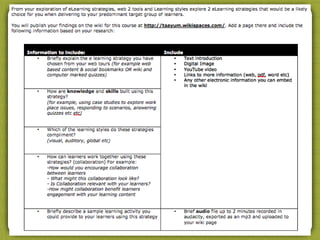
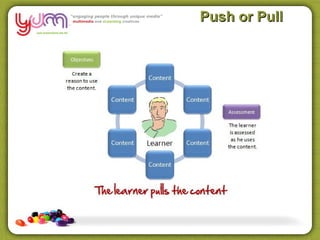
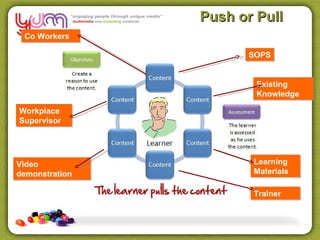
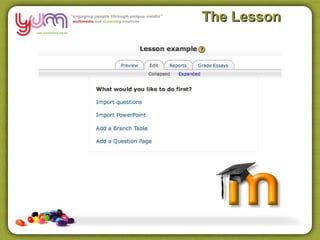
The document discusses using technology and learning design to gather quality assessment evidence. It covers various topics related to online and blended learning assessments including virtual classrooms, decision making trees, case studies, peer review, and using industry knowledge. Tools that can be used to create online assessments and scenarios are also presented.