Embed presentation
Downloaded 115 times

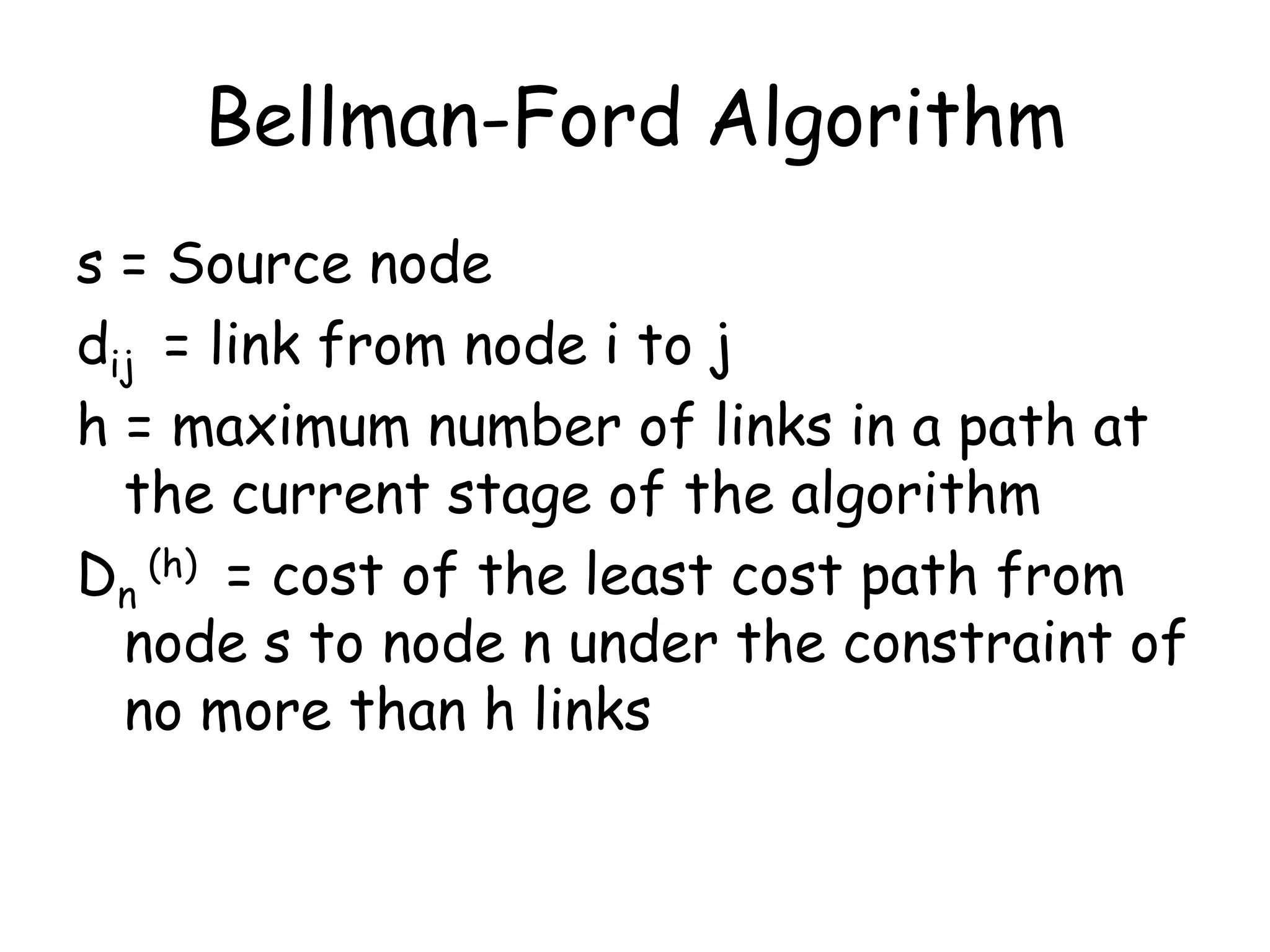
![Algorithm
1. Initialize
Dn(0) = ∞ for all n != s
Ds(h) = 0 for all h
2. For each successive h >= 0
Dn(h+1) = Minj [Dj(h) + djn ]
The path from s to i terminates with the link
from j to i
[Step 2 is repeated until none of the cost
changes]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15-e-131122062307-phpapp02/75/Lecture-15-data-structures-and-algorithms-3-2048.jpg)
