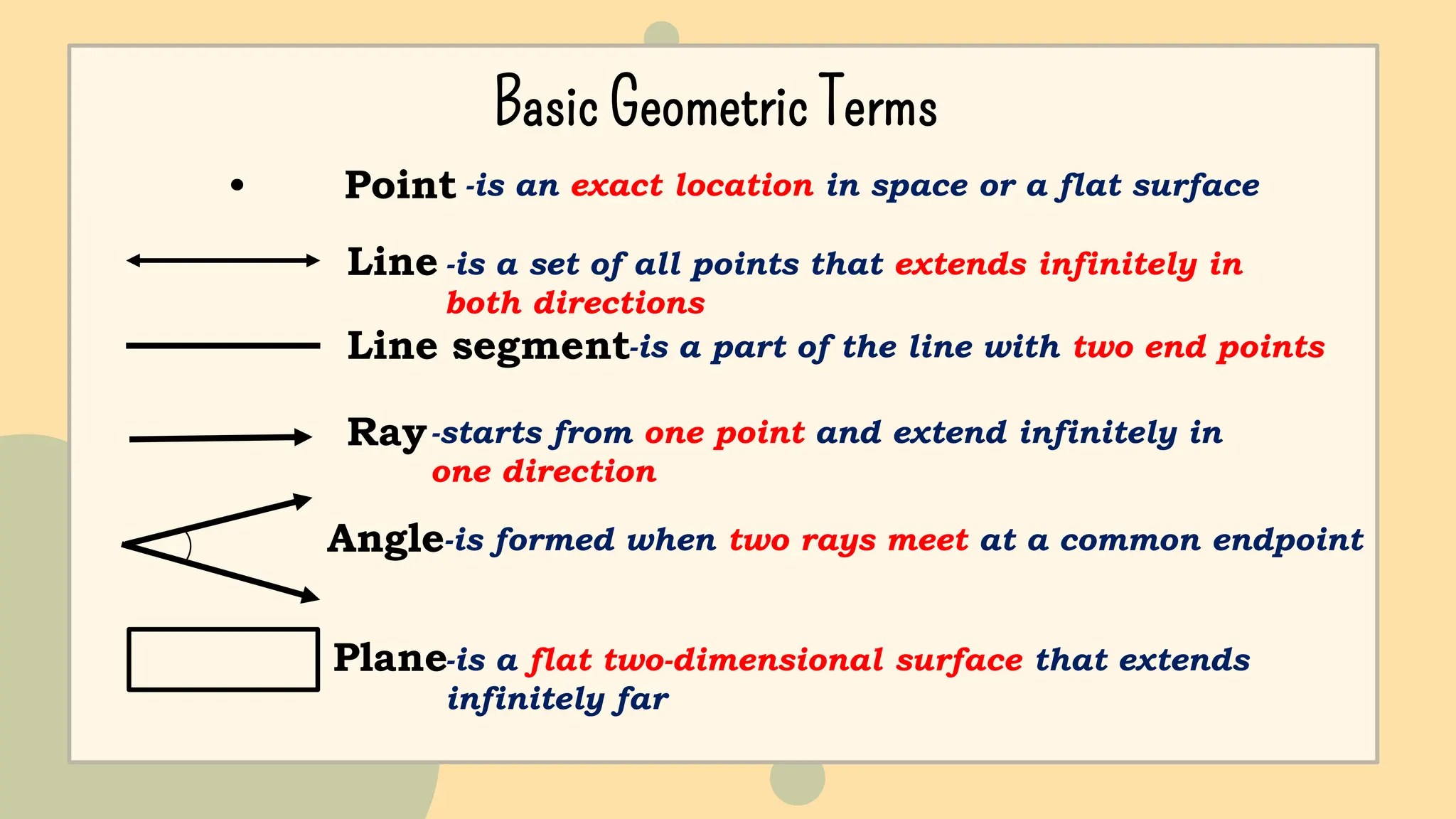
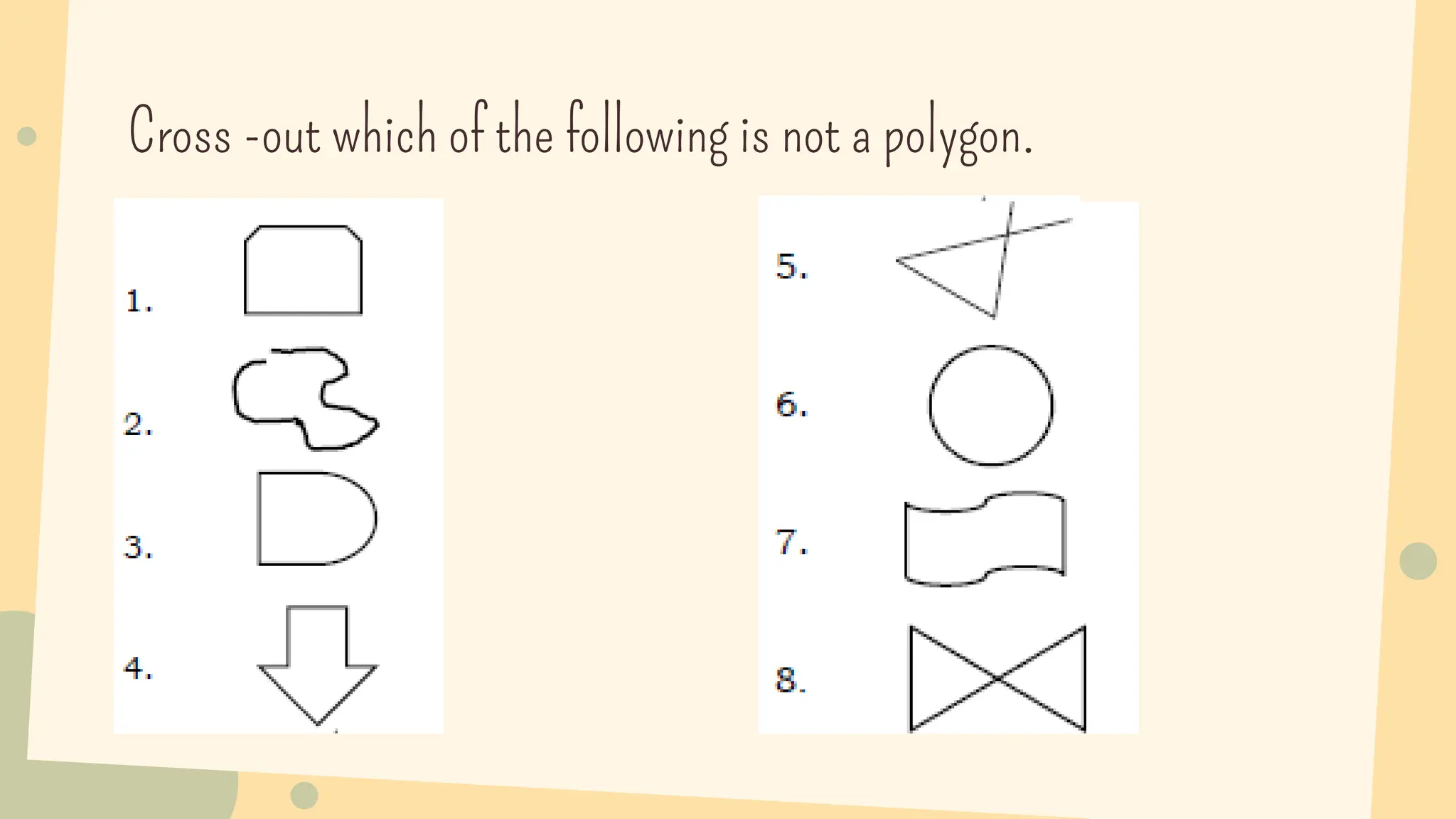
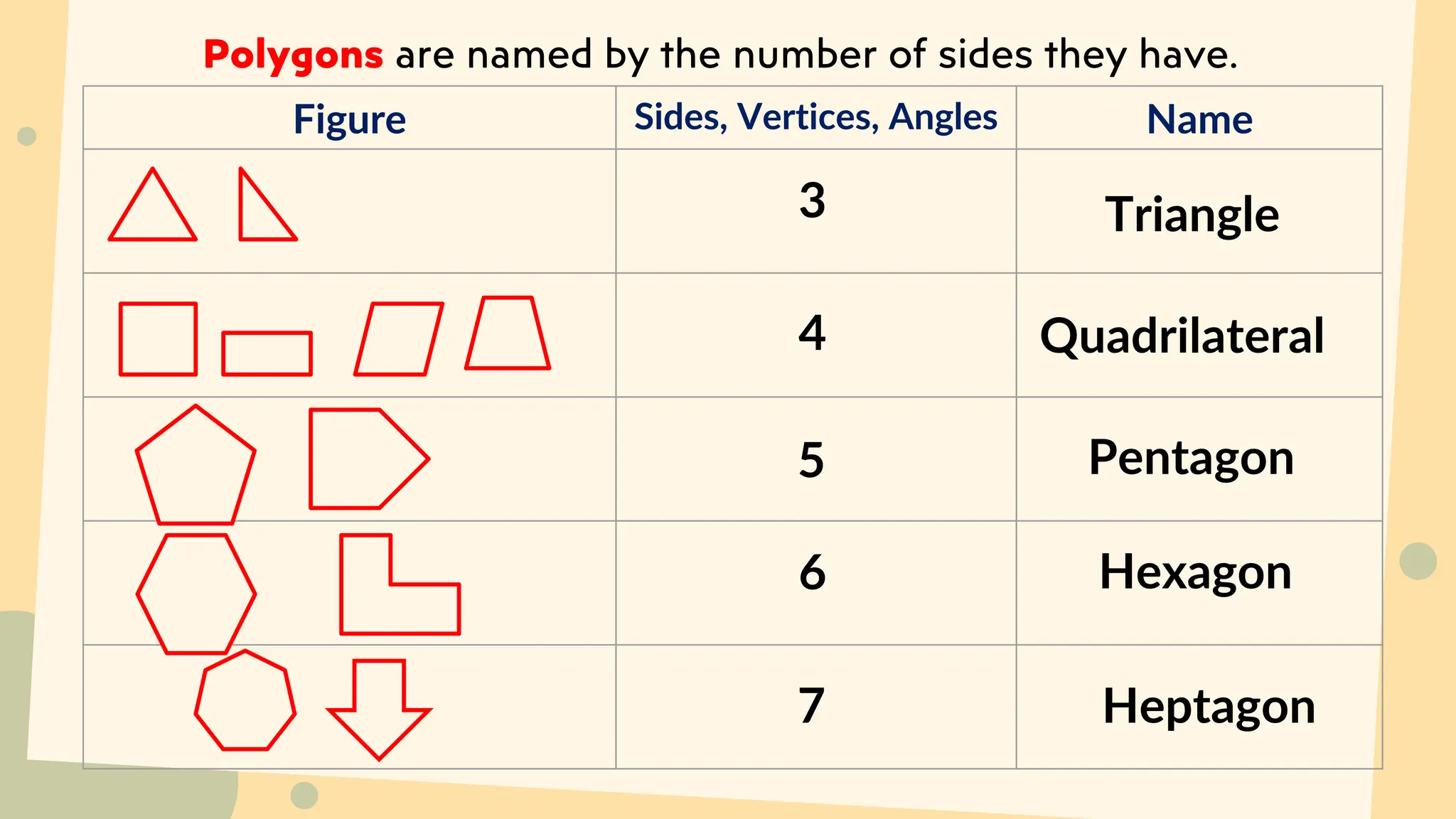
