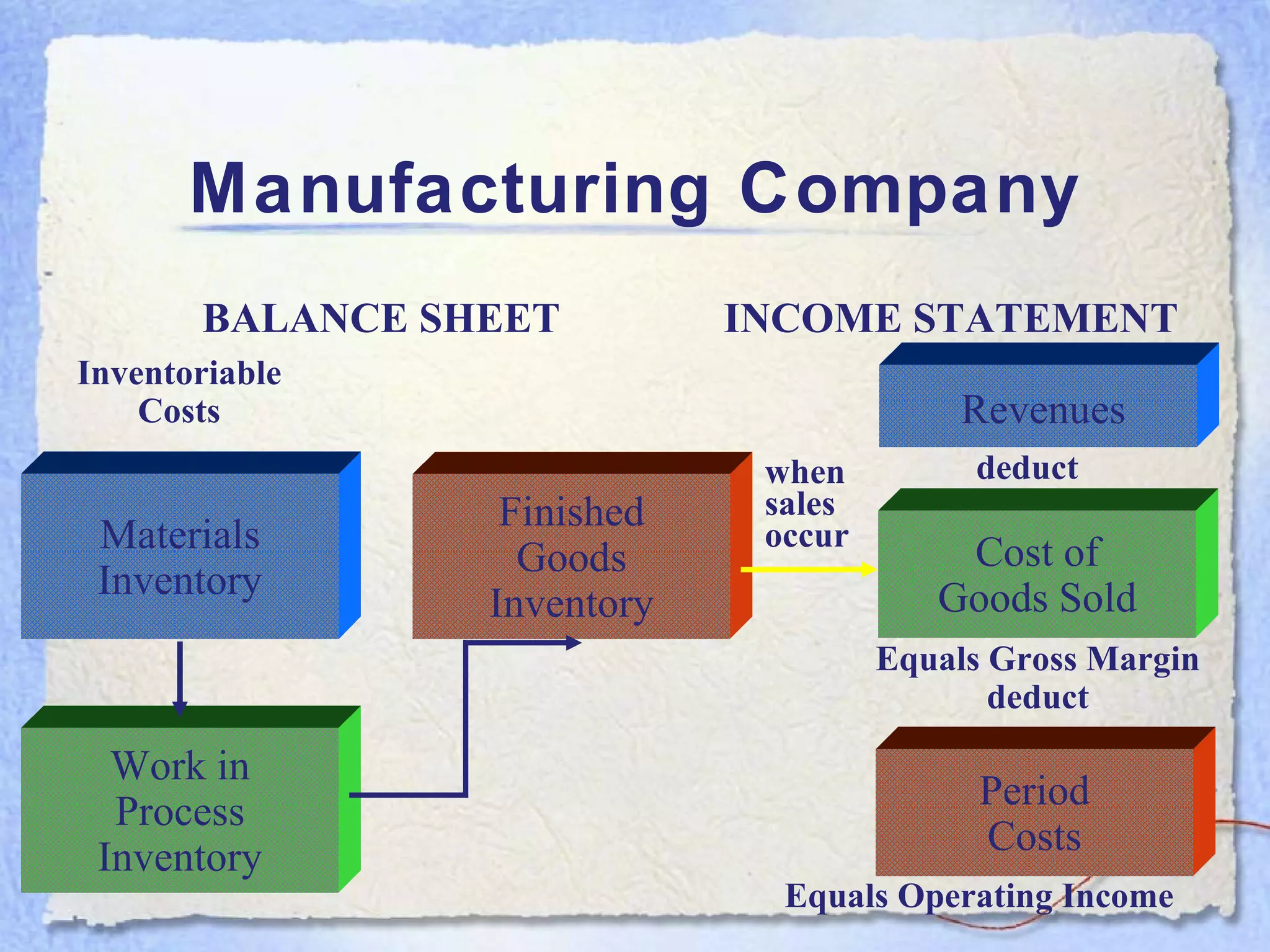
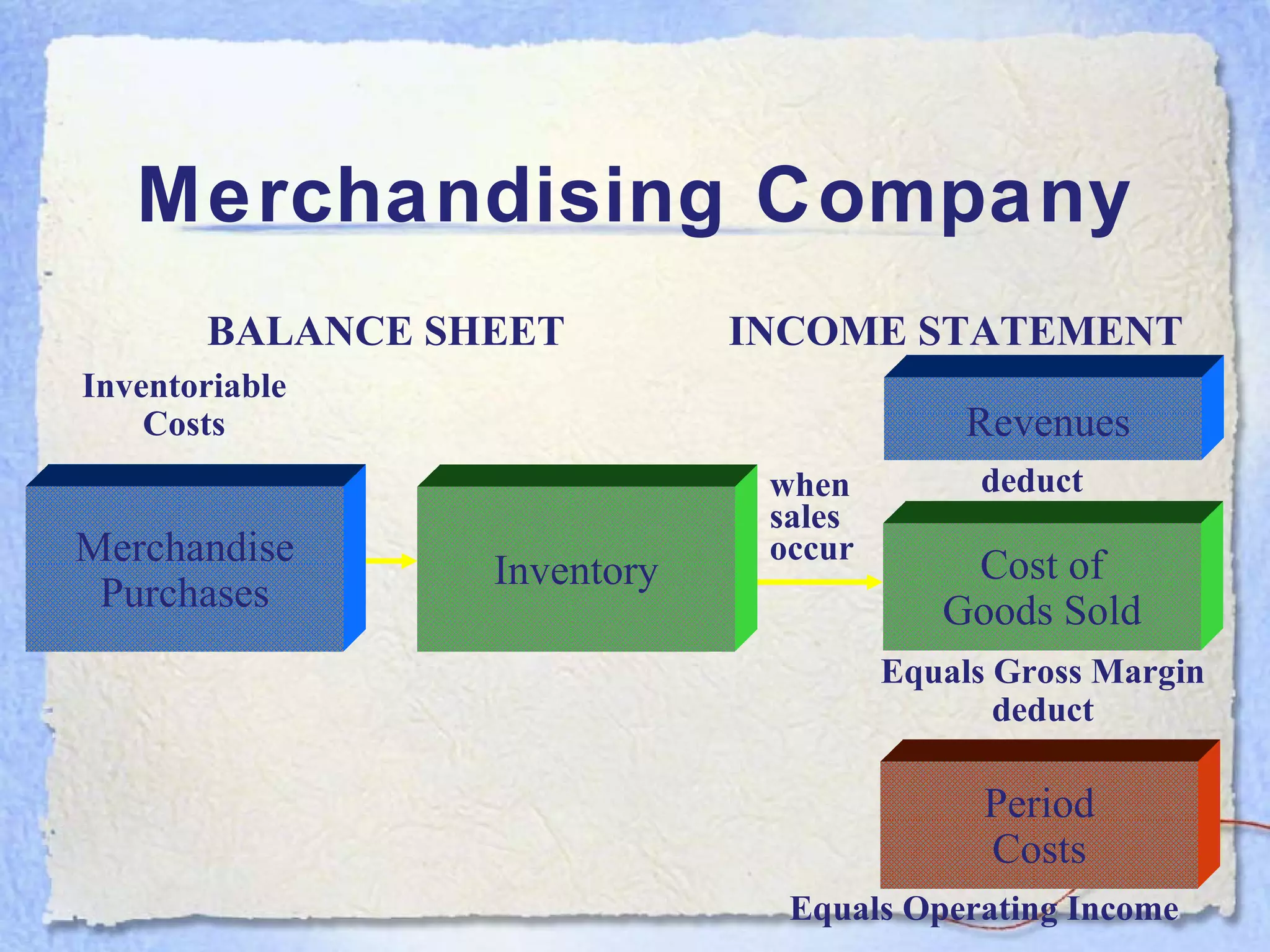
- A balance sheet is a financial statement that lists a business's assets, liabilities, and equity at a point in time. It provides a snapshot of what the business owns and owes.
