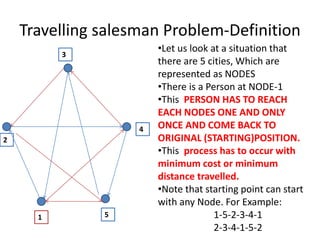
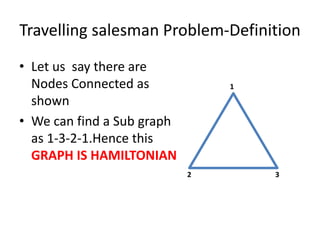
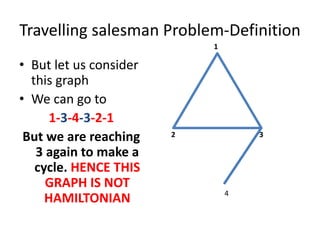
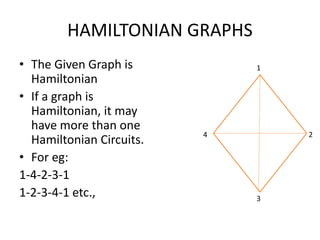
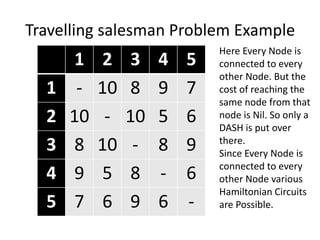
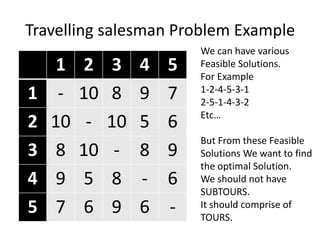
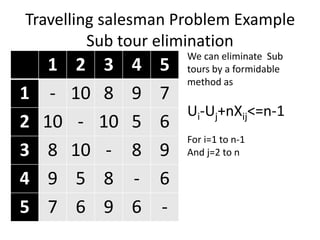
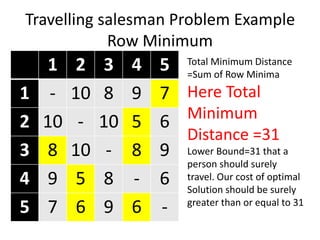
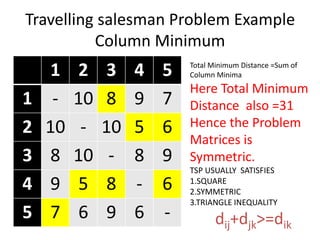
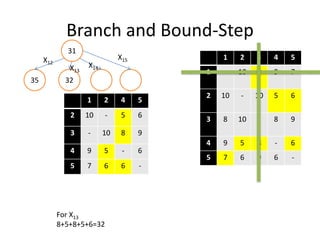
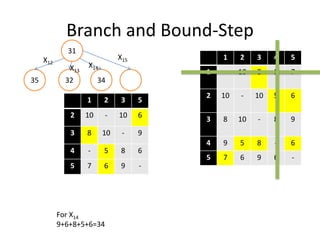
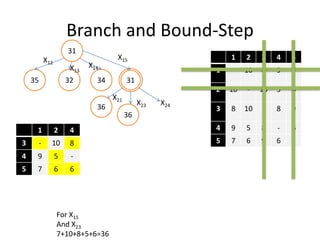
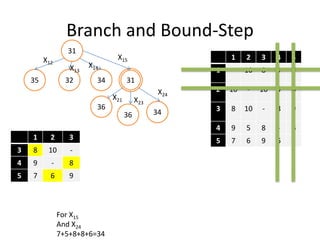
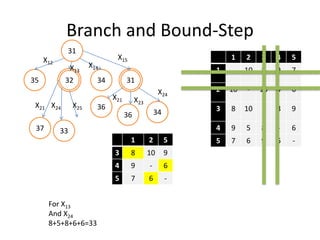
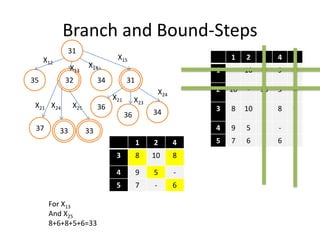
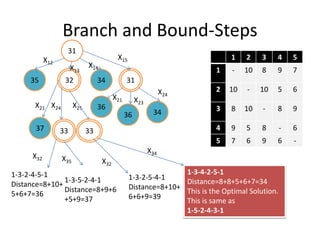
The document discusses the Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP). TSP aims to find the shortest possible route for a salesman to visit each city in a list only once and return to the origin city. It describes the problem as finding the optimal or least cost Hamiltonian circuit in a graph where cities are nodes and distances between cities are edge costs. The document provides an example problem with 5 cities, calculates possible routes and costs, and illustrates the branch and bound algorithm to solve TSP by systematically eliminating suboptimal routes until the optimal route is found.