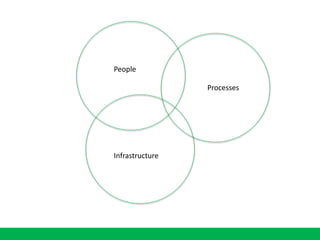
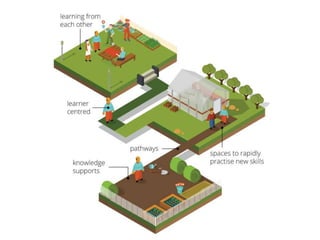
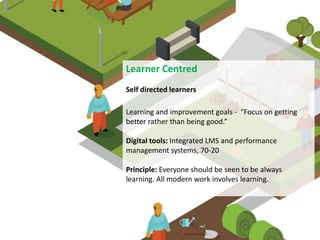
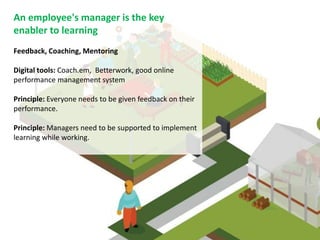
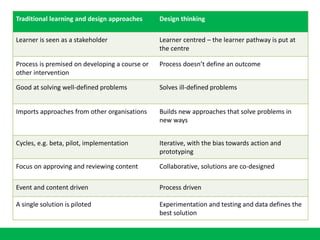
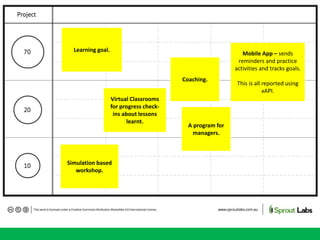
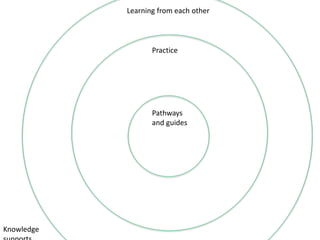
The document discusses the importance of learning ecosystems in capability development, emphasizing a learner-centered approach that integrates digital tools and collaborative practices. It highlights the 70-20-10 learning model and the role of managers as enablers of learning, while advocating for iterative design thinking in creating effective learning pathways. Examples are provided, including the use of digital platforms for feedback, community learning, and safe practice environments to foster continuous improvement and engagement.