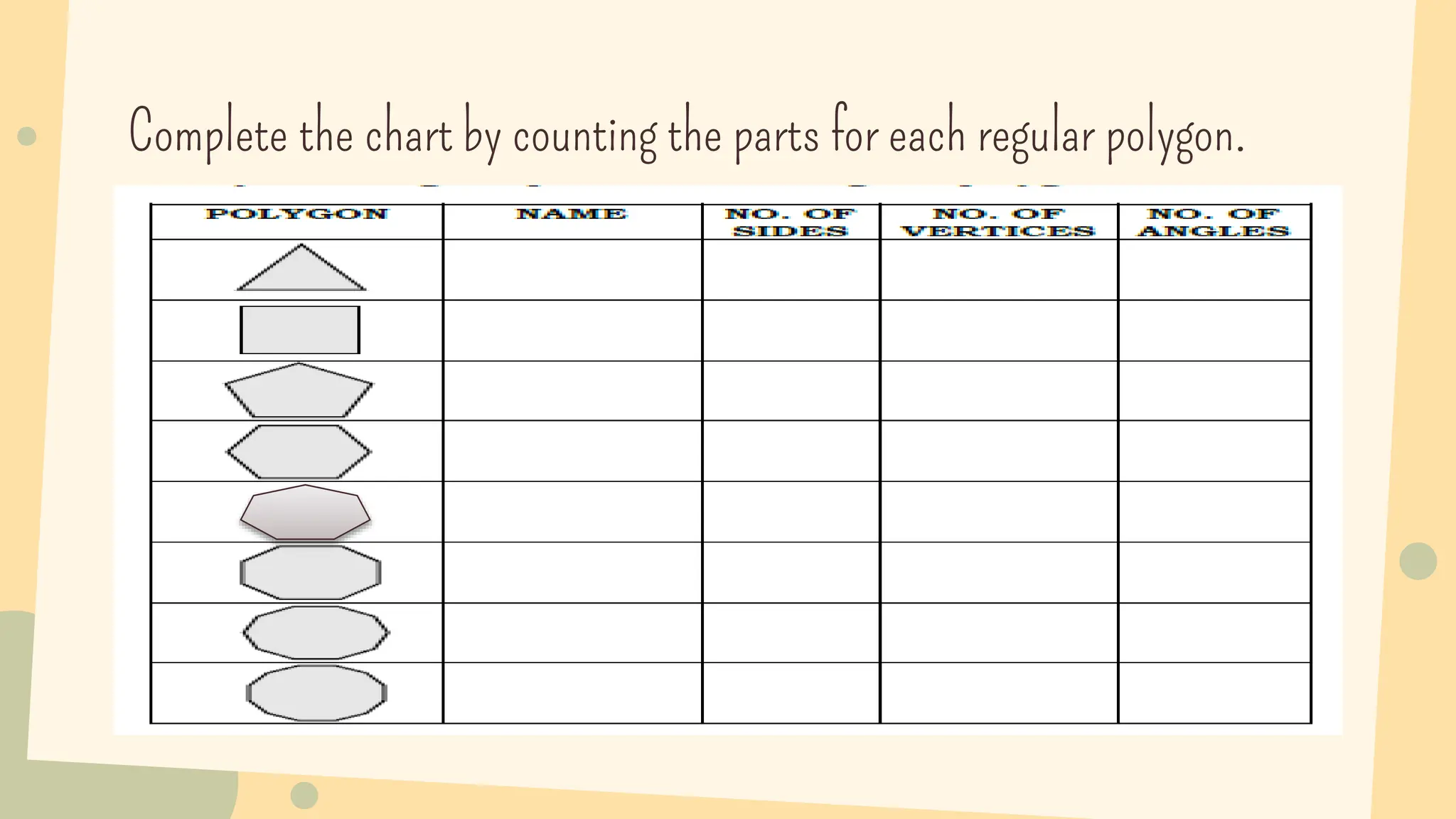
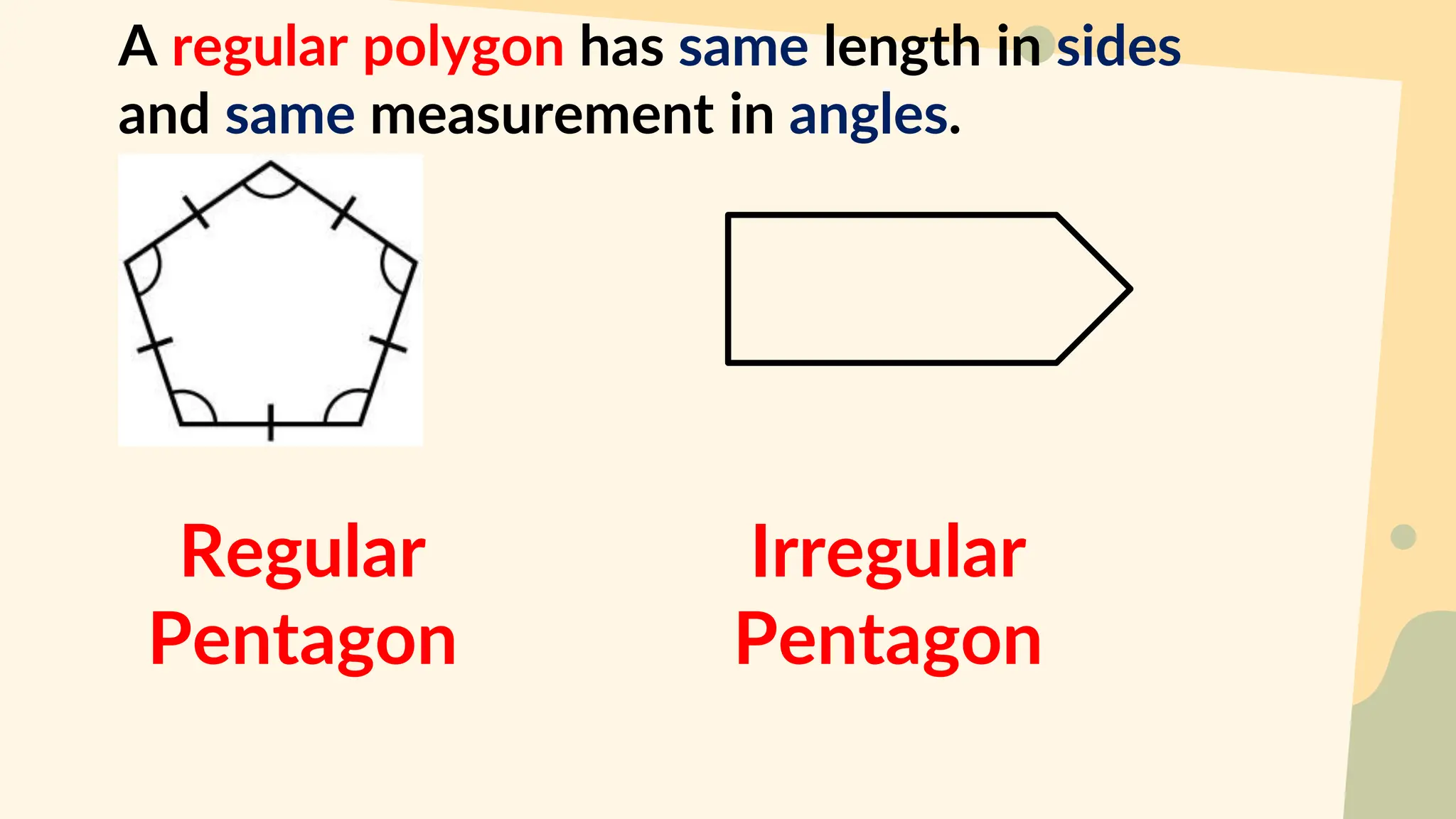
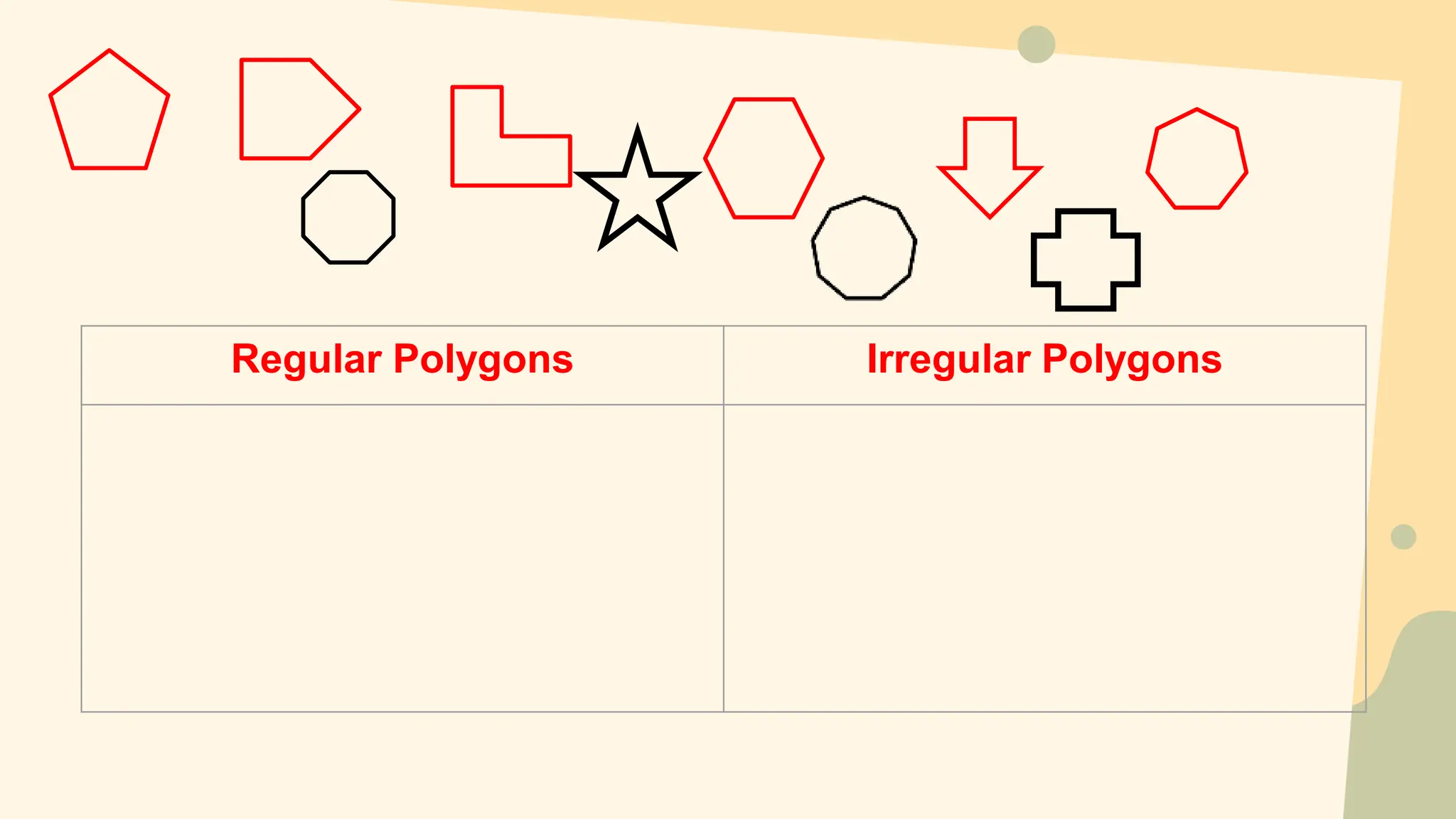