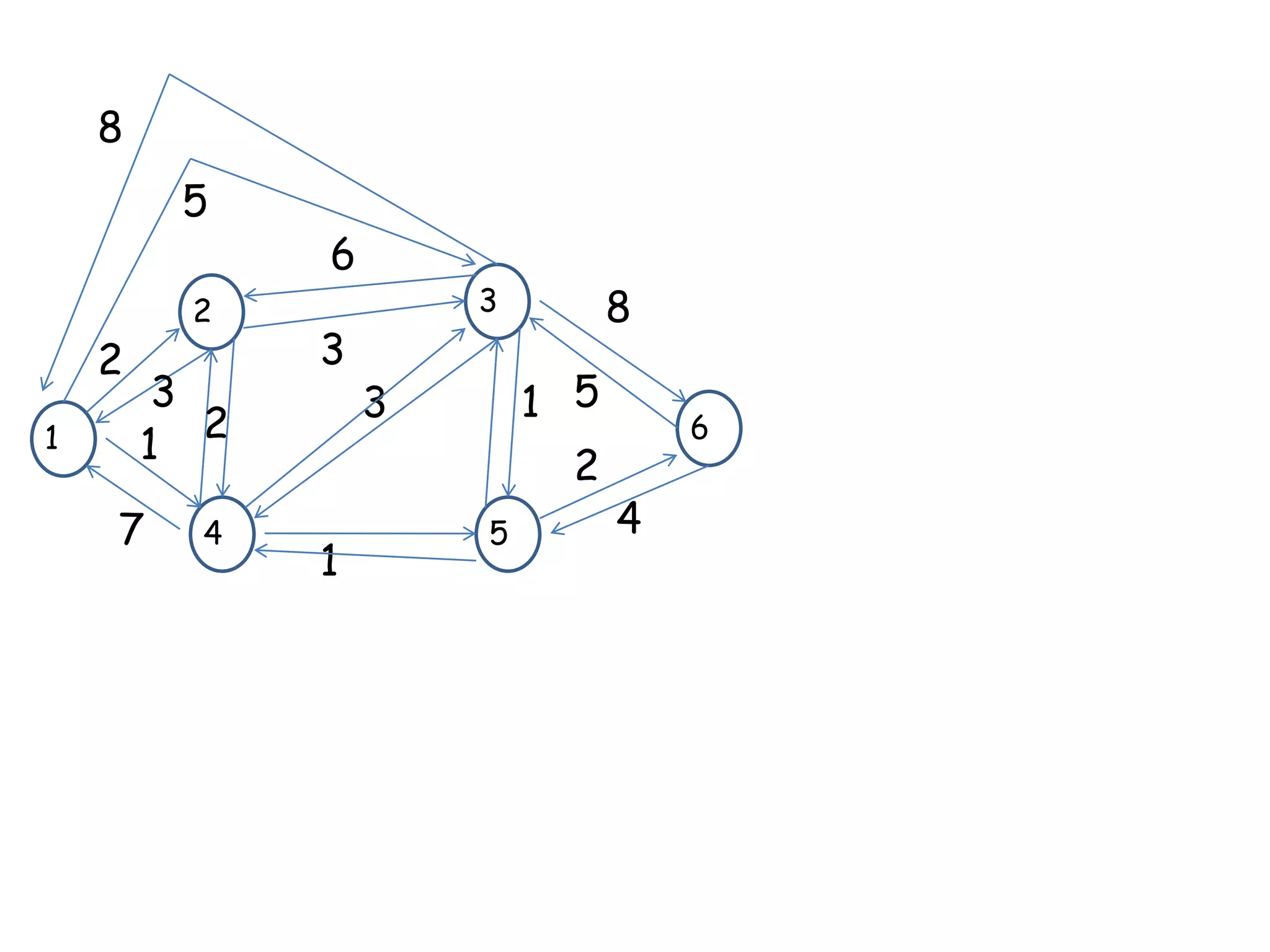
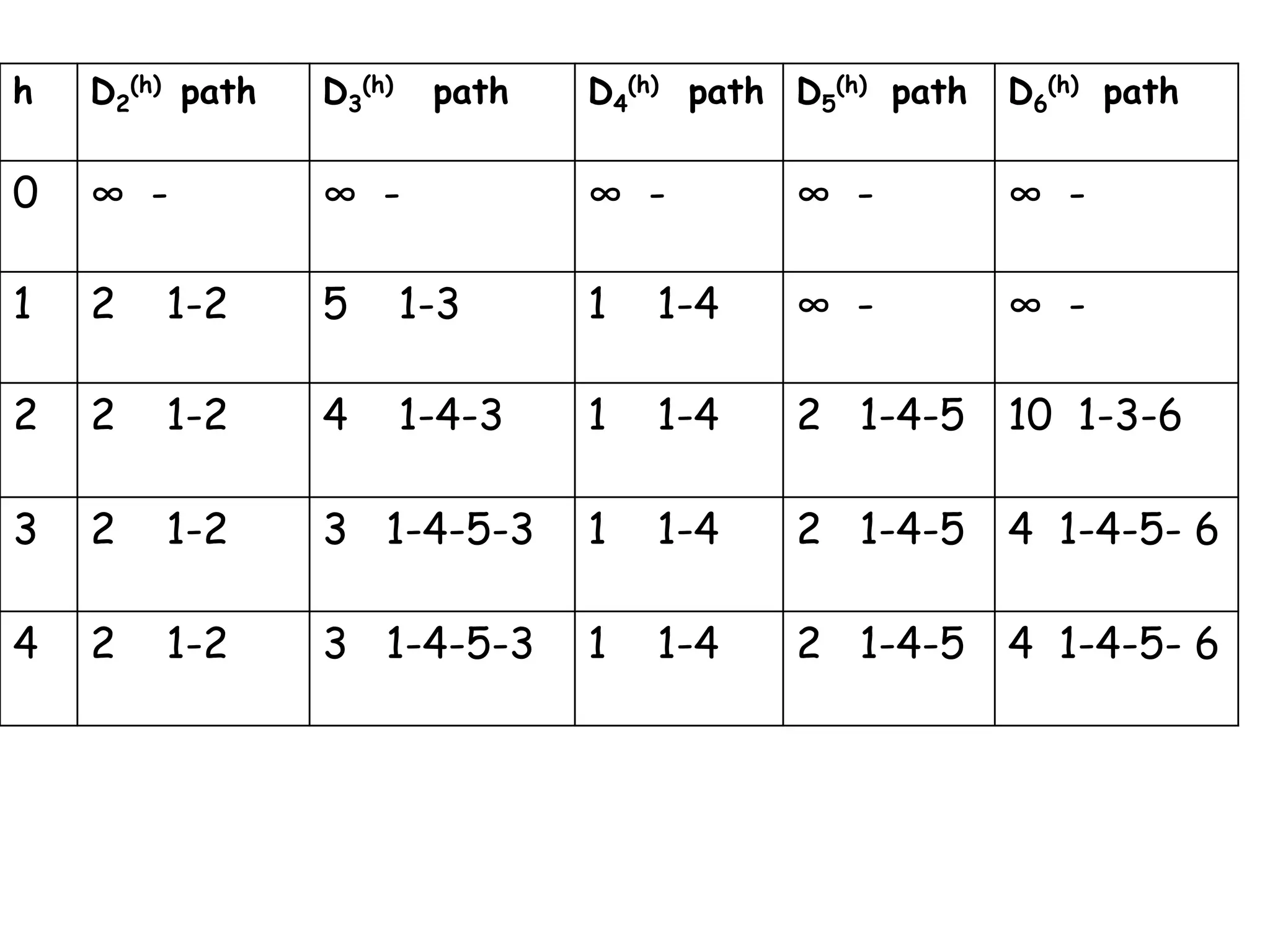

The Bellman-Ford algorithm finds the shortest paths from a source node to all other nodes in a weighted graph. It works by relaxing edges repeatedly to find shorter paths with more edges. The algorithm initializes costs to infinity for all nodes except the source node. It then iterates through the edges, relaxing each edge by updating the cost of neighboring nodes to the minimum of their current cost or the cost of reaching them via the relaxed edge. This process repeats until no more costs decrease.


![Algorithm
1. Initialize
Dn(0) = ∞ for all n != s
Ds(h) = 0 for all h
2. For each successive h >= 0
Dn(h+1) = Minj [Dj(h) + djn ]
The path from s to i terminates with the link
from j to i
[Step 2 is repeated until none of the cost
changes]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15-e-131122062307-phpapp02/75/Lecture-15-data-structures-and-algorithms-3-2048.jpg)

