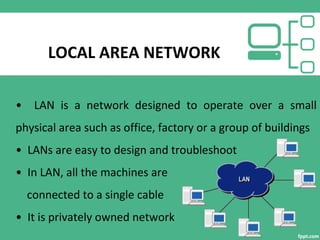
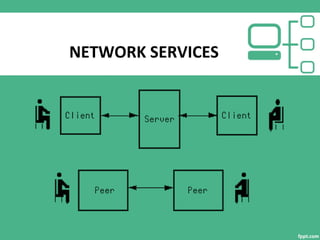
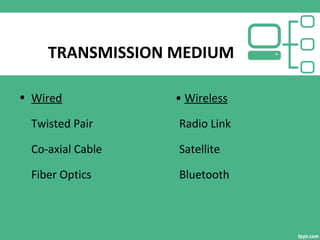
This document provides an overview of computer networking, including its introduction, characteristics, applications, disadvantages, types of networks, network services, transmission mediums, protocols, and conclusion. It defines a computer network as a set of autonomous computers connected by a medium to exchange information. The document outlines different types of networks like LAN, MAN, and WAN and describes their key characteristics. It also discusses various network services, transmission mediums, and protocols that allow networks to function properly.