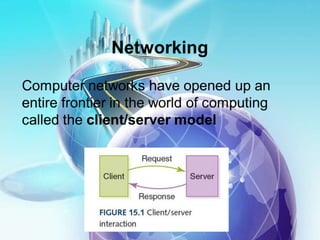
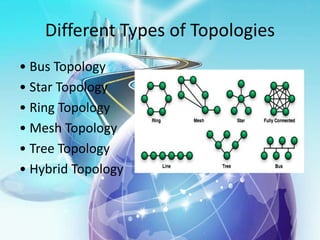
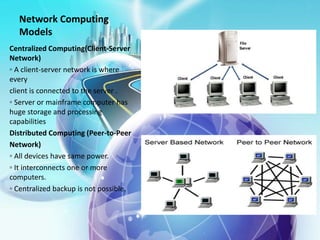
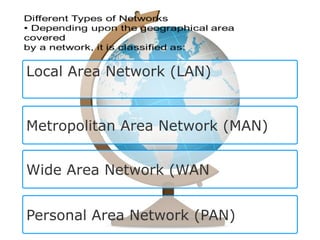
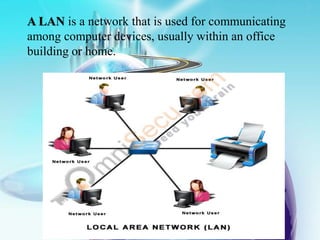
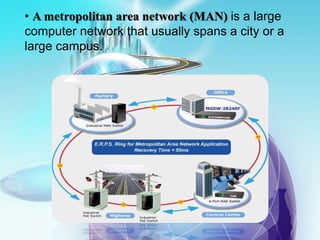
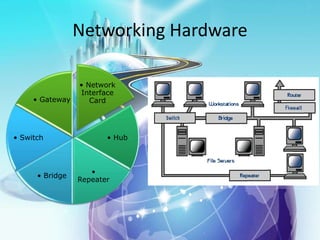
This document provides an overview of computer networks. It defines what a computer network is and some common network types, including local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). It also discusses network topologies, hardware components, and protocols like SLIP and PPP. The key topics covered include the basic components of a computer network, common network models, networking devices, and differences between SLIP and PPP protocols.