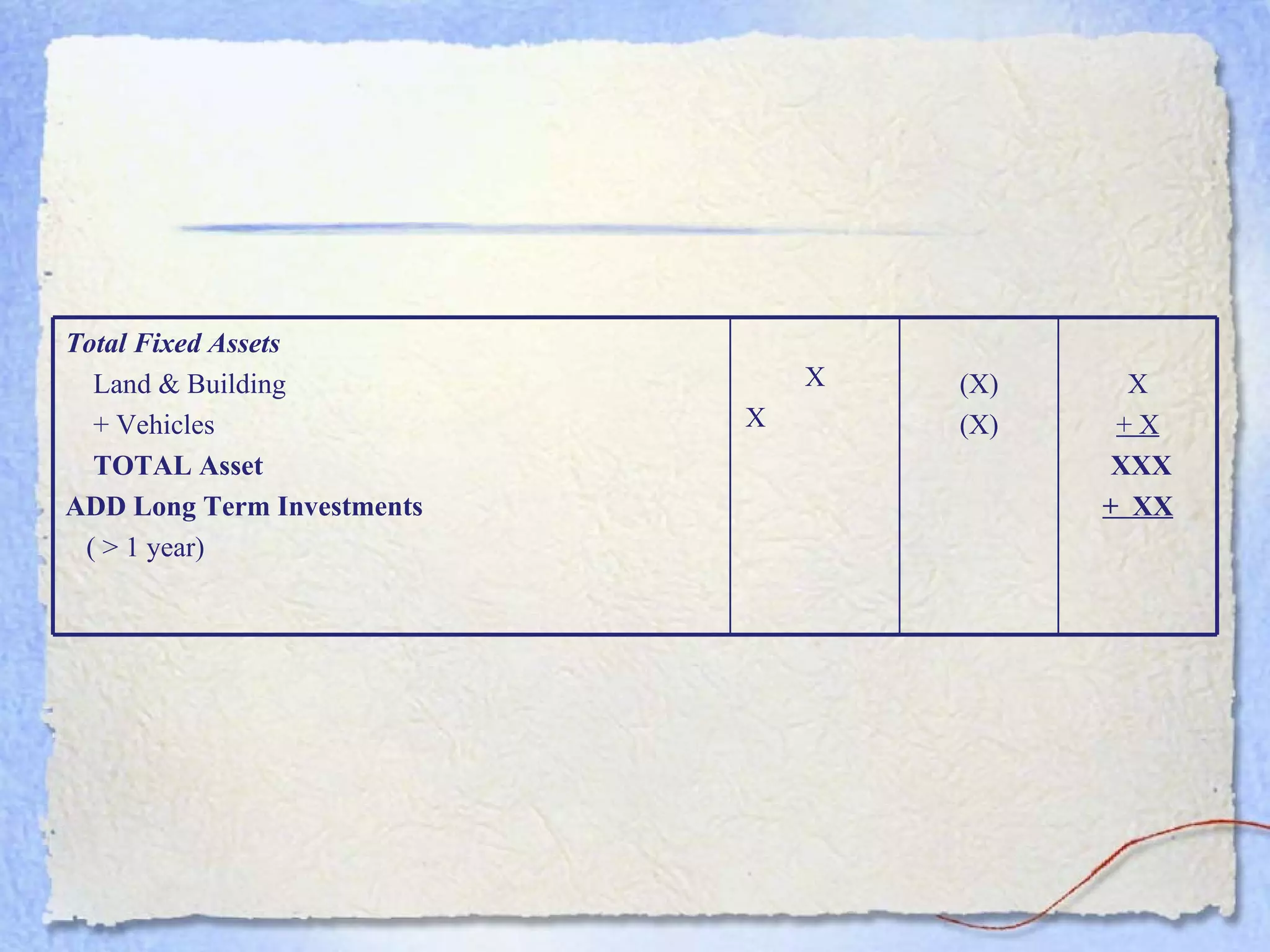
- The key components of a balance sheet are assets (what the business owns), liabilities (what the business owes), and equity (the owner's investment and retained earnings). Assets must equal the sum of liabilities and equity.
