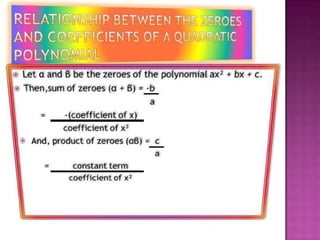
A polynomial is an algebraic expression involving variables and constants that is formed using addition, subtraction, and multiplication, but not division. The degree of a polynomial refers to the highest power of the variable. Polynomials can be classified based on their number of terms as monomials (one term), binomials (two terms), or trinomials (three terms). They can also be classified based on degree as constant (degree 0), linear (degree 1), quadratic (degree 2), cubic (degree 3), or of higher degrees. The number of zeros of a polynomial is equal to its degree.