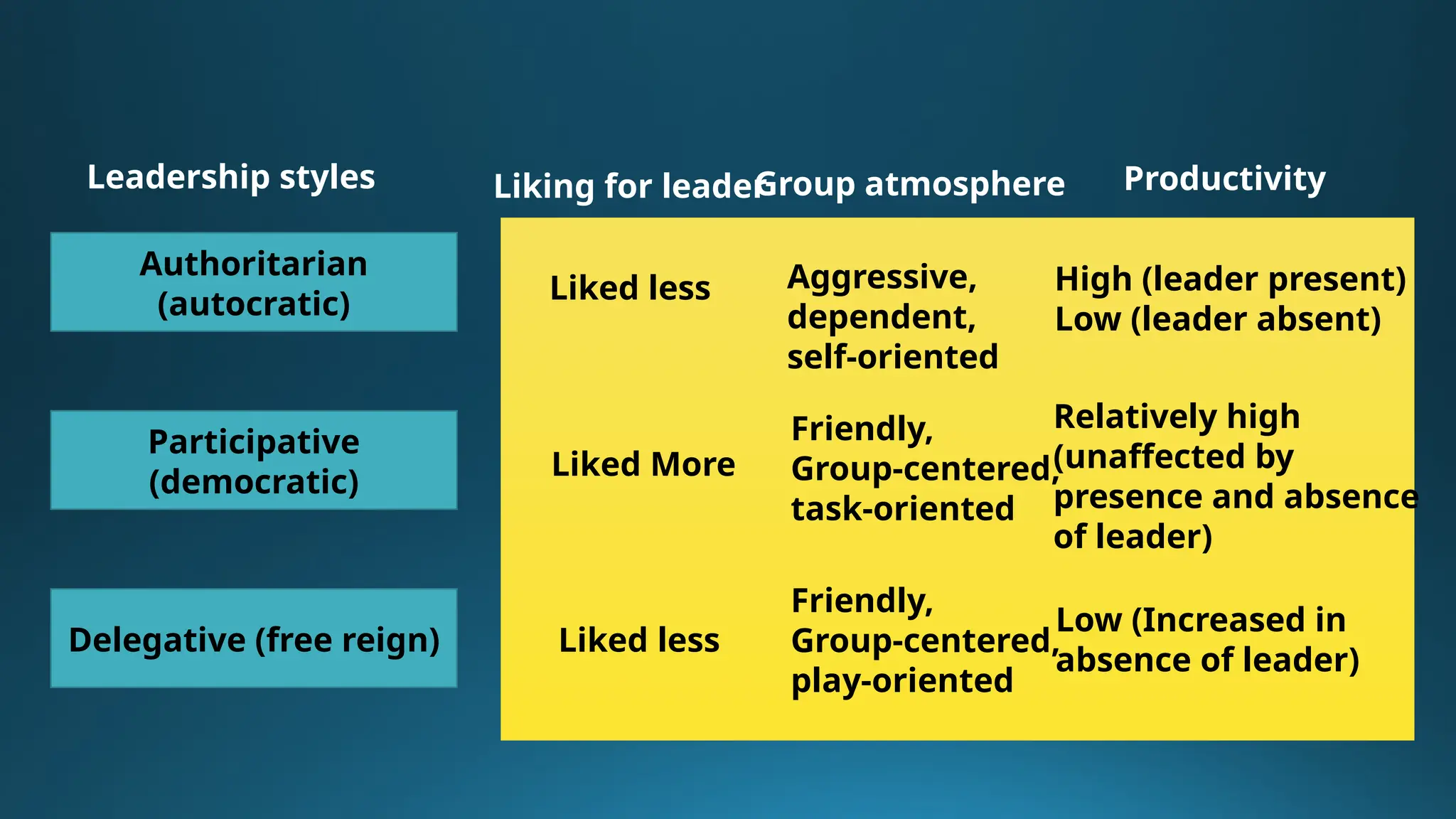
The document discusses leadership through the lens of social psychology, emphasizing the influence of individual behaviors in social contexts. It outlines various leadership styles, including authoritarian, participative, and delegative, while identifying key leadership qualities and theories on how people become leaders. The text distinguishes between managers and leaders, highlighting that effective leaders focus on inspiring and motivating people rather than merely managing tasks.