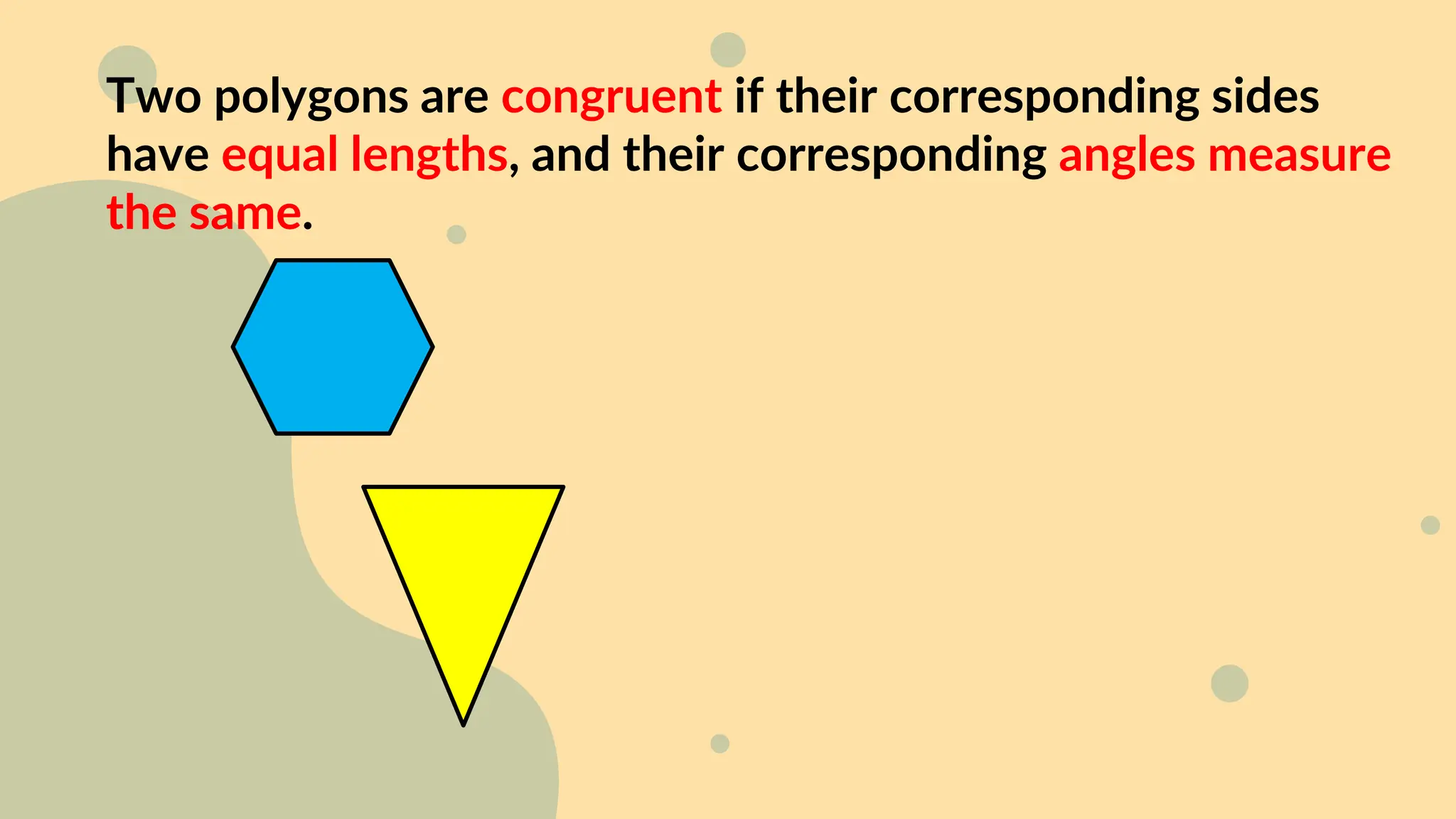
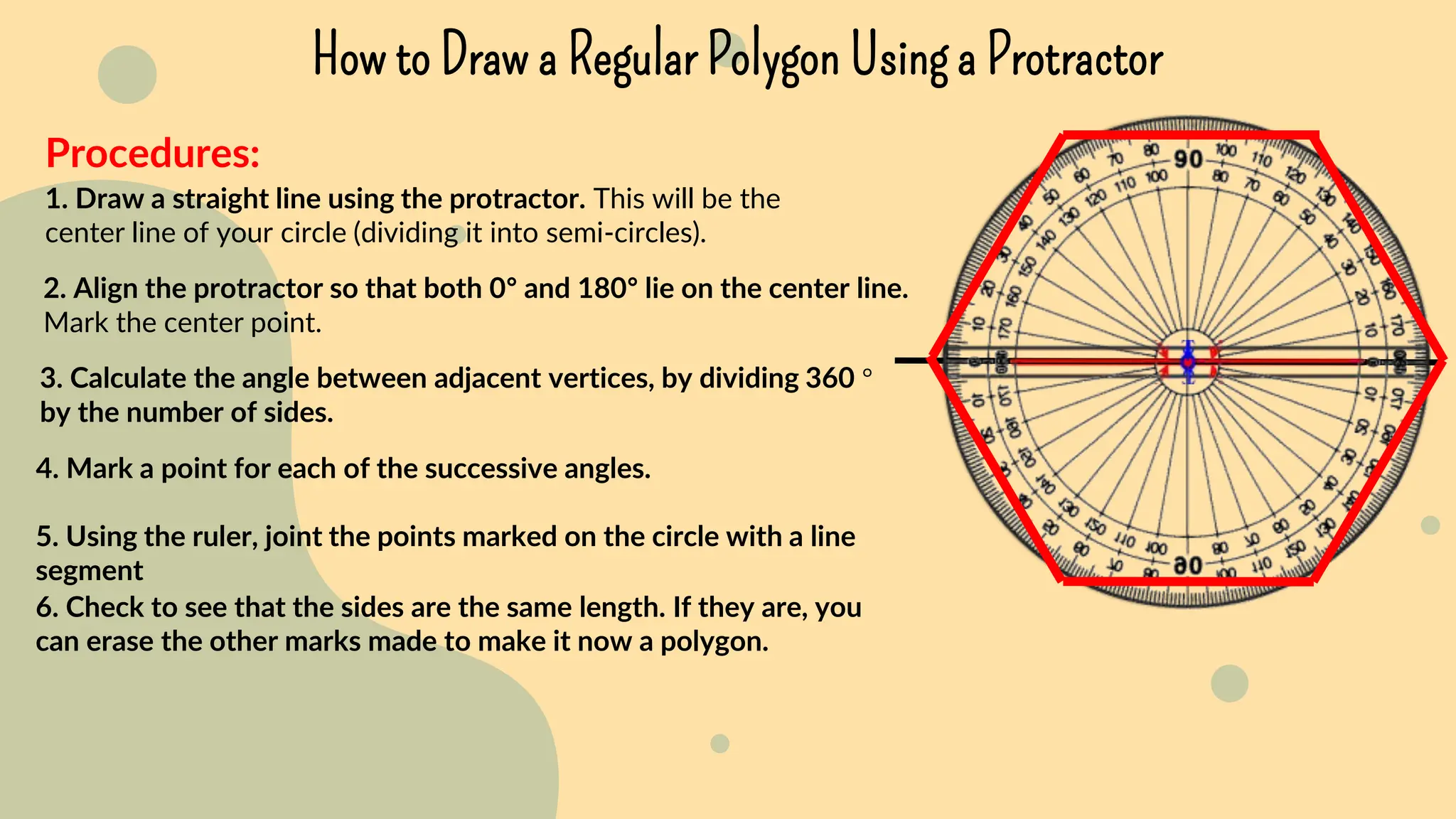
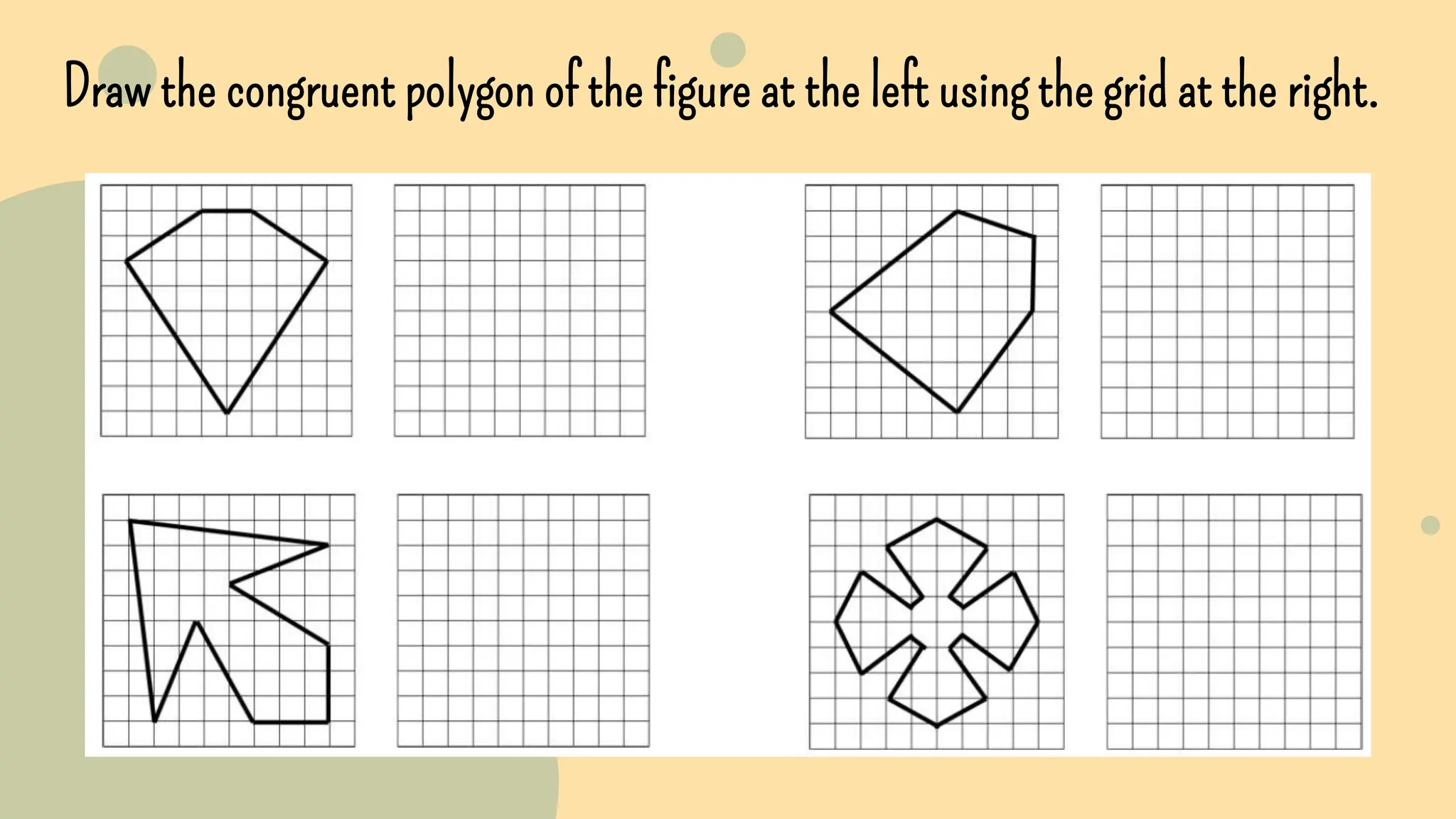
