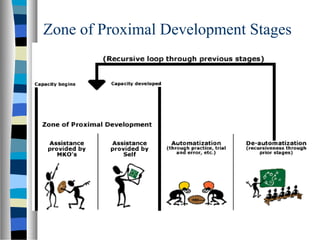
Vygotsky's sociocultural theory posits that cognitive development occurs through social interaction and is mediated by language and culture. It emphasizes how learning occurs in the Zone of Proximal Development through collaboration with more knowledgeable others. According to the theory, higher order thinking develops first on a social level through interaction, then on an individual level. The implications for education include using strategies like scaffolding that support student learning within their ZPD.



























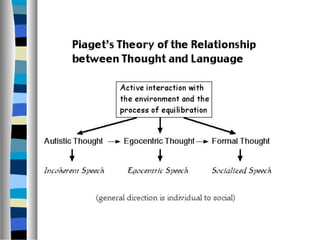
![Note:
Formal thought is internalized language;
language comes from society; hence the
mind is a product of society.
[Back to Vygotsky’s basic concepts.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vygotsky-121108231029-phpapp01/85/Vygotsky-33-320.jpg)




