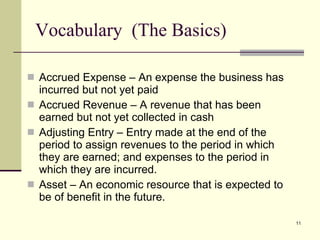
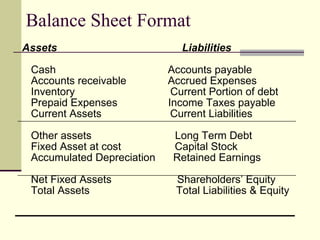
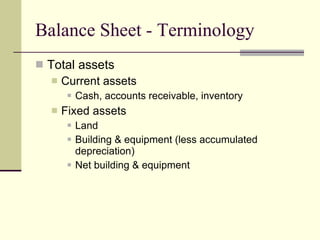
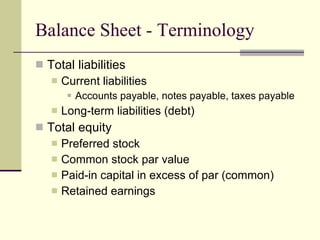
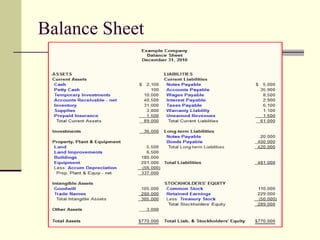
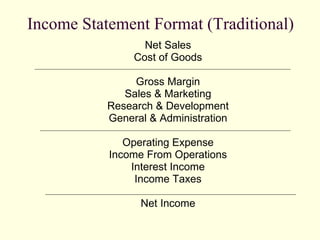
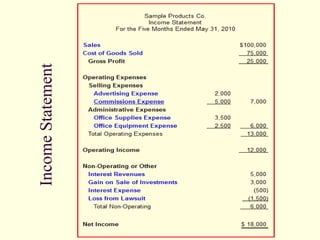
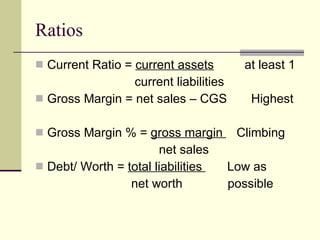
The document provides an overview of a class on financial projections and entrepreneurial studies. It discusses understanding personal financial obligations, preparing basic financial sheets like income statements and balance sheets, accounting terminology, business record keeping requirements, and calculating basic financial ratios. Students are expected to learn how to prepare a personal budget, understand minimum living expenses, grasp basic accounting concepts, and know what financial records are required to be kept and how to maintain them properly.
![Financial Projections HACC Institute for Entrepreneurial Studies David McNaughton 221-1213 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialprojections2011-hu-110830011710-phpapp02/75/Financial-projections-2011-hu-1-2048.jpg)