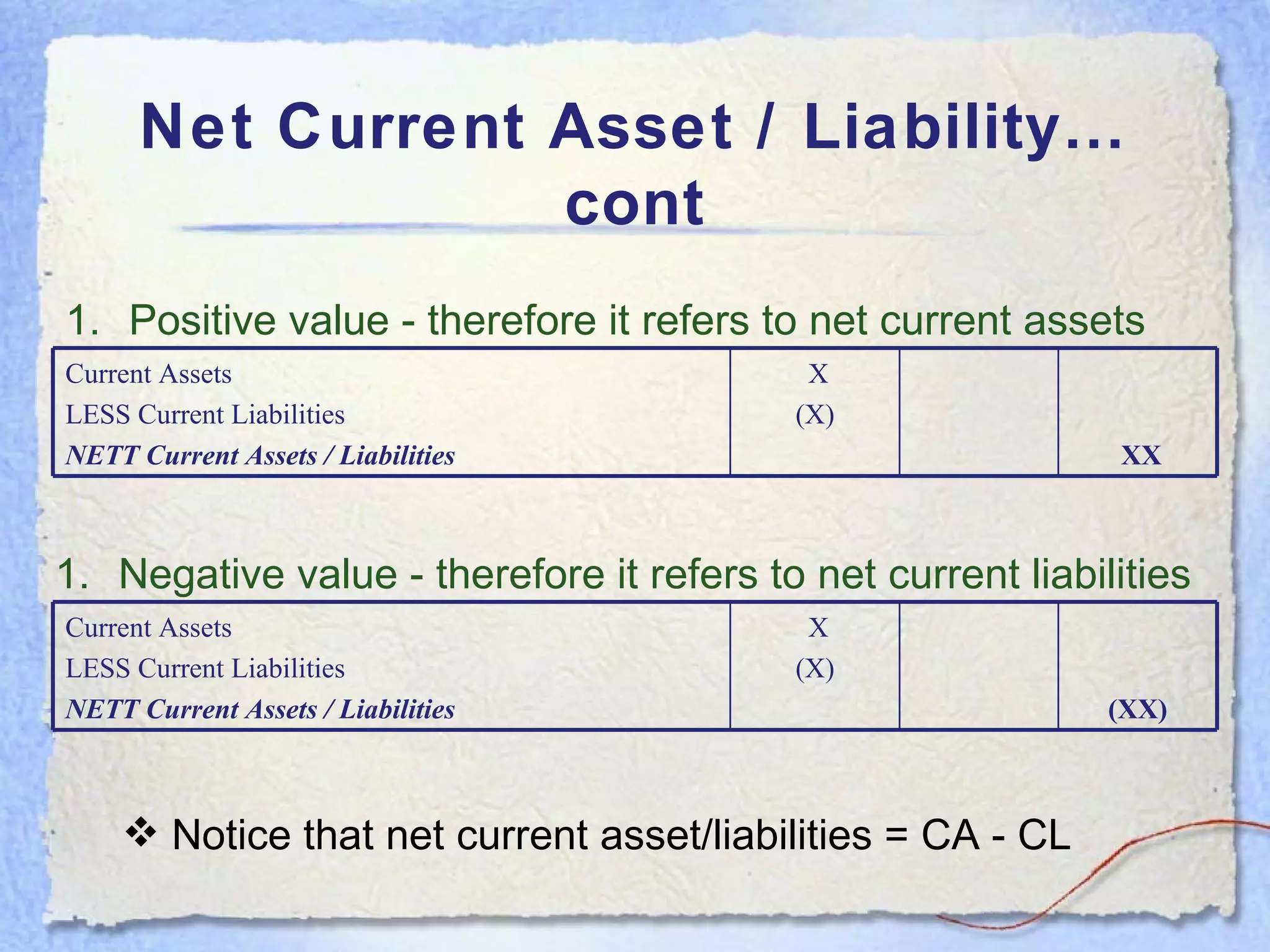
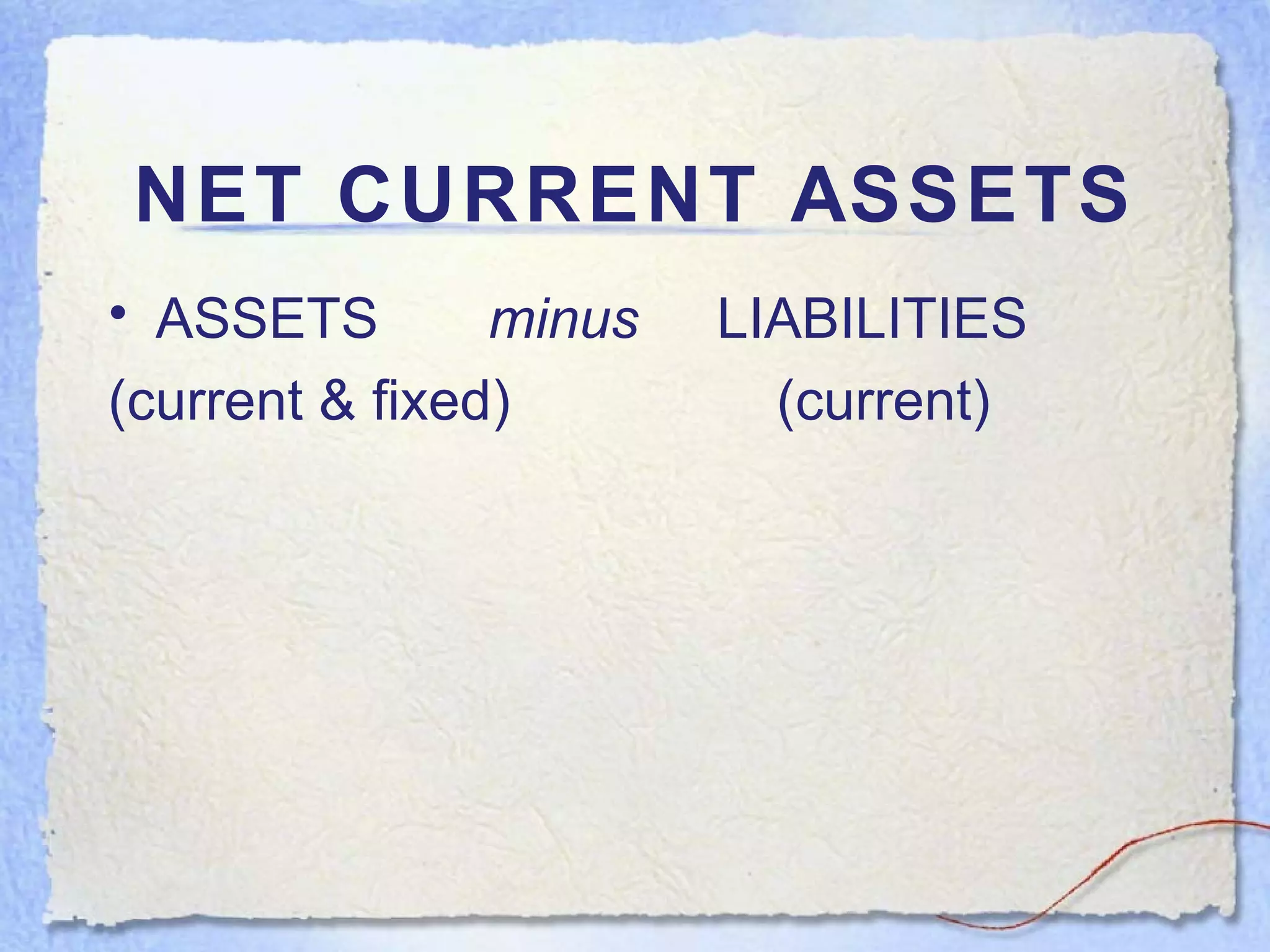
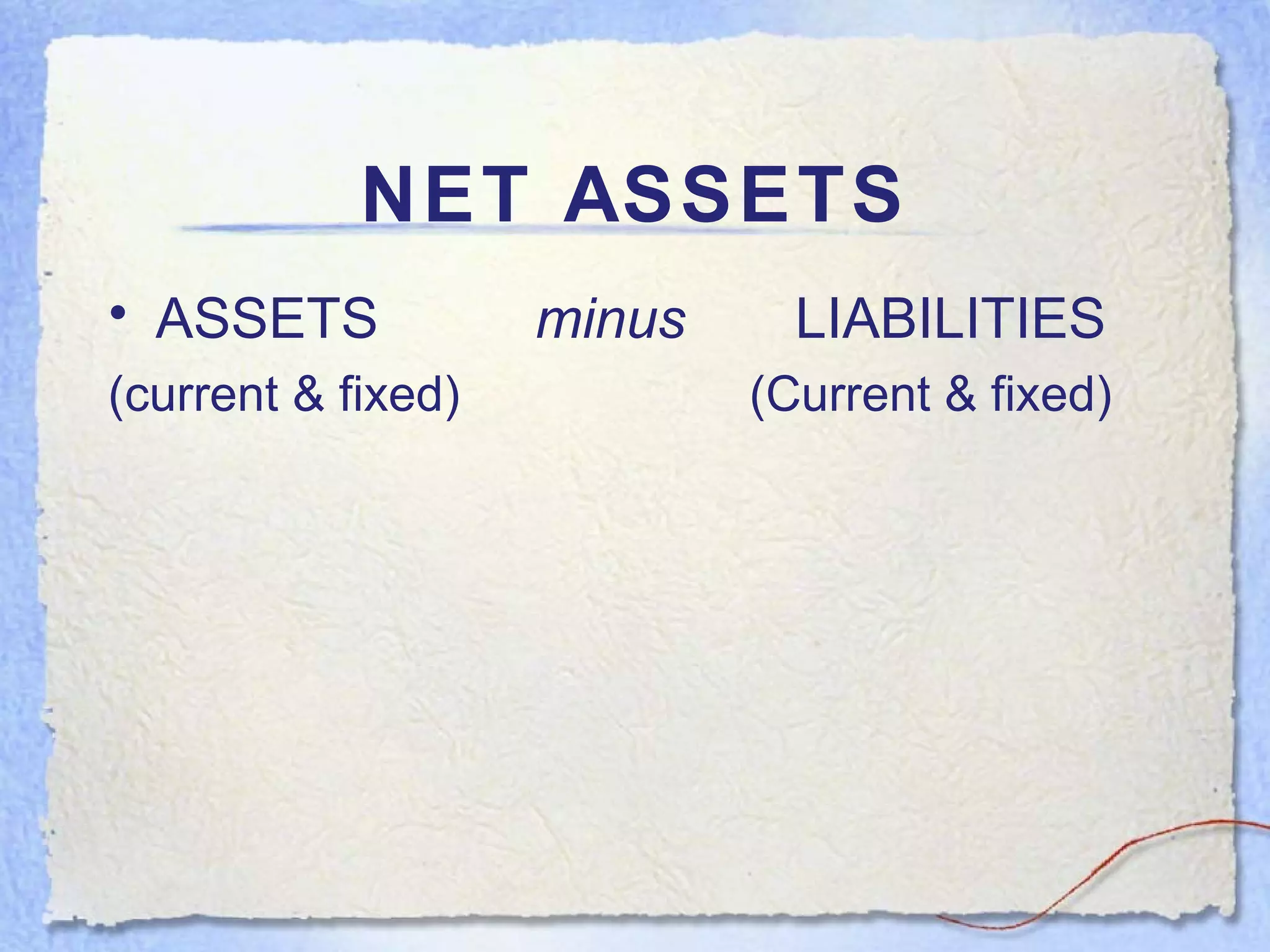
- Current assets are items expected to be converted to cash within one year. Current liabilities are debts to be paid within one year. Net current assets is current assets minus current liabilities.