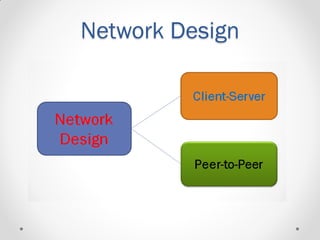
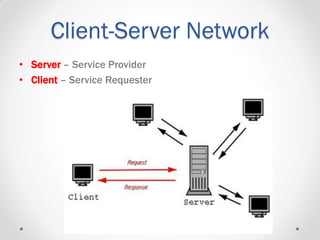
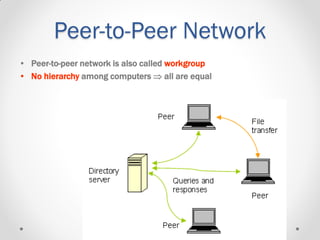
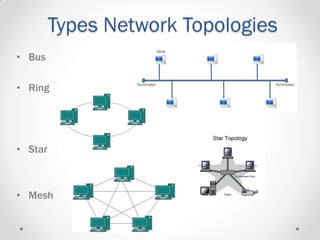
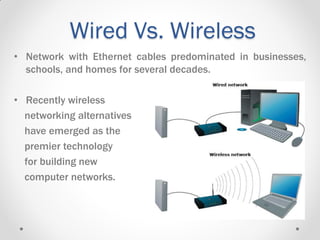
This document provides an introductory lecture on computer networks by Shahzad Ali. It defines what a network is and discusses different types of computer networks including personal area networks (PAN), local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN), and wide area networks (WAN). The document also covers network design topics such as client-server and peer-to-peer networks, common network topologies (bus, ring, star, mesh), network protocols, and whether networks are wired or wireless. It provides examples and details for each topic.