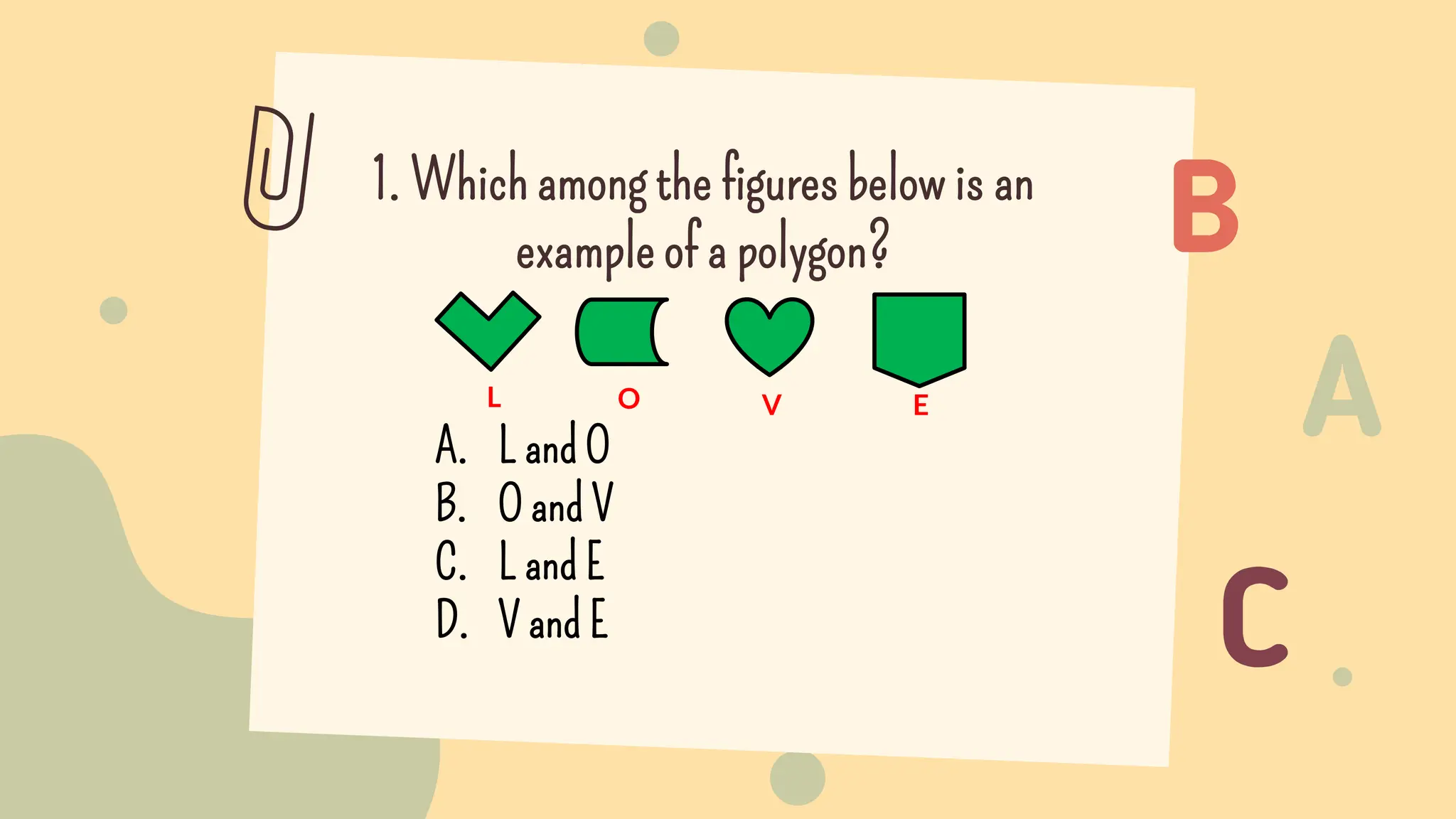
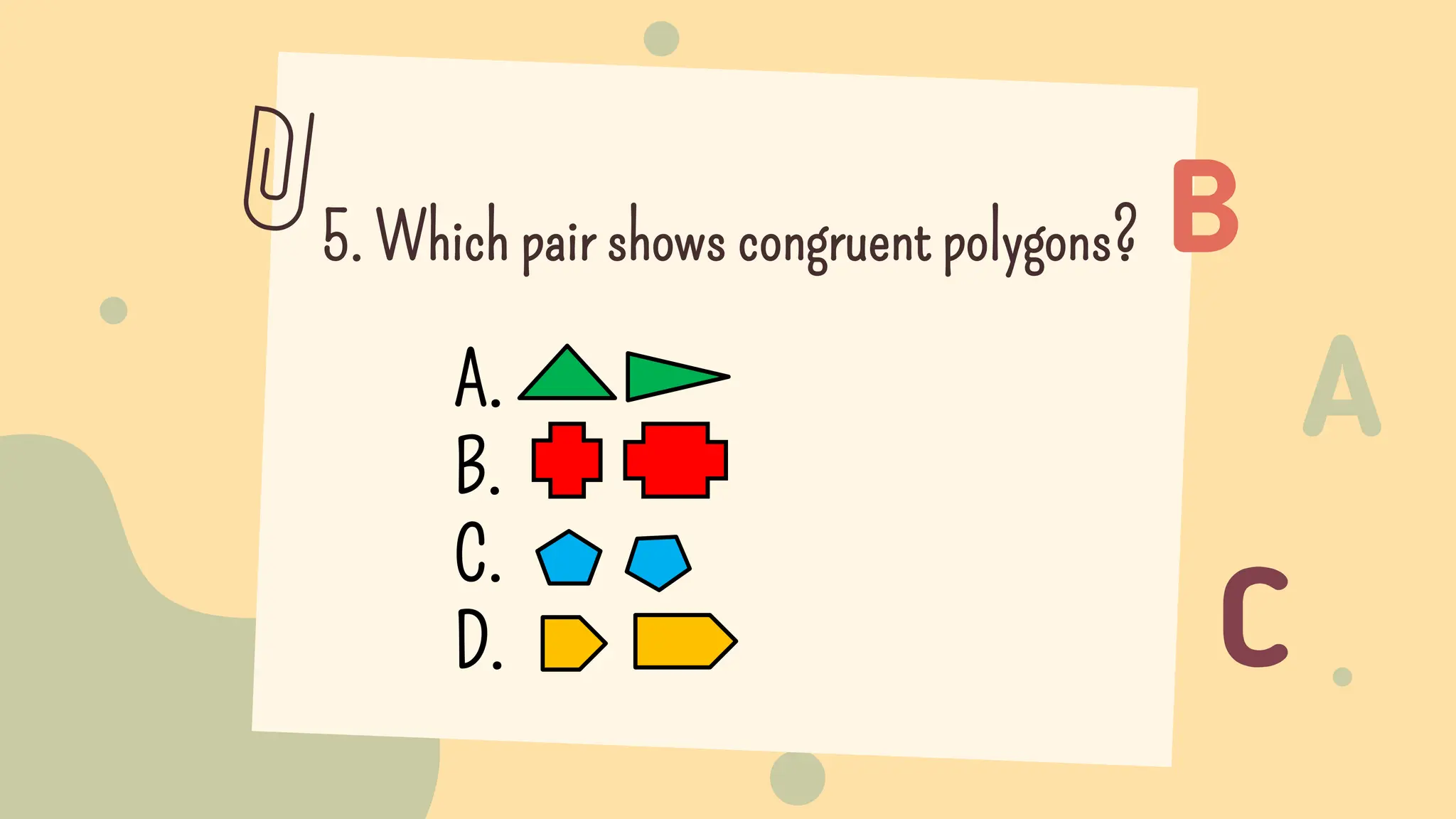
This document discusses polygons and their properties. It defines a polygon as a closed 2D shape made of three or more straight line segments. Polygons are named based on the number of sides, such as triangles having 3 sides, quadrilaterals having 4 sides, and pentagons having 5 sides. Regular polygons have equal side lengths and equal interior angles, while irregular polygons do not have these properties. The document provides instructions for drawing regular polygons using a protractor and discusses congruent polygons as those with equal corresponding side lengths and angles.